The Chevrolet Corvair holds a singular and often debated position in the annals of American automotive history. Launched by General Motors in 1960, this compact car represented a bold, unconventional venture, challenging the prevailing norms of Detroit engineering. It emerged as a direct response to a shifting market landscape, where smaller, more fuel-efficient vehicles, particularly European imports and successful domestic compacts, were carving out a significant niche.
From its inception, the Corvair was designed to be different. Eschewing the traditional body-on-frame construction and front-mounted V8 engines that defined American cars, it embraced a rear-engined, air-cooled layout with independent suspension at all four corners. This innovative approach, while earning accolades and patents, also laid the groundwork for a legacy marked by both fervent admiration for its engineering prowess and intense controversy over its handling characteristics.
This in-depth exploration will delve into the various facets that shaped the Corvair’s journey, from its ambitious development and celebrated early years to the challenges it faced, its diverse model range, and the factors that ultimately led to its discontinuation. Join us as we uncover why the Corvair remains an iconic symbol of American innovation and enduring debate.

1. **The Market Imperative: Why the Corvair Was Born**By the late 1950s, the automotive landscape in the United States was undergoing a significant transformation. The “Big Three” American domestic auto manufacturers—General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler—had steadily increased the physical size of their entry-level models, inadvertently abandoning the market segment for smaller, more economical vehicles. This left a void that was quickly filled by others, signaling a clear shift in consumer preference.
A modern “compact car” market segment had already been firmly established in the U.S., notably by the successful 1950 Nash Rambler. Simultaneously, a burgeoning demand for small cars was evident through the growing sales of European imports. Vehicles like the Volkswagen Beetle, Renault, and Fiat were gaining traction, often serving as a practical second vehicle or an affordable primary option for budget-minded consumers seeking efficiency.
While the “Big Three” pursued a strategy of ever-larger cars, the newly formed American Motors Corporation (AMC) adopted a contrasting approach. Years ahead of its time, AMC strategically focused on smaller, fuel-efficient automobiles, positioning itself as an underdog. Their compact Rambler models proved immensely successful, propelling AMC to an impressive third place in domestic automobile sales and demonstrating the viability of this segment. Studebaker followed suit in 1959, restyling its economy sedan into the Lark compact, which also enjoyed initial success. These market signals forced the “Big Three” to reconsider their strategy and plan their own compact car introductions for 1959 and 1960, with GM’s response being the radically conceived Corvair.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.
2. **Ed Cole’s Vision: The Man Behind the Machine**The Chevrolet Corvair’s unconventional journey into American automotive history is intrinsically linked to the visionary leadership of Ed Cole. As a pivotal figure at General Motors, Cole’s influence was profound and far-reaching. He was promoted to chief engineer of the Chevrolet Motor Division in 1952, and just four years later, in July 1956, he ascended to the prestigious role of general manager of Chevrolet, GM’s largest automotive division, simultaneously becoming a GM vice president.
Cole was widely recognized as a driving force behind numerous significant engineering and design advancements introduced across Chevrolet’s car and truck lines between 1955 and 1962. His impact extended beyond the Corvair, notably shaping the development of the Corvette sports car. He is also famously known as the “father” of the small-block Chevy V8, a testament to his engineering acumen and forward-thinking approach.
His commitment to innovation, even in the face of past failures, was clear; Chevrolet had experimented with an air-cooled engine as early as 1923 with the Chevrolet Series M Copper-Cooled, a venture that had been deemed a failure due to engineering challenges. Despite this historical setback, Cole championed the air-cooled, rear-engine concept for the Corvair, pushing the boundaries of what was considered conventional for Detroit automakers at the time. His unwavering vision for a truly different compact car was instrumental in bringing the Corvair to fruition.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.

3. **A Radical Departure: Unconventional Engineering for Detroit**In an era dominated by front-engine, body-on-frame designs, General Motors embarked on a truly audacious path with the Chevrolet Corvair. While Ford and Chrysler opted for scaled-down versions of conventional American cars, the Corvair represented a profound and deliberate departure from these norms. Its engineering philosophy was highly unconventional for Detroit, setting it apart as a true innovator.
At its heart, the Corvair was powered by an air-cooled, horizontally opposed flat-six engine. This unique power plant, with many major components constructed from aluminum, marked Chevrolet’s second attempt at an air-cooled engine, a testament to their persistence in exploring alternative designs. The engine was strategically mounted in the car’s rear, driving the rear wheels through a compact transaxle, a configuration more commonly associated with European sports cars and economy vehicles like Porsche and Volkswagen.
