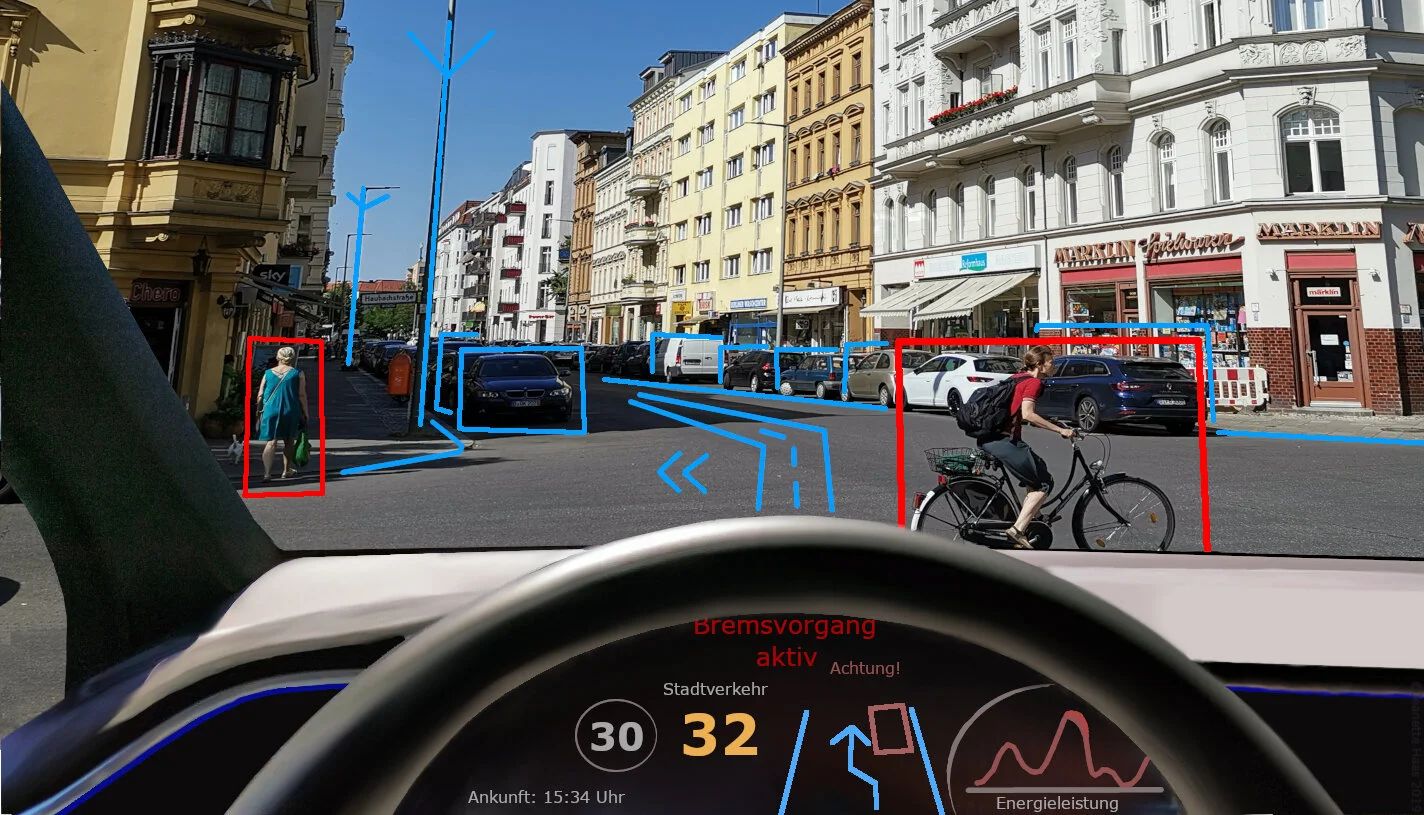
Self-driving cars have long been a vision of the future, promising to revolutionize transportation, reduce accidents, and unlock massive economic potential. After years of dedicated development and incremental progress, 2025 marks a truly pivotal moment for the autonomous vehicle (AV) industry, particularly within the United States. Advancements in artificial intelligence, sophisticated sensor technology, and evolving regulatory frameworks are collectively propelling self-driving cars beyond experimental prototypes. They are moving into tangible, real-world applications across urban streets and highways, transforming how we perceive and experience mobility.
The immense potential impact from self-driving technology cannot be overstated. Projections from as early as 2023 by ARK Invest’s “Big Ideas” report indicated massive potential revenues for robotaxis, possibly reaching as high as $9 trillion by 2030. This enormous economic forecast is underpinned by the fundamental idea that robotaxis could significantly reduce the need for personal car ownership, provided ride fares become sufficiently cheap. Such affordability could ignite a powerful positive feedback loop. If service providers can drop the cost to $0.25 per mile, autonomous taxi services would surpass 95% of short-haul journeys in cost-effectiveness.
Developing truly autonomous vehicles that can operate flawlessly in all conditions, however, remains an incredibly challenging endeavor. While the dream of Level 5, or full automation requiring no driver input under any circumstances, remains elusive, the industry is seeing significant breakthroughs. Deployments are increasingly common at Level 4. This high automation level allows vehicles to operate fully autonomously within defined operational design domains (ODDs), eliminating the need for human intervention within these specific conditions. In this comprehensive review, we delve into some of the leading self-driving car companies that are shaping the future of mobility in 2025.
