The emergence of Ukraine’s Sapsan ballistic missile system, also known by several other names, represents a significant development in the country’s defense landscape. Its presence in the operational theatre has prompted discussion and analysis regarding its capabilities, status, and implications for the ongoing conflict and potentially for broader European defense dynamics. This domestically developed system has been a subject of interest and varying reports, and recent information sheds further light on its current role and potential impact.
Facing ongoing security challenges and navigating the complexities of securing sufficient military aid, Ukraine has increasingly focused on bolstering its indigenous defense production capabilities. The development and fielding of a domestic ballistic missile system like Sapsan is viewed within this context as a critical step. It is seen by some experts not only as a military necessity but also as a strong political statement regarding Ukraine’s resolve and independence in defense matters.
Recent statements from Ukrainian military officials and analysis from defense experts, based solely on the information available, provide a clearer picture of the Sapsan’s status and attributes. These insights move the understanding of the system beyond speculation, detailing its confirmed deployment, operational readiness, technical characteristics, and the strategic rationale behind its development. What follows is a structured examination of some of the key facts and reported capabilities surrounding this notable Ukrainian weapon system.

1. **Confirmed Deployment and Recent Long-Range Strike (700km)**:
The Sapsan system, specifically an improved variant of the Hrim-2 short-range ballistic missile system, has now been deployed. This confirmation came from Brigadier General Serhiy Baranov, head of the Main Directorate of Missile Forces and Artillery and Unmanned Systems of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of Ukraine.
General Baranov revealed this information during an interview with Armiya FM on November 3, 2023. According to his statement, the system was successfully used to strike a Russian target. The distance of this strike was reported to be 700 km.
The successful execution of a strike at this considerable range, confirmed by a high-ranking military official, was described as a “surprising revelation.” This reported action highlights the extended reach and demonstrated capability of the improved Hrim-2 variant now in Ukraine’s possession, according to the statement.
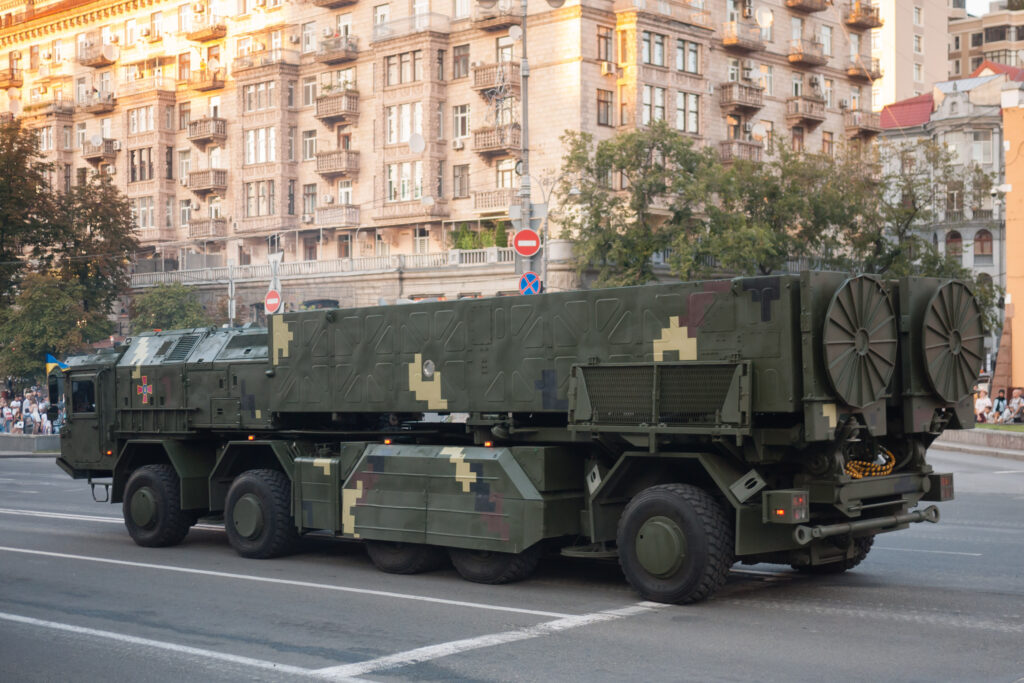

2. **Official Shift from Development to Operational/Improved Status**:
For a considerable period leading up to recent announcements, the Hrim-2 system was officially categorized as being in the development stage. Its status was widely understood to be that of a project still undergoing testing and refinement rather than active service.
Brigadier General Baranov’s interview fundamentally altered this official understanding. He announced that the system is not only operational, indicating it has moved beyond development and into active deployment for military use.
Furthermore, General Baranov stated that the system is currently undergoing further improvements. This suggests that the deployed variant is not the final iteration and that efforts are ongoing to enhance its capabilities even as it is being used operationally.