Further distinguishing the Corvair was its fully independent suspension on all four wheels, a rare luxury for mass-produced American cars of the era, which often relied on simpler, less sophisticated designs. It also adopted unibody construction, eschewing the traditional body-on-frame method, contributing to a lighter, more rigid structure. The car was equipped with a wider, low-profile tire design mounted on wider wheels, influencing its unique handling characteristics. Visually, its clean, boxy styling, notably lacking the prevalent tail fins or a grille, broke away from Detroit’s established aesthetic trends, cementing its status as an engineering marvel and a bold design statement.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.
4. **Initial Acclaim and Early Challenges (1960-1961)**Upon its introduction, the Chevrolet Corvair was met with considerable enthusiasm and critical acclaim, heralding what many believed to be a new era of automotive innovation. Time magazine prominently featured Ed Cole and the 1960 Corvair on its cover for the car’s introduction in 1959, declaring that “its fresh engineering is hailed as the forerunner of a new age of innovation in Detroit.” This sentiment was echoed by Motor Trend, which honored the Corvair as its prestigious “1960 Car of the Year,” recognizing its groundbreaking design and engineering.
The initial market reception was equally impressive, with Chevrolet selling an astounding 26,000 Corvairs in its first two days alone. This represented over 35% of Chevrolet’s total sales during that period, far exceeding the initial target of one Corvair for every five Chevrolets. By March 1960, the Corvair accounted for a significant 13% of Chevrolet’s overall sales, underscoring its immediate popularity and promising trajectory in the compact car segment.
However, despite this early success and critical praise, the Corvair was not without its initial teething problems. As Time reported in 1960, “many were the minor bugs that often afflict a completely new car.” These issues included an engine cooling fan belt that had a tendency to pop off its 2-axis pulleys, which could lead to overheating and engine seizure if the fan did not run constantly. Carburetor icing and surprisingly poor fuel mileage, sometimes “well under 20 m.p.g.,” also plagued early models. The optional 1960 model gasoline heater was a concern as well, consuming up to a quart of gas an hour. Chevrolet engineers quickly moved to modify the Corvair’s carburetors to improve economy and address these early challenges, aiming to solidify its reputation further. The car, along with designers William L. “Bill” Mitchell and his styling staff, also received an Industrial Designers Institute (IDI of NY) award, underscoring its aesthetic and functional appeal.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.

5. **Expanding the Horizon: Wagons, Vans, and Trucks (Corvair 95)**The versatility of the Corvair platform extended far beyond passenger cars, as Chevrolet leveraged its unique rear-engine layout to introduce a diverse range of light-duty trucks and vans in 1961. This new subseries, marketed as the Corvair 95 (referencing its 95-inch wheelbase), adopted a “forward-control,” or “cab over,” design, with the driver positioned over the front wheels, reminiscent of the Volkswagen Type 2.
Among the notable additions was the Lakewood station wagon, which joined the lineup in 1961. Its innovative design placed the engine neatly under the cargo floor, freeing up an impressive 68 cubic feet (1.9 cubic meters) of cargo room—58 cubic feet in the main passenger compartment and an additional 10 cubic feet in the front trunk. This made the Lakewood a highly practical option for families and businesses alike, showcasing the adaptability of the Corvair’s architecture.
The Corvair 95 line also included commercial variants like the “Corvan 95” panel van and two distinct pickup truck versions. The Loadside was a relatively conventional pickup for its era, albeit with the Corvair’s signature rear engine and forward controls, featuring a unique pit in the middle of the bed. More distinctively, the Rampside offered a truly innovative solution with a large, fold-down ramp on the side of the bed, significantly easing the loading of wheeled items. The Greenbrier Sportswagon, sharing the Corvan 95 body but with side windows, was marketed as a station wagon and offered passenger car trim options, further diversifying the Corvair’s appeal and utility.