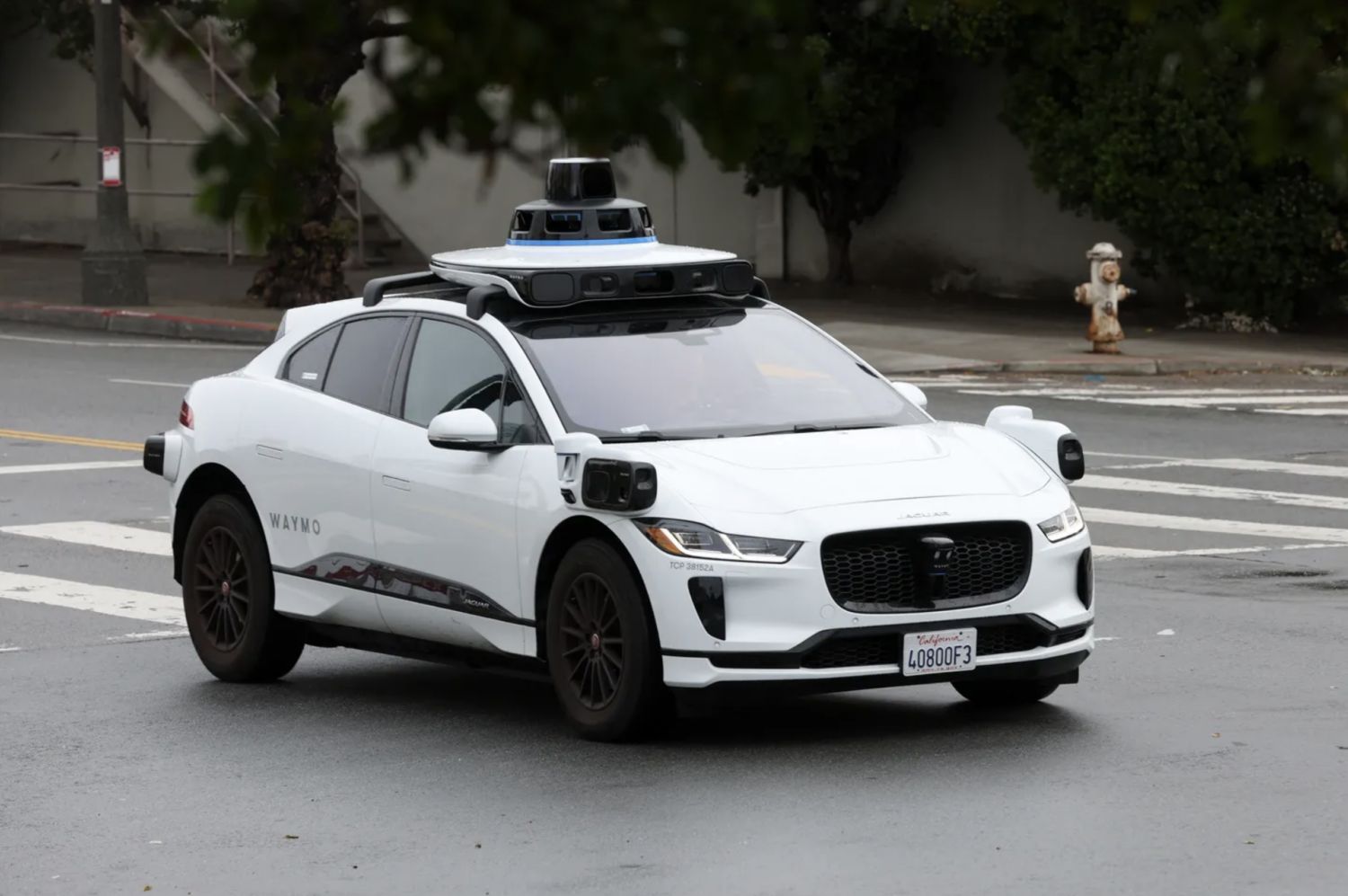

1. **Waymo**Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., has unequivocally solidified its position as a frontrunner in autonomous vehicle technology. It currently operates the most advanced Level 4 robotaxi service in the United States. Tracing its origins back to Google’s pioneering self-driving car project in 2009, Waymo has accumulated an unparalleled wealth of experience, boasting over 100 million autonomous miles driven. Its success is built upon a robust multi-sensor strategy, meticulously combining LiDAR, radar, and cameras, all harmonized by sophisticated AI-driven decision-making processes. This cautious, geofenced approach has enabled Waymo to prioritize and win the race to safe autonomous deployment, albeit initially limited to select geographic areas.
The period between 2024 and 2025 has been particularly dynamic for Waymo, marked by significant expansions and technological refinements. As of June 2025, Waymo’s Waymo One robotaxi service is fully driverless in major US cities, including Phoenix, Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Austin, reporting an impressive 250,000 paid rides per week. Further expansion is underway through a partnership with Uber, bringing Waymo to Atlanta. Plans are set to launch in Miami, Washington, D.C., and other key metropolitan areas by 2026. This aggressive rollout is supported by the unveiling of its sixth-generation autonomous driving system in 2024, which boasts a more cost-effective sensor suite.