3. **Contradiction of Russian Claims of Destruction**:
The announcement of the Hrim-2’s operational status and successful use directly contradicted prior statements issued by the Russian Armed Forces. These Russian assertions had previously claimed the destruction of Hrim-2 missile systems.
Specifically, the Russian claims included assertions that they had destroyed both Hrim-2 missile systems themselves and their associated production facilities. These claims suggested that Ukraine’s efforts to field this system had been thwarted.
General Baranov’s confirmation that the system is operational and striking targets serves as a direct refutation of these specific prior claims made by Russian military authorities. It indicates that despite Russian efforts or claims, the system has become active.

4. **Links to Prior Attacks (Saki, Feodosia)**:
Within the Ukrainian information space, the Hrim-2 missile system has been previously linked to several notable attacks on Russian military targets. These links have been part of ongoing discussions and analysis regarding the system’s suspected early uses.
Among the incidents cited in these discussions are the attack on the military airfield in Saki. This event reportedly occurred on August 9, 2022, and was speculated by some to have involved the Hrim-2 system.
Another incident frequently linked to the system in Ukrainian discussions is the attack on Feodosia. This attack took place on April 8, 2023. These links, while part of information space discussions, highlight the system’s presence in speculative analyses of past significant strikes.
5. **Russia’s Own Official Interception Claim (March 30, 2023)**:
Adding a layer of complexity and intrigue to the Hrim-2’s history is an official statement from the Ministry of Defense of Russia. This statement pertains to an event that occurred before the recent confirmation of deployment.
According to the Russian Ministry of Defense’s official statement, they claimed to have intercepted a missile fired by the Hrim-2 system. This reported interception occurred on March 30, 2023.
The fact that Russia’s own defense ministry officially reported encountering and intercepting a missile attributed to the Hrim-2 system on this date adds to the documented instances involving the system. It supports the notion that the system was at least being tested or used in some capacity before the later announcement of full operational status.

6. **System Identity, Development History, and Purpose**:
The system known as Sapsan is also identified by multiple other names, reflecting its development history or possibly variations in terminology. These names include Hrim-2, Grim-2, Grom-2, and Thunder, alongside OTRK Sapsan.
The development initiative for this short-range ballistic missile system began in 2013. This places its origin nearly a decade before its recent confirmed operational status and strikes.
The primary intent behind the initiation of the Hrim-2/Sapsan development was to serve as a replacement for the Tochka-U short-range ballistic missiles. The Tochka-U currently serves as the primary ballistic missile utilized by the Ukrainian Army, possessing a range of 120 km, indicating the Sapsan was envisioned as a successor with presumably enhanced capabilities.