Car Model Information: 2021 Buick Envision FWD Preferred
Name: Chevrolet Corvair 95
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Greenbrier Sportswagon
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Aka: Corvan,Greenbrier,Corvair Rampside,Corvair Loadside
Production: 1961–1965
Platform: GM Z platform
Related: Chevrolet Corvair
Layout: RR layout
BodyStyle: van,van,pickup truck,pickup truck
Wheelbase: 95 in
Abbr: on
Length: {{convert,179.7,in,mm,0,abbr=on
Width: 70 in
Height: {{convert,68.5,in,mm,0,abbr=on
Engine: Chevrolet Turbo-Air 6 engine,2.7 L Turbo-Air H6
Transmission: Corvair Powerglide,Manual transmission,4-speed manual
Successor: Chevrolet Van
Categories: 1960s cars, Articles with short description, Cab over vehicles, Cars discontinued in 1965, Cars introduced in 1961
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair 95 is a subseries of the Chevrolet Corvair line produced from 1961 until 1965. It is the general term applied to the van and pickup truck variants of the rear-engined Corvair, named for their shortened 95 in (2,413 mm) wheelbase. It was Chevrolet’s first attempt at a van as well as their first and only van-based pickup truck in North America.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair 95
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair 95
Price: $20,775 Mileage: 37,332 mi.

6. **The Rise of the Monza and the Turbo Spyder (1961-1962)**The Corvair’s appeal broadened significantly with the strategic introduction and expansion of the Monza trim level. Following the success of the “Mr. and Mrs. Monza” styling concept cars at the 1960 Chicago Auto Show, Chevrolet management approved the neatly appointed bucket-seat DeLuxe trim of the 900 series Monza. Initially introduced as a two-door club coupe in April 1960, its immediate popularity, with over 11,926 Monza club coupes sold in its partial year, revealed a crucial market insight: the Corvair was increasingly viewed as a specialty or sporty car rather than just an economy competitor to the more conventional Ford Falcon or Chrysler Valiant.
This realization prompted Chevrolet to introduce the Monza upscale trim to four-door sedans in 1961, alongside the club coupe. With its newly available four-speed floor-mounted transmission, DeLuxe vinyl bucket seats, and refined trim, the Monza Club Coupe soared in sales, with nearly 110,000 units produced. This sporty iteration captivated the younger market, earning it the affectionate moniker “the poor man’s Porsche” in various car magazines. The Monza series alone contributed to about half of the total Corvair sales in 1961, cementing its status as a pivotal model for the brand.
Further cementing the Corvair’s performance credentials, 1962 saw the introduction of a convertible version and, most notably, a high-performance 150 hp (112 kW) turbocharged “Spyder” option for Monza coupes and convertibles. This made the Corvair the second production automobile in the U.S. to offer a factory-installed turbocharger, following the Oldsmobile F-85 Turbo Jetfire earlier that year. The Turbocharged Spyder equipment group featured a distinctive multi-gauge instrument cluster, including a tachometer, cylinder head temperature, and intake manifold pressure gauges, along with Spyder fender script and Turbo logo deck emblems. Automotive visionary John Fitch further capitalized on the Corvair’s sporting potential, choosing it as the basis for his “Sprint” models, which offered various performance and appearance improvements, even authorized for installation by several Chevrolet dealers. These developments solidified the Corvair’s image as a truly innovative and performance-oriented American compact.
Navigating the landscape of automotive history, we continue our deep dive into the Chevrolet Corvair, a vehicle whose journey from audacious innovation to eventual discontinuation is as complex as it is compelling. Having explored its unconventional origins and initial successes, we now turn our attention to the challenges it faced, the transformative redesign it underwent, and the enduring legacy it carved out amidst controversy and shifting market tides.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.

7. **First Generation: Evolution and Handling Adjustments (1962-1964)**The first generation Chevrolet Corvair, while celebrated for its groundbreaking design and engineering, was not without its evolving challenges, particularly concerning its dynamic handling characteristics. Introduced with a sophisticated, for its time, swing-axle independent rear suspension, the Corvair offered a unique driving experience distinct from its American contemporaries. However, under certain extreme conditions, or when driven by inexperienced drivers who were accustomed to the more predictable understeer of front-engine American cars, the first-generation Corvair’s propensity for significant rear wheel camber change could lead to abrupt oversteer.
Chevrolet engineers were actively engaged in refining the Corvair’s handling throughout its first generation. By 1962, a heavy-duty suspension package became available as an option for all passenger cars, excluding wagons. This package included a front anti-roll bar, rear-axle limit straps, revised spring rates, and specially recalibrated shock absorbers. These early modifications were crucial in mitigating the more pronounced rear wheel camber changes, thereby significantly improving the car’s stability and predictability during spirited driving or sharp maneuvers.