This latest system offers enhanced resolution, extended range, and greater computing power. It is specifically designed to improve performance in diverse weather and complex urban settings. Waymo has also strategically forged new vehicle partnerships to scale its fleet. The company is transitioning from Jaguar I-Pace vehicles to agreements with Hyundai, utilizing the Ioniq 5, and Zeekr for future fleet expansion. A notable recent feature introduced in July 2025 in Metro Phoenix is teen accounts, allowing adolescents aged 14-17 to use Waymo independently, linked to a guardian’s account, enhancing safety for young drivers.
Read more about: The AI Revolution: 15 Key Careers Set to Transform (Or Disappear) by 2030 – Are You Ready to Pivot?
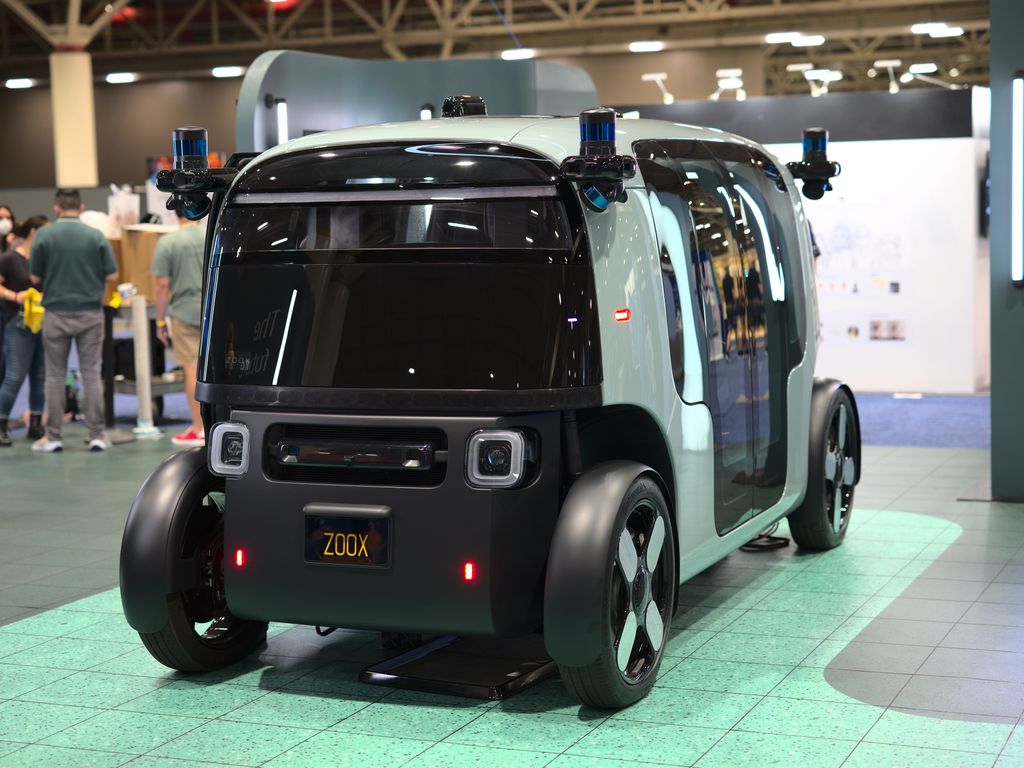

2. **Zoox**Zoox, a forward-thinking subsidiary of Amazon since its acquisition in 2020, is carving out a uniquely innovative path in the autonomous vehicle space. The company is pioneering a bespoke, bidirectional, and fully electric robotaxi, fundamentally designed without a driver’s seat or traditional steering wheel or pedals. This radical approach is geared towards urban ride-hailing, with a strategic aim to seamlessly integrate its services into Amazon’s vast ecosystem. This could potentially transform last-mile delivery and personal mobility within urban centers. Zoox’s dedication to this purpose-built design signifies a vision of future mobility where vehicles are conceived from the ground up specifically for autonomous operation.
The journey for Zoox has been marked by several significant milestones between 2024 and 2025, underscoring its rapid progress. In 2023, the company achieved a historic first fully autonomous ride on public roads in California, a critical validation of its technology. By 2025, Zoox had broadened its testing footprint to include San Francisco, Las Vegas, and Foster City, initially offering employee-only rides in its distinctive custom vehicles. The company has ambitious plans to roll out commercial services by 2026, targeting initial launches in Las Vegas, San Francisco, and subsequently in Austin and Miami within the next few years. This expansion is supported by the launch of its first production line in June 2025, with an aggressive goal of manufacturing over 10,000 robotaxis annually.
Zoox’s innovative robotaxi design features a symmetrical, “toaster-like” aesthetic, complete with four-wheel steering and sliding doors, all optimized for passenger comfort and unparalleled urban maneuverability. Safety is paramount to Zoox, with its vehicles incorporating over 100 safety innovations, including critical redundant systems for perception and control. Furthermore, Zoox made a significant regulatory breakthrough in August 2025, securing an exemption from certain Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) from the NHTSA. This landmark exemption permits Zoox to operate its purpose-built, driverless vehicles—devoid of conventional controls—for research and demonstration on public roads.