7. **Aeroballistic Trajectory and Air Defense Evasion Capability**:
One of the notable technical features highlighted for the Hrim-2 is its ability to navigate its flight path in a sophisticated manner. The system can reportedly follow not only a predictable ballistic trajectory but also an aeroballistic one.
The use of an aeroballistic trajectory is significant because it allows the missile to change its flight path unpredictably during its flight. This unpredictability makes tracking and intercepting the missile more challenging for defensive systems.
This capability is specifically reported to enable the Hrim-2 system to bypass existing air defense systems. This includes sophisticated Russian systems such as the S-300 and S-400, positioning the Sapsan as a missile designed with survivability against modern air defenses in mind.
Expanding on the confirmed operational status and historical context, further details emerge regarding the technical attributes and strategic positioning of Ukraine’s Sapsan system, as well as the broader implications of its domestic production. The missile’s capabilities, development trajectory, and the challenges and significance of its serial production effort are key aspects shaping its role in the current conflict and European defense. Analysis of its specific characteristics provides insight into its intended use and potential impact on the battlefield.
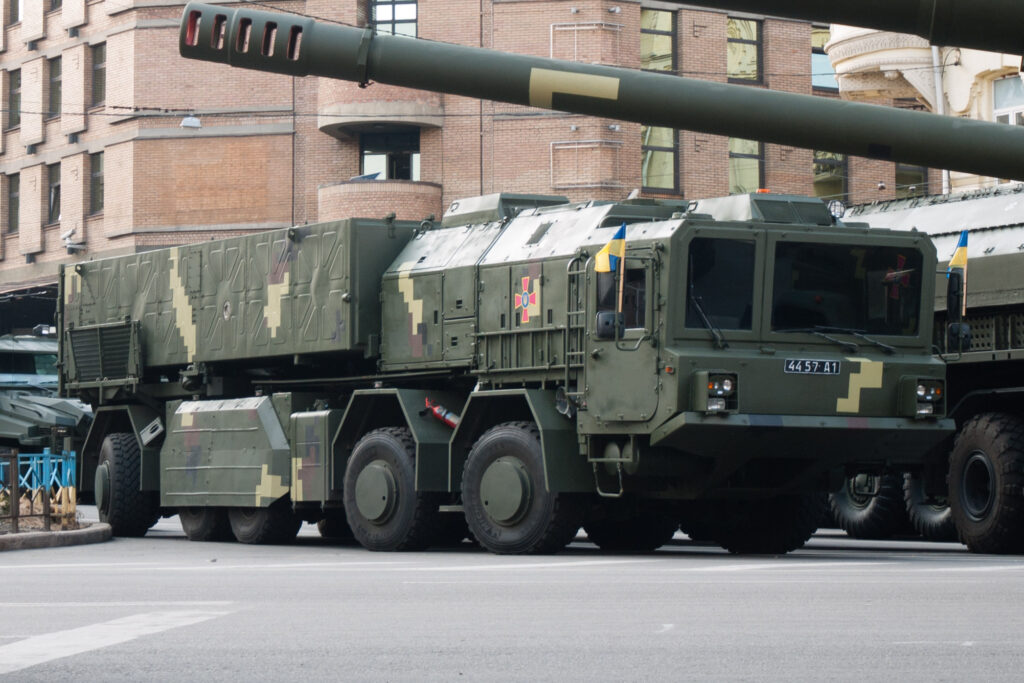

8. **Expanded Operational Range Capabilities**:
While earlier reports or export specifications might have indicated a shorter reach, the Sapsan system’s operational range for Ukrainian forces has been significantly extended. The confirmed successful strike at 700 km, as reported by Brigadier General Baranov, demonstrates a capability that goes well beyond previous estimates of 450 to 500 km or the export version’s range of 50 to 280 km. This extended range capability allows Ukraine to target objectives at greater distances.
The achievement of a 700 km strike range enhances Ukraine’s deep strike potential, enabling it to reach targets previously considered less vulnerable to domestic systems. This increase in range is critical for influencing the conflict dynamics by holding a wider array of distant military assets at risk. The stated modification for Ukrainian needs represents a specific tailoring of the system beyond its originally conceived export parameters.
This demonstrated long-range capability fundamentally alters the strategic calculus for both sides. For Ukraine, it provides a new tool for striking key infrastructure or concentrations far behind the front lines. For adversaries, it necessitates adjusting defensive postures and considering threats originating from a wider area.

9. **Warhead Configuration and Strike Power**:
The Sapsan ballistic missile is equipped with a substantial warhead. According to available information, the warhead has a mass of 480 kilograms. This significant payload suggests a focus on delivering considerable destructive power upon impact.
The warhead can reportedly be configured in either unitary or cluster options. This versatility in warhead type allows the system to be adapted for different target sets, whether seeking to achieve concentrated damage on a single point target or distribute effects over a wider area against dispersed targets. The choice of a large warhead is seen by some experts as an indication that Ukraine is prioritizing strike power, potentially at the expense of maximizing range, highlighting the system’s intended role as a potent strike weapon.
Experts suggest that such a large warhead should make the Sapsan effective against a wide array of targets within its operational reach. The capacity to deliver over 480 kilograms of explosives or submunitions means the missile is designed to inflict significant damage on military installations, infrastructure, or concentrations of forces, contributing to Ukraine’s ability to degrade adversary capabilities.

10. **Guidance Systems and Versatility**:
The Sapsan system incorporates a sophisticated onboard control system to guide its flight. This system is described as inertial and integrates various navigation and guidance components. Among these components are radar-based and optoelectronic systems.
The combination of inertial navigation with radar and optoelectronic guidance likely provides the missile with accuracy and the ability to operate effectively in different environments and against various target types. Inertial systems provide primary navigation, while radar and optoelectronic systems can enhance terminal guidance accuracy, particularly against specific targets or in conditions where satellite navigation might be contested.
Beyond its guidance features, the Sapsan is noted for its versatility as a launch platform. It is capable of launching both ballistic and cruise missiles, according to the provided information. This dual capability allows for operational flexibility, enabling strikes with different flight profiles and engagement tactics. Its design is also noted as being suitable for a range of applications, extending from traditional air defense roles to potential use in coast guard duties, indicating a multi-purpose design philosophy.