The culmination of these efforts to refine the first-generation Corvair’s dynamics came in the 1964 model year. This year saw the implementation of several significant engineering changes aimed at fostering more neutral handling. Most notably, a transverse leaf spring was added to the rear suspension, working in conjunction with softer rear coil springs. This innovative setup was specifically designed to reduce rear roll stiffness, which in turn helped to maintain more consistent tire contact patches and reduce the tendency for snap oversteer. Furthermore, the front anti-roll bar, previously an option, became standard on all models, and braking performance was enhanced with the introduction of finned rear drums. Despite these substantial improvements, made to create a more balanced and safer vehicle, external factors would soon cast a long shadow.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.

8. **The Nader Controversy: “Unsafe at Any Speed”**In a pivotal and often tumultuous chapter of its history, the Chevrolet Corvair became the central figure in a national conversation about automotive safety, largely instigated by Ralph Nader’s explosive 1965 book, “Unsafe at Any Speed.” Nader’s work aggressively critiqued the perceived deficiencies in American automobile design, singling out the Corvair’s first-generation swing axle rear suspension as inherently dangerous and prone to instability. He argued that the design made the car susceptible to loss of control, especially during cornering at higher speeds or when encountering sudden evasive maneuvers, painting a stark picture of manufacturer negligence.
The publication of “Unsafe at Any Speed” struck a resonant chord with the public, transforming Nader into a prominent consumer advocate and turning the Corvair into a symbol of corporate irresponsibility, whether justly or not. This intense and widespread media attention severely damaged the car’s public image and eroded consumer confidence, contributing to a precipitous decline in sales. It’s crucial to note that the book’s most damning criticisms primarily focused on the handling characteristics of the 1960–1963 models, and largely overlooked the significant design improvements implemented in the 1964 model and the entirely redesigned 1965 second-generation Corvair.
Years after the controversy first erupted and well after the Corvair had ceased production, a comprehensive 1972 report by a Texas A&M University safety commission for the National Highway Traffic Administration (NHTSA) offered a more nuanced and ultimately exonerating assessment. This rigorous study concluded that the 1960–1963 Corvair, when compared to contemporary compacts, possessed “no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations.” While acknowledging the Corvair’s unique handling characteristics, the report effectively tempered Nader’s aggressive claims. However, by the time this official vindication arrived, the public perception of the Corvair had been irreversibly tainted, and its commercial fate was already sealed.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.
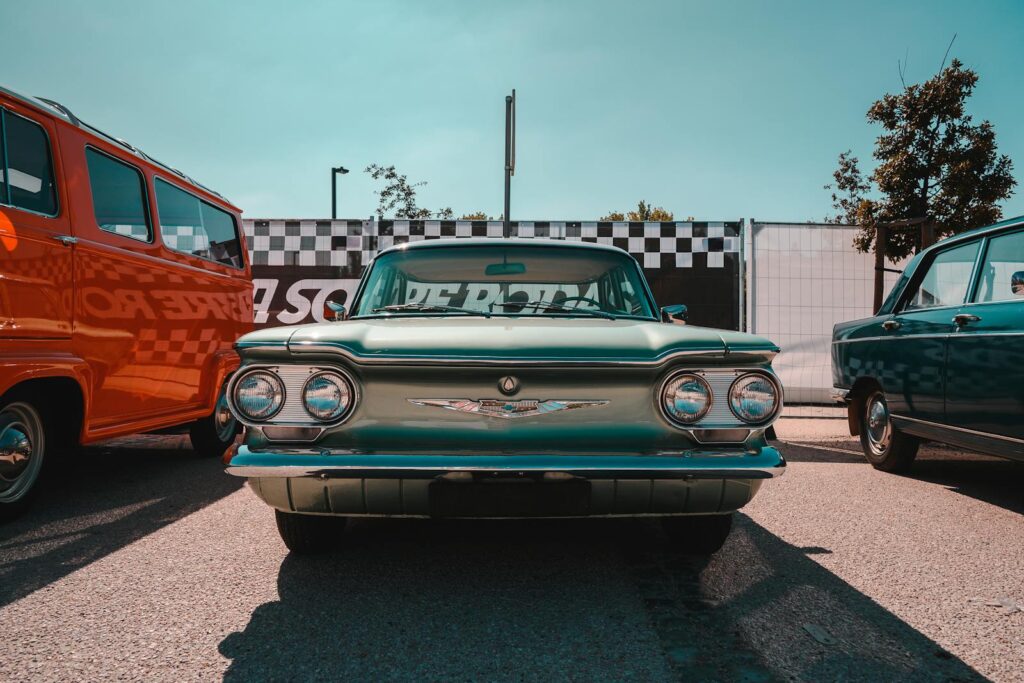

9. **The Second Generation: A Transformative Redesign (1965)**The arrival of the second-generation Chevrolet Corvair for the 1965 model year marked a dramatic and comprehensive transformation, effectively re-establishing its credentials as a truly advanced and desirable American compact. This extensive redesign began with a striking new Fisher Z-body, which immediately set it apart with its elegant, pillarless hardtop styling across all models. This aesthetic upgrade contributed to a sleek, modern silhouette that was widely acclaimed, making it arguably one of the most beautiful American cars of its era.