Product on Amazon: TESLA’S ROBOTAXI AND WAYMO: The Real Story Behind the Future of Autonomous Rides: A step-by-step exploration of how self-driving cars are shaping our world—today and beyond
Binding: Kindle Edition Product Group: Digital Ebook Purchas
Price: 7.99 USD
Shopping on Amazon >>
Read more about: Navigating the AI Revolution: Is the Intelligence in Our Machines a Friend or a Formidable Foe?

3. **May Mobility**May Mobility distinguishes itself within the competitive autonomous vehicle landscape by focusing on a specialized niche: autonomous shuttles tailored for short-range urban transport. The company’s core mission revolves around providing microtransit solutions for cities and corporate campuses, with a strong emphasis on enhancing accessibility and fostering community integration. This targeted approach aims to address specific transportation gaps, offering efficient, shared autonomous rides that complement existing public transit systems and cater to localized travel needs, particularly for those who may not own cars or have limited mobility options.
Recent updates between 2024 and 2025 highlight May Mobility’s expanding operational footprint and technological refinements. The company is currently operating driverless Sienna minivans, offering paid public rides in Ann Arbor, Michigan; Sun City, Arizona; and Peachtree Corners, Georgia. Further expansion is on the horizon, with plans for autonomous rides in Atlanta and Dallas slated for 2025, facilitated by a strategic partnership with Lyft. This growth is supported by continuous enhancements to its technology, including its drive-by-wire system integrated into Toyota Sienna vehicles, leveraging a sophisticated array of LiDAR, radar, and cameras to achieve Level 4 autonomy.
Product on Amazon: Hip & Joint Health Max Strength – Natural Joint Supplement for Dogs Chews – Glucosamine, Omega-3s, Chondroitin, Green Lipped Mussel – Help Improve Mobility, May Reduce Discomfort (90 ct)
Brand: Pet Honesty
Binding: Misc. Product Group: Pet Products
Price: 42.99 USD
Rating: 4.4 Total reviews: 13619
Flavor: Max Strength – Bacon
Item Form: Chew
Item Weight: 360 Grams
Manufacturer: PetHonesty
Shopping on Amazon >>
Read more about: Can an Electric Car Have “Soul”? Kia’s e-Soul vs. EV6 Puts the Debate in Motion

4. **Motional**Motional, a significant player in the autonomous vehicle arena, stands as a joint venture between the automotive giant Hyundai and the technology leader Aptiv. This collaboration positions Motional at the forefront of developing Level 4 autonomous vehicles specifically designed for ride-hailing and delivery services. The company has established a particularly strong operational presence in Las Vegas, a city known for its early adoption of autonomous technology, where it has been rigorously testing and deploying its self-driving fleet. Motional’s strategy leverages the robust manufacturing capabilities of Hyundai with Aptiv’s expertise in advanced safety and autonomous driving software, aiming to deliver scalable and reliable driverless solutions.
The period spanning 2024 and 2025 has seen Motional continue to advance its commercial offerings, despite facing certain challenges. Since 2018, Motional has successfully operated over 125,000 autonomous rides on the Lyft network in Las Vegas, demonstrating its capability in real-world ride-hailing scenarios. Building on this experience, the company commenced driverless rides for Uber passengers in 2022, with further expansion planned throughout 2025. Despite Aptiv’s decision to cease funding in 2024, Hyundai’s continued commitment and the appointment of a new CEO, Laura Major, underscore ongoing investment and a determined push forward for the company. Motional’s all-electric IONIQ 5 robotaxi also achieved a notable certification under the U.S. Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS).
Product on Amazon: MigPio Jesus Plush Doll Religious Gifts for Women Baptism Gifts for Women Christian Bible Verse Decor Jesus Figurese Motional Support Nuggets Faith Spiritual Catholic Gift Christian Desk Decor
Brand: MigPio
Binding: Product Group: Toy
Price: 5.99 USD
Shopping on Amazon >>
Read more about: 21 Highly Underrated Movies You Need To Watch Right Now

5. **Tesla**Tesla, Inc. stands as a highly influential and often controversial contender in the fiercely competitive race to develop widely adopted self-driving cars and robotaxis. The company boasts a unique and significant advantage: all its vehicles sold are factory-equipped with a comprehensive suite of cameras. Tesla boldly claims these cameras are sufficient to train its artificial intelligence system, entirely bypassing the need for expensive LiDAR or even radar sensors. This camera-only strategy translates into a colossal data advantage. Tesla effectively gains millions of miles of real-world training data “for free,” continuously provided by its vast global customer base driving in diverse conditions.
Despite this unique data acquisition model, the rollout of Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) software has been characterized by perpetual “soon” pronouncements and repeated delays over several years. This has led to considerable criticism for setting unrealistic expectations, with initial availability hoped for as early as 2018. However, a potential turning point appears to be emerging, with Texas granting Tesla Robotaxi a permit to operate a ride-hailing service in August 2025. This follows a test run in Austin since June 2025. Crucially, a Tesla employee currently remains on board as a safety monitor during these operations, signaling that true unsupervised autonomy is still in development.