11. **Comparison to Russian Iskander System**:
The development and fielding of the Sapsan system positions it as a direct counterpart to Russia’s Iskander missiles, according to analysis. The Iskander is a modern and capable short-range ballistic missile system widely used by Russia. Establishing a domestically produced system with comparable capabilities is strategically significant for Ukraine.
While the specific technical parameters might differ, the Sapsan’s reported ability to evade advanced air defenses, including systems like the S-300 and S-400 (as mentioned in Section 1), places it in a category of modern ballistic missiles designed to challenge contemporary defense networks, much like the Iskander. Having a domestic counterpart reduces reliance on external supply for such critical strike capabilities and provides Ukraine with symmetrical response options.
The existence of a domestic ballistic missile system comparable to the Iskander signifies Ukraine’s progress in developing advanced military technology. This capability is crucial in a conflict environment where ballistic missiles are used, offering Ukraine a means to conduct similar types of high-speed, difficult-to-intercept strikes against priority targets, thereby influencing the operational balance.
12. **Status of Mass Production and Testing Completion**:
A key development regarding the Sapsan system is its transition to mass production. Ukrainian officials have announced that the system has successfully completed combat testing and is now in the process of serial production. This marks a significant step from the earlier development phase.
The completion of combat testing is a critical milestone, indicating that the system has demonstrated its effectiveness under operational conditions. One reported combat test successfully struck a Russian military target at a range of nearly 300 km. While production is underway, information indicates that it is not yet known when these domestically produced missiles will be seen in regular operational use on the battlefield.
The move to serial production is essential for Ukraine to build a sufficient inventory of these missiles for sustained use. However, the timeline for their widespread deployment remains unconfirmed. The transition from successful testing and initial production runs to large-scale availability on the front lines will be a crucial factor in the system’s overall impact on the conflict.
13. **Geopolitical Implications and European Context**:
The production of the Sapsan system holds notable geopolitical significance, particularly within the European context. Experts highlight that Ukraine is the first European country since the Cold War era to resume the production of a conventional ballistic missile. This places Ukraine in a unique position regarding defense industrial capabilities.
This development positions Ukraine “definitely ahead of the rest of Europe” in this specific area, as no other European nation currently produces conventional short or medium-range ballistic missiles. While France produces sea-launched nuclear ICBMs for deterrence, and the UK does not manufacture its own ballistic missiles, Ukraine’s effort focuses on conventional systems for ground-based strikes, distinguishing its program.
The necessity of this domestic production is also underscored by the challenges Ukraine faces in securing sufficient weapons, including missiles, from Western partners. As one expert noted, if external supplies are limited or unavailable, domestic production becomes a vital necessity. While there were initial concerns among some Western countries regarding Ukraine obtaining such offensive capabilities and potential Russian escalation, a consensus appears to have emerged that a Ukrainian-built and operated weapon is distinct and less subject to external constraints.

14. **Production Challenges and Future Scale-up**:
Scaling up the production of advanced missile systems like Sapsan presents significant challenges for Ukraine. A primary concern is the vulnerability of large, above-ground production facilities to Russian strikes. Protecting such critical infrastructure is paramount for ensuring continuous production.
To mitigate the risk of attack, there is likely a need to construct protected or underground facilities for missile production. Such endeavors are described as complex, costly, and time-consuming, representing a major hurdle in rapidly increasing manufacturing output. The transition from initial serial production to achieving substantial numbers of missiles is not a simple process and will require significant investment and effort.
While the production process is underway, experts estimate that Ukraine would need to produce a considerable number of missiles annually, potentially around 80 to 100 per year, to build a sufficient stockpile for conducting meaningful strike operations against Russian targets. Achieving this scale of production will take time and overcoming the inherent logistical and security challenges, making the scale-up a critical factor in the Sapsan’s long-term strategic impact.
The emergence and ongoing production of Ukraine’s Sapsan ballistic missile system underscore a strategic pivot towards indigenous defense capabilities. Moving from the development stage to confirmed operational use and serial production highlights Ukraine’s determination to build its own tools for national defense. While challenges remain in scaling production and integrating the system into regular use, the Sapsan represents a notable advancement in Ukraine’s military-industrial complex and provides a new dimension to its strike capabilities, influencing the operational landscape and reinforcing the nation’s resolve. Its role as a domestically produced counterpart to advanced adversary systems and its potential to challenge existing air defenses signal its importance in the evolving dynamics of the conflict. The path ahead involves overcoming production hurdles to realize the full potential of this system.