The annual launch of a new iPhone invariably ignites a fervent discussion among tech enthusiasts and casual users alike. With each successive iteration, Apple consistently pledges a leap forward in features and functionality, solidifying its position as a vanguard in smartphone technology. Yet, as with any major technological stride, the promise doesn’t always perfectly align with the practical experience, leaving a segment of users with lingering questions about the true advancements.
This year, with the arrival of the iPhone 17 Pro, Apple has once again commanded the spotlight, showcasing a suite of camera upgrades designed to entice photographers and videographers. From a completely redesigned physical aesthetic to substantial sensor enhancements, the technical specifications present a compelling case for improved imaging. However, beneath the surface of these impressive numbers and marketing narratives, a persistent challenge in smartphone photography continues to plague even the most advanced systems, often frustrating users who expect perfection from a premium device.
Our extensive testing of the new iPhone 17 Pro camera system reveals a powerful and versatile tool, undoubtedly capable of stunning results under optimal conditions. Yet, a critical examination uncovers certain limitations and long-standing issues, particularly in areas where Apple’s computational photography has historically faced scrutiny. It’s these subtle yet significant discrepancies between marketing ideal and real-world performance — especially concerning low-light capabilities and the nuances of image processing — that form the core of a ‘flaw’ Apple would perhaps prefer remained in the shadows. Join us as we dissect the iPhone 17 Pro’s camera, layer by layer, to uncover its true potential and its lingering imperfections.

1. **The Redesigned Camera Plateau: A Bold New Look for Durability and Integration**
For the iPhone 17 Pro and 17 Pro Max, Apple has introduced a striking new design for the device’s rear, moving away from the traditional camera bump to what it calls a ‘camera plateau.’ This innovative design choice sees the camera system span almost the entire back of the iPhone, creating a seamless and integrated look. The absence of a protruding bump is not merely aesthetic; it signifies a deeper integration of the camera modules within the phone’s overall structure.
This ‘forged plateau’ camera bar is part of a broader redesign, featuring a slightly thicker aluminum unibody construction for the Pro series. The entire camera housing is now a single machined block of aluminum, providing enhanced durability. This construction, along with the new Ceramic Shield 2 on the display and ceramic on the back, contributes to a more rugged and robust device, designed to withstand the daily rigors that smartphones typically face.
The redesign also hints at functional improvements beyond mere aesthetics. The unibody design and the use of ceramic on the back are not just tougher than older glass designs but also offer better thermal performance. This is a crucial detail, especially considering the overheating complaints associated with prior iPhone models. Apple claims this new design provides far more capacity to absorb and shed excess heat, aiming to resolve any major overheating issues and maintain optimal camera performance during extended use.

2. **The Revamped Telephoto Lens: Ushering in New Zoom Capabilities and Clarity**
The iPhone 17 Pro models introduce a significantly upgraded Telephoto lens, addressing what was considered a weak link in previous iterations. This new Fusion Telephoto lens boasts a 48-megapixel sensor, marking a substantial upgrade from the 12-megapixel Telephoto lens found in the iPhone 16 Pro models. The enhanced resolution immediately suggests a potential for greater detail and clarity in zoomed images.
This advanced telephoto system supports both 4x zoom, equivalent to a 100mm focal length, and 8x zoom, which translates to a 200mm focal length. Crucially, at 4x zoom, users can capture full 48-megapixel images, offering unparalleled detail for a smartphone telephoto. However, a notable nuance is that 8x zoom images are limited to 12 megapixels, indicating that while the reach is extended, there’s a trade-off in raw resolution at the longest optical setting.
Further enhancing its capabilities, Apple states that the Telephoto sensor is 56 percent larger than its predecessor, a significant improvement that promises enhanced performance in challenging low-lighting conditions. The lens also integrates Hybrid Focus Pixels, 3D sensor-shift optical image stabilization, and autofocus, alongside the tetraprism design introduced last year. This combination of hardware and stabilization technology aims to deliver sharper, more stable zoomed shots, even when pushing the limits of its 40x digital zoom potential, though it doesn’t quite match competitors like Samsung’s 100x zoom.

3. **The 48-Megapixel Wide Lens (Fusion Main): A Consistent Core of Imaging Excellence*
The Wide lens, which Apple refers to as the Fusion Main lens, remains a formidable component of the iPhone 17 Pro’s camera system. With a consistent 48-megapixel resolution, it serves as the primary workhorse for everyday photography, building upon the strong foundation established in the iPhone 16 Pro. While it hasn’t undergone radical changes this year, its proven capabilities continue to deliver high-quality results across various shooting scenarios.
Users have the flexibility to capture images at either 24-megapixel or 48-megapixel resolution at the standard 24mm focal length, catering to different needs for file size and detail. Additionally, it offers a 12-megapixel 2x Telephoto option at a 48mm focal length, effectively providing a versatile mid-range zoom without switching to the dedicated telephoto lens. This ‘hybrid zoom’ functionality, as Apple often highlights, leverages the high-resolution sensor for greater flexibility.
Underpinning the Wide lens’s performance are several advanced features, including second-generation sensor-shift optical image stabilization, which ensures sharper images by counteracting camera shake. It also utilizes 100 percent Focus Pixels for fast and accurate autofocus and boasts an f/1.78 aperture, allowing for considerable light gathering. This combination makes the Fusion Main lens a reliable and high-performing component, consistently delivering vibrant and well-exposed images.