The company’s approach remains a subject of intense debate. Some view the Texas approval as the vital first step toward large-scale FSD deployment and the human safety monitor as a temporary measure. Others express skepticism about Tesla’s ability to ever deliver truly autonomous robotaxis without additional sensors. The philosophical underpinnings of Tesla’s camera-only approach are rooted in the belief that if humans can drive using only their eyes, then an advanced AI should theoretically be capable of doing the same. This bold ambition has the potential to redefine car ownership and mobility. It hinges, however, on overcoming seemingly insurmountable technical challenges.
Read more about: Beyond the Showroom: 8 Astonishingly Expensive Car Customizations Defining Automotive Luxury
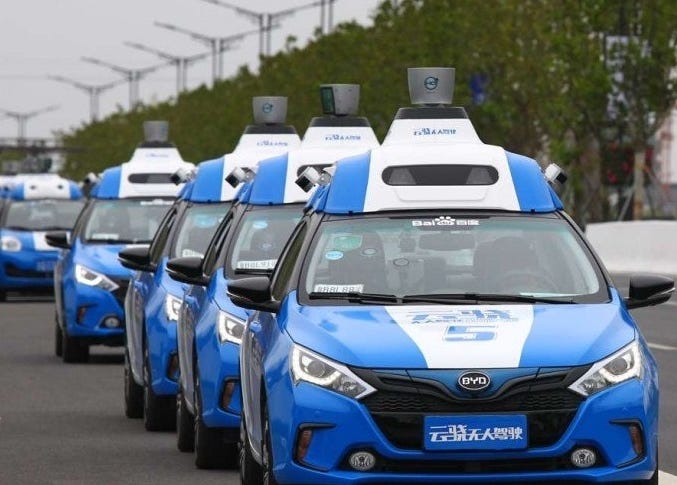

6. **Baidu**Baidu, widely recognized as China’s leading search engine, has aggressively entered the autonomous vehicle space, mirroring Google’s early foray with its own self-driving division, Apollo Go. The company has made substantial strides, notably transitioning to fully driverless operations in several prominent Chinese cities, effectively removing human safety drivers from its autonomous vehicles. This critical step demonstrates a high level of confidence in its AI and sensor systems. It establishes Baidu as a significant global player in the deployment of robotaxi services.
A pivotal development for Baidu’s global aspirations came in July 2025 with a groundbreaking deal with Uber. This agreement is designed to introduce its driverless cars to international markets beyond the United States and China. This multi-year partnership aims to deploy “thousands” of Baidu’s Apollo Go autonomous vehicles on the Uber platform worldwide. This signifies a major push for international expansion and market penetration. The scale of Baidu’s operations is already impressive, having provided 899,000 rides in the second quarter of 2024 alone, with plans in place to expand pilot zones to 20 cities by 2025.”
,”_words_section1″: “1924
Product on Amazon: VICSEED Tesla Phone Mount【Strongest Magnet Power】 Foldable Hidden Tesla Phone Holder Fit for All Phones, Tesla Model 3/Y/Cybertruck Accessories, Tesla Model 3 Model Y for MagSafe Car Mount
Brand: VICSEED
Binding: Product Group: Wireless
Price: 31.99 USD
Rating: 4.4 Total reviews: 1173
Color: Black
Compatible Devices: MagSafe case/ Magnetic case/ Thick case etc., Smartphones and Tesla Model 3/Y
Mounting Type: Foldable & Hidden
Shopping on Amazon >>
Read more about: China’s Affordable EVs Reshape the Global Auto Market as Western Carmakers Retreat to Luxury

7. **WeRide**WeRide, a company with roots in Silicon Valley since 2017 and headquartered in China, stands as a notable international contender in the autonomous vehicle arena. The company has actively expanded its global footprint, conducting numerous tests across various regions worldwide. Significantly, WeRide is now extending its operations into the UAE market through a strategic partnership with Uber, marking a substantial step in its international expansion. Concurrently, it has initiated a 24/7 robotaxi service in Beijing, demonstrating its capability for continuous, round-the-clock autonomous operations in a major metropolitan area.
The technological prowess of WeRide’s robotaxis is evident in their sophisticated sensor array and processing capabilities. Each vehicle is equipped with more than 20 sensors, including high-precision, high-dynamic cameras and high-line LiDAR systems strategically placed across the vehicle. This extensive sensor suite is crucial for addressing potential visibility challenges, particularly during nighttime operations, ensuring robust perception in diverse conditions.
Complementing this hardware is WeRide’s advanced multi-sensor fusion algorithm and a high-performance computing platform. This integrated system allows the robotaxi to achieve comprehensive 360-degree blind-spot-free coverage, detecting objects within an impressive range of up to 200 meters. Such a robust perception system is fundamental to enabling safe and reliable autonomous driving, especially in complex and dynamic urban environments, solidifying WeRide’s position among the leading AV developers.

8. **Mobileye**Mobileye, an Israel-headquartered company with a long history in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous technology, became a subsidiary of Intel in 2017 before being re-IPOed in 2022. The company has distinguished itself with a camera-first approach to autonomous driving, leveraging its expertise in computer vision and proprietary Road Experience Management (REM) HD mapping technology. This strategy has allowed Mobileye to establish a broad OEM footprint, integrating its solutions into a wide range of consumer vehicles and continually evolving its autonomy capabilities.