Beneath its stunning new exterior, the most significant engineering change addressed the very heart of the previous controversies: the rear suspension. The problematic swing axle system was entirely replaced with a sophisticated, fully independent trailing arm rear suspension, a design remarkably similar to that found in the highly regarded Corvette Sting Ray of the same period (though the Corvair utilized coil springs instead of the Sting Ray’s transverse leaf). This revolutionary upgrade virtually eliminated the undesirable camber changes that had characterized earlier models, delivering vastly improved handling, ride comfort, and overall stability, eliciting effusive praise from automotive critics.
The 1965 Corvair’s refinements extended beyond the chassis. The standard 95 hp and optional 110 hp engines were carried over from 1964, but the performance-oriented models received significant upgrades. The previous 150 hp Spyder engine was superseded by a normally aspirated 140 hp unit for the new Corsa series, boasting four single-throat carburetors, larger valves, and a dual exhaust system. For those craving even more power, a formidable 180 hp turbocharged engine remained optional on the Corsa. Further enhancements included a superior heater system, larger brakes borrowed from the Chevelle, a more robust differential ring gear, and the switch from a generator to a more modern alternator, collectively elevating the 1965 Corvair to a pinnacle of American compact car engineering.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.
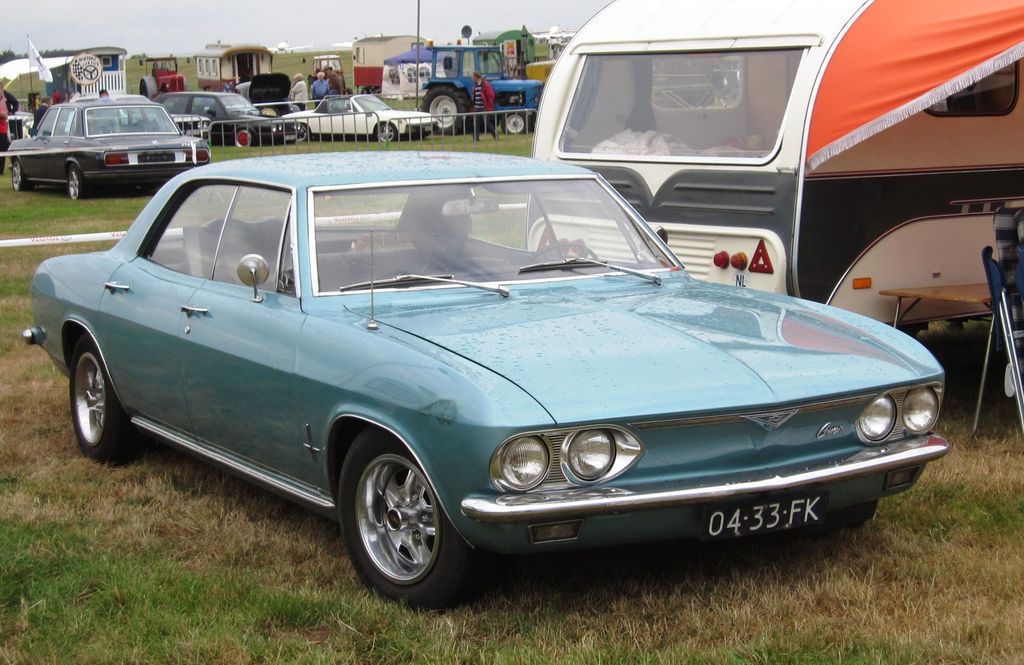

10. **The Second Generation’s Evolution: Refinements and Streamlining (1966-1968)**In the wake of its highly successful 1965 redesign, the second-generation Corvair continued to undergo subtle but important refinements through the 1966 to 1968 model years, even as its market position grew increasingly tenuous. For 1966, Chevrolet introduced an improved four-speed synchromesh manual transmission, now using the standard Saginaw gear set, which was shared with other GM 6-cylinder vehicles. A notable safety enhancement, actually a mid-1965 running change, was the adoption of a two-piece steering column with a universal joint, designed to reduce the risk of intrusion into the passenger compartment during a front-end collision. Aesthetic and functional tweaks included a plastic air dam below the front valence panel to conceal the suspension and lessen crosswind sensitivity, alongside revised taillight lenses and emblem placements.