Despite its promising technological foundation and market presence, Mobileye has recently faced potential headwinds. News from July 2025 indicated that its parent company, Intel, was planning significant layoffs and intending to sell an 8% stake in Mobileye. While these actions might reflect broader organizational issues within Intel, they could nevertheless impact Mobileye by potentially reducing the financial backing and resources it can expect from its corporate parent. This situation could place Mobileye at a competitive disadvantage compared to well-funded rivals like Waymo or Zoox, which benefit from the robust support of Alphabet and Amazon, respectively.
The evolving landscape of autonomous driving demands substantial and consistent investment in research, development, and deployment. Any reduction in funding or strategic refocus from Intel could challenge Mobileye’s trajectory, even as it continues to advance its camera-first autonomous stack and expand its OEM partnerships. Its ability to navigate these financial pressures while delivering on its technological promises will be critical in maintaining its competitive edge in the rapidly accelerating autonomous vehicle market.
Product on Amazon: We Ride [Explicit]
Binding: MP3 Music Product Group: Digital Music Purchase
Price: 0.99 USD
Shopping on Amazon >>
Read more about: 2027 Porsche K1 Electric SUV: Flagship Luxury, 1000+ HP, and Revolutionary 900V Charging

9. **Aurora Innovation**Aurora Innovation has carved out a distinct niche within the autonomous vehicle industry by primarily focusing on driverless trucks, specifically targeting highway driving. This strategic emphasis is significant because highway routes account for the vast majority of mileage driven by commercial trucks, making it a highly impactful sector for automation. The company reached a monumental milestone in May 2025, successfully executing its first truly driverless run, a testament to years of development and rigorous testing.
Prior to this landmark achievement, Aurora had already accumulated an impressive record of three million autonomous miles, during which its technology successfully hauled over 10,000 customer loads. This extensive real-world experience underscores the maturity and reliability of its autonomous system. The company’s origins are also noteworthy; it was co-founded by Chris Urmson, an early leader in Google’s pioneering self-driving car project, which later evolved into Waymo. Urmson’s deep expertise and vision have undoubtedly shaped Aurora’s ambitious pursuit of highway autonomy.
Reflecting on the significance of this progress, Urmson once remarked, “I’m cruising down the highway at 65 miles per hour, not behind the wheel, but in the rear seat, watching the scenery unfold as a truckload of pastries are driven by the technology I helped create.” This vividly illustrates the tangible reality of Aurora’s technology. Looking ahead, the company is set to expand its driverless service, with plans to launch in El Paso, Texas, and Phoenix, Arizona, by the end of 2025, further solidifying its leadership in autonomous freight.
Read more about: Debunking the Myth: Unearthing the True Origins of the American Muscle Car Phenomenon

10. **Geofencing vs. Free Driving**A fundamental technological and business decision for companies developing self-driving cars revolves around the choice between “geofencing” and “free driving.” Geofencing refers to a strategy where a self-driving system is specifically designed and trained to operate only within a predetermined, limited geographic area, essentially establishing a virtual boundary for its autonomous capabilities. The core rationale behind this approach is that by restricting the operational domain, the AI system can achieve a high level of proficiency and safety within those particular roads. As Robert Day, Director of automotive partnerships for Arm’s Automotive and IoT, notes, “Limiting the area to more ‘private’ locations, or even sidewalks versus roads, can significantly reduce the type of interactions the vehicle will have with other objects, such as cars, trucks, cyclists and pedestrians.” This specialization greatly reduces the computational complexity and hardware requirements, making deployment potentially faster and safer in controlled settings.
However, the benefits of geofencing come with considerable drawbacks that limit the broader vision of autonomous mobility. The most significant limitation is that it severely restricts the deployment possibilities of autonomous vehicles. Each new city or expanded operational zone necessitates the self-driving company to undertake a custom and labor-intensive process of creating new training data, often involving years of manual driving to map and learn the specific characteristics of those areas. This bespoke approach makes the development and scaling of geofenced solutions inherently costly and slow. Furthermore, it primarily appeals to robotaxi companies, as individual car owners would still require their own vehicles for trips outside these often-limited downtown or single-city geofenced zones. If the industry remains confined to this paradigm, much of the transformative potential and economic gains expected from the mass adoption of truly ubiquitous robotaxis may never materialize.
The alternative, “free driving” or direct-to-full self-driving without geographical limitations, presents its own set of challenges, particularly concerning legal and business implications. While ambitious, attempting to achieve perfect autonomy everywhere from the outset can significantly delay any form of deployment, as it requires the system to be flawless across all conceivable conditions globally before even launching in a single city. Moreover, regulators have shown a willingness to slowly approve geofenced solutions, especially when safety in a defined zone has been rigorously demonstrated. In contrast, the authorization for globally unrestricted, Level 5 autonomous cars would require not just local, but comprehensive national-level laws and regulations that are, for the most part, still non-existent. Given that legal frameworks often lag behind technological advancements, this regulatory inertia could prove to be a formidable barrier to the widespread, unlimited deployment of high-level autonomy, even if the technical challenges are entirely overcome.
Product on Amazon: Roots Organics Uprising Bloom Fertilizer, 9 lb.