The intensifying focus on automotive safety, particularly with nascent federal regulations, drove further standard enhancements. By 1967, the Corvair lineup was streamlined to the 500 and Monza Hardtop Coupes and Sedans, and the Monza Convertible. This year saw the implementation of a collapsible steering column as standard, alongside a dual circuit master cylinder with a warning light, reinforced nylon brake hoses, stronger steel door hinges, and “mushroomed” instrument panel knobs designed to absorb impact. Even the bucket seats in Monza models adopted the new “Astro” style, shared with the new-for-1967 Camaro, featuring a thin-shell design. Chevrolet also demonstrated commitment by introducing a 50,000-mile engine warranty across all its models, including the Corvair, and continued with active marketing campaigns.
The 1968 model year saw further consolidation of the Corvair lineup, with the four-door hardtop being discontinued, leaving only the two-door hardtop coupes and the Monza convertible. A notable functional change was the regrettable discontinuation of air conditioning as an option. This decision was likely driven by concerns about the additional thermal load imposed by the newly mandated Air Injection Reactor, commonly known as a “smog pump,” a move that potentially hurt sales as factory air became increasingly popular. Despite these continuous refinements and safety upgrades, sales continued their precipitous decline, reflecting the mounting external pressures and the company’s internal shift in focus.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.
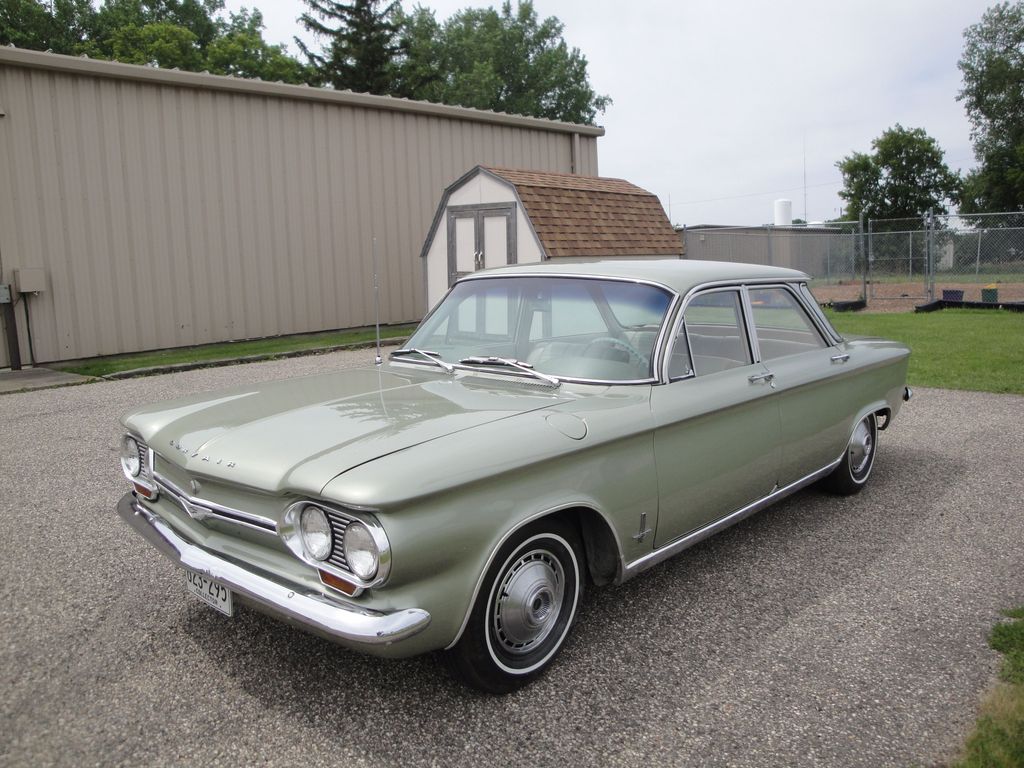

11. **The Final Drive: Factors Leading to Discontinuation**The curtain call for the Chevrolet Corvair was not abrupt but rather the culmination of several powerful converging forces, despite the fact that its second generation was widely lauded as a highly engineered and performance-oriented driver’s car. Perhaps the most significant blow came from the phenomenal market success of the Ford Mustang, introduced with much fanfare on April 17, 1964. The Mustang, presenting a dynamic and affordable package—a four-seat semi-coupe body built on a conventional compact (Falcon) chassis, readily available with small-block V8 engines and four-on-the-floor manual transmissions—captured the imagination of American buyers and shattered all existing sales records for a new car. This new competitor directly and deeply cut into the Corvair’s sales, particularly its sportier Monza and Corsa variants.
General Motors, observing the Mustang’s unprecedented triumph, began to perceive clear strategic advantages in adopting a similar, more conventional approach. Developing a Mustang-style model based on the widely used Nova platform offered significant cost efficiencies and simplified manufacturing processes, as it could be integrated seamlessly into GM’s existing lines of production technology. This internal strategic pivot meant that the vast resources and attention of GM, and particularly Chevrolet’s general manager John DeLorean, gradually shifted away from the unique, complex, and relatively expensive-to-produce Corvair, redirecting focus towards the development of a direct Mustang competitor: the Chevrolet Camaro.
Adding to these formidable competitive and internal pressures was the persistent, albeit largely outdated, shadow cast by Ralph Nader’s 1965 book, “Unsafe at Any Speed.” Despite the fact that the book’s specific handling criticisms primarily targeted the first-generation Corvair and were thoroughly mitigated by the superior, fully independent suspension of the 1965 and later models, the damage to the Corvair’s public image proved to be irreversible. This ongoing negative publicity, combined with the overwhelming appeal of the Mustang and the company’s clear shift in priorities, resulted in a drastic sales plummet of over half in 1966. By 1967, Chevrolet had largely ceased active advertising for the Corvair, and production volumes continued to dwindle rapidly, with a mere 6,000 cars produced in its final model year of 1969, marking a quiet end to a revolutionary car.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.
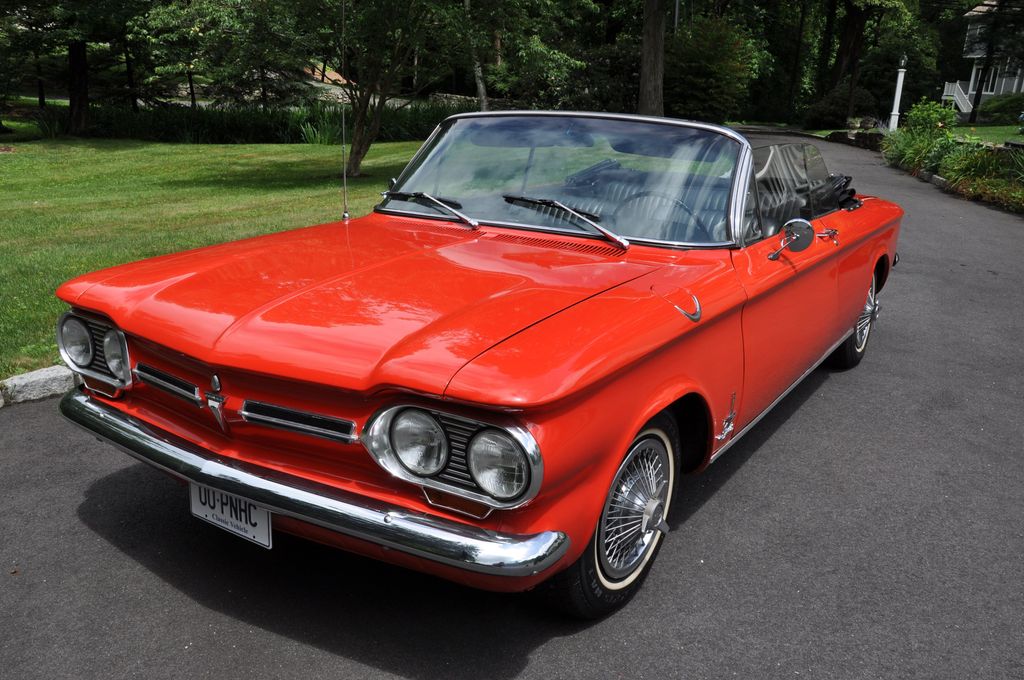

12. **The Corvair’s Enduring Legacy: Innovation, Controversy, and Icon Status**Despite its relatively short production run and controversial narrative, the Chevrolet Corvair forged an indelible and complex legacy in the annals of American automotive history. It stands as a monumental testament to Chevrolet’s audacious spirit of innovation, a bold and visionary attempt by a mainstream American automaker to break free from conventional Detroit engineering. Its pioneering rear-engined, air-cooled flat-six engine, sophisticated fully independent suspension, and advanced unibody construction were genuinely revolutionary for its time, earning it critical acclaim and securing its place as an engineering marvel that dared to be different.