Brand: Aurora Innovations
Binding: Lawn & Patio Product Group: Lawn & Patio
Price: 50.28 USD
Rating: 4.7 Total reviews: 79
Item Weight: 1.34 Kilograms
Item Form: Powder
Coverage: 1
Specific Uses For Product: Organic
Features:
1. A Diverse Blend Of Natural And Organic Ingredients Specially Formulated For Maximum Results
2. Effective Alone As An Amendment Or As A Top Dress For Encouraging Vigorous Flowering And Fruiting
3. Most Effective When Used In Conjunction With Roots Organics Uprising Grow For A Plant’S Vegetative Phase And Roots Organics Uprising Foundation As A Supplement
4. Uprising Bloom Is Most Effective When Used In Conjunction With Roots Organics Uprising Grow For A Plant’S Vegetative Phase And Roots Organics Uprising Foundation As A Supplement
Shopping on Amazon >>
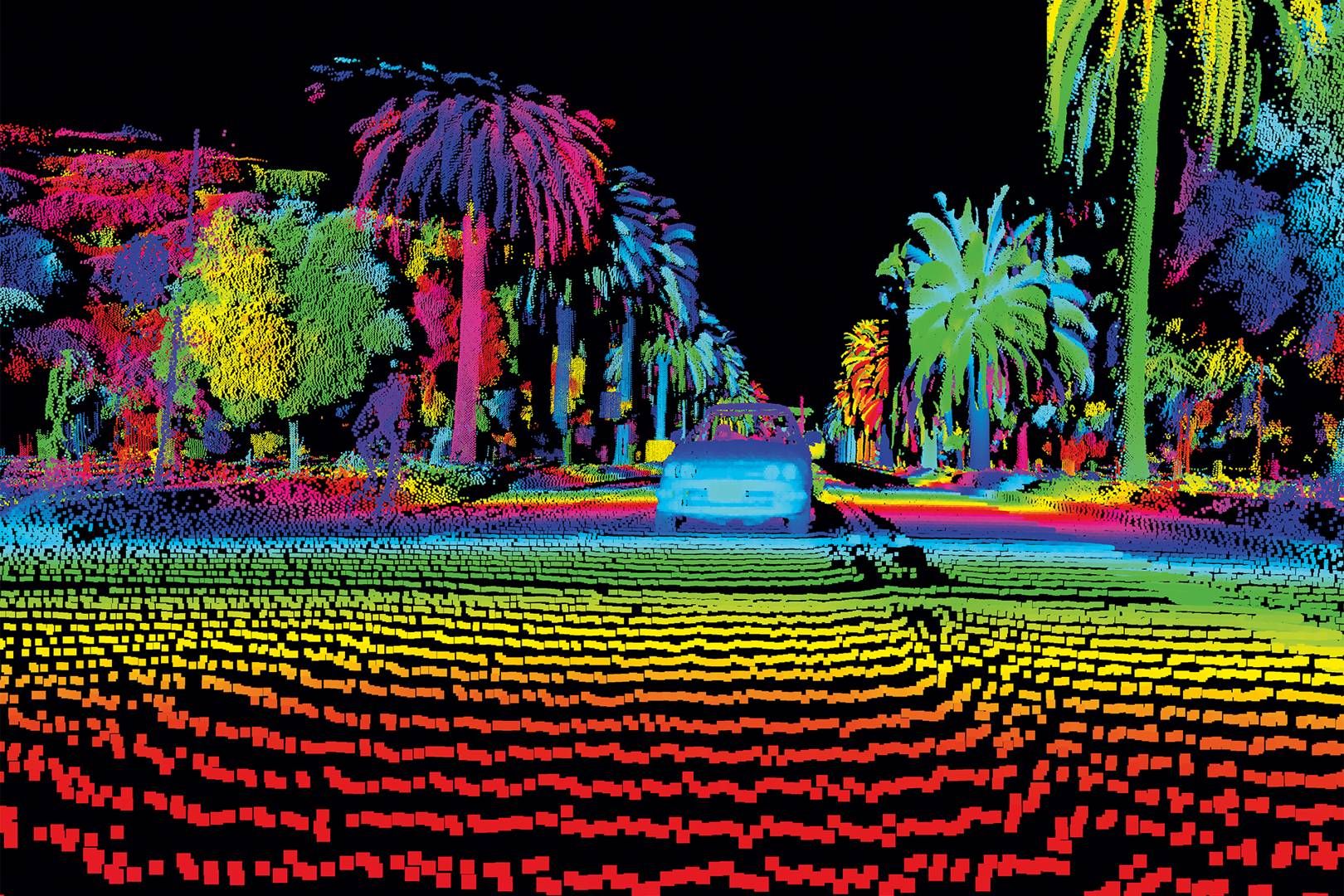
11. **LIDAR vs. Cameras-Only**Another prominent and often contentious debate within the autonomous vehicle industry centers on the primary sensor technology used for perception: Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) versus a cameras-only approach. LIDAR systems utilize laser beams to detect nearby objects, meticulously creating a real-time, highly detailed 3D model of the vehicle’s environment. These systems are typically mounted on top of self-driving cars, appearing as somewhat bulky additions. A key advantage of LIDAR is its superior ability to perceive more than cameras alone, excelling at precisely evaluating distances and making it exceptionally effective for accident avoidance, particularly at higher speeds. Furthermore, LIDAR operates flawlessly in complete darkness or low-light conditions and is often paired with radar to detect objects reliably even in challenging environments like fog, enhancing overall safety and resilience.