However, the Corvair’s story is inextricably intertwined with the dramatic and far-reaching controversy ignited by Ralph Nader’s “Unsafe at Any Speed.” While subsequent governmental reports ultimately found the Corvair to be no more dangerous than its contemporaries, Nader’s criticisms, however disproportionate to the improved later models, indelibly stamped the car’s public perception. This highly publicized episode became a watershed moment for consumer safety advocacy in the United States, permanently influencing how automotive manufacturers approached design, testing, and public accountability for vehicle safety, forever changing the industry landscape.
Today, the Chevrolet Corvair is revered as a true automotive icon, recognized not only for its distinctive styling and surprisingly agile performance, particularly in its second generation, but also for its pivotal role in shaping the discourse around vehicle safety. It represents a daring gamble by General Motors, a project that, while ultimately discontinued due to a combination of market pressures and its controversial image, demonstrated a profound capacity for genuine engineering leadership. The Corvair’s unique character, combined with the compelling narrative of its rise, challenges, and eventual quiet departure, ensures its continued fascination for automotive enthusiasts, historians, and anyone captivated by the intricate tapestry of American industrial ingenuity.
Car Model Information: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Caption: 1964 Chevrolet Corvair Monza
Name: Chevrolet Corvair
Manufacturer: Chevrolet
Production: 1960–1969
Platform: GM Z platform
Chassis: Unibody
ModelYears: 1960–1969
Assembly: United States,Kansas City, Missouri,Oakland, California,Van Nuys,St. Louis,Flint, Michigan,Belgium,Canada,Mexico,South Africa,Switzerland,Venezuela
Class: Compact car
Successor: Chevrolet Vega
Layout: Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Categories: All Wikipedia articles written in American English, All articles lacking in-text citations, All articles needing additional references, All articles with dead external links, All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
Summary: The Chevrolet Corvair is a rear-engined, air-cooled compact car manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet over two generations between 1960 and 1969. The Corvair was a response to the increasing popularity of small, fuel-efficient automobiles, particularly the imported Volkswagen Beetle and the success of American-built compacts like the Rambler American and Studebaker Lark.
The first generation (1960–1964) was offered as a four-door sedan, two-door coupe, convertible, and four-door station wagon. A two- and four-door hardtop and a convertible were available second generation (1965–1969) variants. The Corvair platform was also offered as a subseries known as the Corvair 95 (1961–1965), which consisted of a passenger van, commercial van, and pickup truck variant. Total production was approximately 1.8 million vehicles from 1960 until 1969.
The name “Corvair” was first applied in 1954 to a Corvette-based concept with a hardtop fastback-styled roof, part of the Motorama traveling exhibition. When applied to the production models, the “air” part referenced the engine’s cooling system.
A prominent aspect of the Corvair’s legacy derives from controversy surrounding its handling, articulated aggressively by Ralph Nader’s Unsafe at Any Speed and tempered by a 1972 Texas A&M University safety commission report for the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) which found that the 1960–1963 Corvair possessed no greater potential for loss of control in extreme situations than contemporary compacts.
To better counter popular inexpensive subcompact competitors, notably the Beetle and Japanese imports such as the Datsun 510, GM replaced the Corvair with the more conventional Chevrolet Vega in 1970.
Get more information about: Chevrolet Corvair
Buying a high-performing used car >>>
Brand: Chevrolet Model: Corvair
Price: $29,988 Mileage: 74,787 mi.
From its unconventional birth as a response to evolving market demands to its transformative redesign and its entanglement in a landmark safety controversy, the Chevrolet Corvair’s journey is a compelling saga of ambition, innovation, and the unpredictable forces of public perception. It remains a fascinating anomaly in the history of American automobiles, a car that dared to challenge the status quo and, in doing so, left an undeniable and lasting imprint on the industry and the driving public. The Corvair truly stands as an enduring symbol of a bygone era of bold experimentation, forever securing its place in the pantheon of automotive legends.