Despite these significant benefits, LIDAR technology comes with several notable drawbacks, which explain why one major player, Tesla, has opted for a camera-only strategy. The most immediate concern is cost. High-end LIDAR systems can cost around $70,000-$80,000 per unit, which significantly inflates the overall price of a self-driving car. However, there are signs that these costs are rapidly decreasing, especially for lower-end LIDARs, potentially making them more commercially viable in the near future. Li Chuanhai, Vice-president of Geely Auto Group, highlighted this trend, stating, “A LiDAR unit, for instance, used to cost 30,000 yuan (about $4,100), but now it costs only around 1,000 yuan (about $138) — a dramatic decrease.” Beyond cost, LIDAR is a complex technology, often involving numerous moving parts like rotating mini-mirrors, which can introduce maintenance challenges and impact long-term reliability.
A crucial long-term implication for companies committing to LIDAR is that any AI system trained with LIDAR data will likely forever require these sensors to perform optimally. The need for LIDAR becomes deeply embedded into the neural network’s architecture, creating a fundamental dependency. This contrasts sharply with Tesla’s bold camera-only approach, which aims to replicate human vision. While Tesla’s method potentially offers a more cost-effective and scalable solution in the long run, it has faced considerable skepticism regarding its ability to achieve Level 5 autonomy without the redundant and precise data provided by LIDAR and radar. The choice between these two sensor philosophies represents a fundamental fork in the road for autonomous vehicle development, with profound implications for cost, complexity, safety, and ultimate scalability.

12. **Understanding SAE Levels of Autonomy**Before fully appreciating the nuances of self-driving car capabilities and the progress of the companies discussed, it is absolutely critical to understand the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) levels of driving automation. This standardized classification system provides a clear framework for defining the degree to which a vehicle can drive itself, ranging from no automation to full automation under all conditions. These levels are fundamental to assessing current achievements, understanding regulatory discussions, and envisioning the future of mobility, serving as a common language for the industry, regulators, and consumers alike.
The lower end of the spectrum, Levels 0 to 2, primarily involves human drivers. Level 0, “No Automation,” means the human driver performs all driving tasks, including steering, acceleration, and braking, with full control and monitoring required, characteristic of most traditional vehicles. Moving to Level 1, “Driver Assistance,” the vehicle offers basic assistance with either steering or acceleration/braking, such as adaptive cruise control or lane-keeping assist, but the human remains responsible for monitoring and controlling most tasks. Level 2, “Partial Automation,” sees the vehicle simultaneously controlling both steering and acceleration/braking. However, a human driver must constantly monitor the driving environment and be prepared to intervene at any moment, as exemplified by systems like Tesla FSD (Supervised) and Cadillac Super Cruise. These early levels underscore that the human driver remains firmly in the loop as the primary operator.
The more advanced stages of autonomy begin with Levels 3 and 4, and culminate in the aspirational Level 5. Level 3, “Conditional Automation,” allows the vehicle to handle most driving tasks under specific conditions, but the human driver must still be ready to take over when requested by the system. Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot offers a limited example of this, requiring human intervention. Level 4, “High Automation,” represents a significant leap, where the vehicle is fully autonomous within a defined operational design domain (ODD) and requires no human intervention within that specific area. The human driver is not required to monitor the driving, but simply sets the destination, as seen with Waymo, Zoox, and Motional robotaxis. Finally, Level 5, “Full Automation,” envisions a vehicle that is fully autonomous in all conditions and environments, requiring absolutely no human input for any task. As of 2025, Level 5 remains an unachieved ideal, the holy grail of autonomous driving that continues to drive intense research and development efforts across the industry.
Product on Amazon: Intel RealSense LiDAR Camera L515
Brand: Intel
Binding: Electronics Product Group: Camera
Price: 499.99 USD
Rating: 4.0 Total reviews: 22
Photo Sensor Technology: CMOS
Video Capture Resolution: 1080p
Flash Memory Type: SD
Video Capture Format: MPEG 4
Screen Size: 1
Connectivity Technology: USB
Special Feature: Infrared
Camcorder type: Video Camera
Included Components: L515 Camera
Features:
1. Package Dimensions: 5.9 cms (L) x 11.4 cms (W) x 5.9 cms (H)
2. Product Type: Surveilance Systems
3. Package Quantity: 1
4. Country Of Origin: China
Shopping on Amazon >>
Read more about: ADAS Technology: The Revolution Transforming Vehicle Safety and the Driving Experience
As we conclude our deep dive into the 2025 landscape of self-driving cars, it’s clear that the industry is experiencing an unprecedented acceleration. From the cautious, geofenced deployments of leaders like Waymo and Zoox to the ambitious, camera-only pursuit of Tesla, a diverse array of technological approaches and business models are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. The ongoing debates surrounding sensor choices and operational domains highlight the complex challenges that still need to be addressed. Yet, with robotaxis becoming a routine sight in major cities and autonomous trucks making their first driverless runs, the vision of a future transformed by self-driving technology is rapidly shifting from a distant dream to a tangible reality, promising a safer, more efficient, and perhaps, more enjoyable journey for all.