4. **The 48-Megapixel Ultra Wide-Angle Lens (Fusion Ultra Wide): Expanding the Perspective**
Apple’s 48-megapixel ultra wide lens, branded as the Fusion Ultra Wide, significantly broadens the creative possibilities for iPhone 17 Pro users. With a 13mm focal length, it captures an expansive 120-degree field of view, making it ideal for sweeping landscapes, architectural shots, or fitting large groups into a single frame. This wide perspective allows users to tell a more complete visual story, immersing viewers in the scene.
Beyond its capacity for vast vistas, the Ultra Wide lens is also adept at capturing intricate details through close-up 48-megapixel macro shots. This dual functionality is particularly impressive, enabling users to switch seamlessly from grand scale to microscopic examination without needing additional lenses. The precision required for macro photography is supported by Apple’s Hybrid Focus Pixels, ensuring sharp and detailed close-ups.
Equipped with an f/2.2 aperture, the Ultra Wide lens performs commendably in various lighting conditions, though slightly less light-sensitive than the main Wide lens. The context also mentions ‘Lens correction’ as a feature for the Ultra Wide, which is crucial for eliminating the distortion typically associated with such wide-angle optics. This digital correction ensures that images captured with this lens maintain natural lines and perspectives, enhancing the overall professional quality of the output.
5. **The New Front-Facing Camera with Center Stage: Elevating Selfies and Video Calls**
Apple has significantly upgraded the front-facing camera across the entire iPhone 17 family, introducing a brand-new 24-megapixel sensor, which in its widest frame, outputs an 18-megapixel final image. This improvement is not just about resolution; it’s about enhancing the user experience for selfies, video calls, and content creation. The front camera now boasts a square sensor, a unique design choice that allows more to fit in the frame than before.
One of the standout features of this new front camera is the inclusion of Apple’s renowned ‘Center Stage’ technology. As its name suggests, Center Stage automatically keeps subjects centered in the frame during video calls, even as they move around. This intelligent reframing, made possible by the additional pixels and wide-angle lens, is particularly useful for dynamic interactions or when multiple people enter the frame, ensuring everyone remains visible and engaged.
Furthermore, this updated front camera addresses practical usability concerns. Users can now take front-facing photos and videos in landscape or portrait mode without having to physically rotate their phone, offering greater flexibility and convenience. Apple has also improved stabilization when capturing video with the front camera. The Dual Capture feature, which records simultaneously from the front and rear cameras, opens up new avenues for creative content, such as reaction videos or capturing both sides of a conversation, supporting up to 4K Dolby Vision recording at 30 frames per second.

6. **Advanced Computational Photography: The Unseen Hand and its Hidden Compromises**
Apple’s computational photography is a powerful suite of algorithms designed to optimize image quality by analyzing elements like tone mapping, lighting, color balance, and HDR. This technology is intended to compensate for imbalances and enhance photos, often kicking in for low-light images via the Photonic Engine or improving texture and detail in mid-to-low lighting with Deep Fusion. The intent is to produce stunning, consistently high-quality images with minimal user intervention.
However, this ‘aggressive computational photography,’ as some users describe it, often acts as a double-edged sword. While it aims to deliver an optimized result, the processing can sometimes lead to images that deviate significantly from the actual scene or the user’s intended capture. This ‘overprocessing’ is a frequent complaint, manifesting as altered skin tones, unnatural background lighting, or colors that appear overly saturated, creating a discrepancy between the initial capture and the final processed image.
The implications of this overprocessing are particularly frustrating for content creators who rely on their phone cameras for consistent and accurate production. The context explicitly notes user videos depicting this inconsistency on social media, highlighting a genuine concern that the iPhone’s camera might not always capture ‘real-world scenes’ faithfully. While enabling the ProRAW option on Pro models offers a workaround, it essentially requires users to bypass the very computational magic Apple champions, underscoring a ‘flaw’ in the automated process Apple might prefer to downplay.

7. **The Critical Challenge of Low-Light Photography: A Persistent Area of Concern**
Despite advancements in sensor technology and computational photography, low-light performance remains a significant area of criticism for the iPhone camera. Users expect their premium devices to perform exceptionally well in dim environments, yet reports suggest a recurring struggle. This is particularly disappointing given Apple’s marketing emphasis on enhanced light capture and improved performance in challenging conditions, like the larger Telephoto sensor for poor lighting.
Common complaints regarding low-light photography revolve around two primary issues: grainy images and focus inaccuracy. Users frequently observe that the camera produces noticeable noise and graininess in photographs taken in dim situations, detracting substantially from the overall image quality. This compromises the clarity and fine detail that one would anticipate from a high-end smartphone camera, making low-light shots appear less refined than desired.
The second major pain point is the camera’s difficulty in achieving precise focus under low-light conditions. Reports indicate that low-light focus is often a struggle, leading to blurred or soft images even when the subject is relatively still. This inconsistent performance in critical moments, where lighting is often beyond the user’s control, can result in missed opportunities for sharp captures, directly impacting overall user satisfaction and highlighting a persistent gap between expectation and reality in a crucial performance metric. The Night mode feature attempts to mitigate this by aggregating multiple images, but it cannot entirely eliminate these underlying hardware and software challenges.” , “_words_section1”: “1945

8. **Expanded Video Capabilities: From Cinematic Storytelling to ProRes RAW**
The iPhone 17 Pro models usher in a new era for mobile videography, presenting a suite of advanced features designed to empower filmmakers and casual creators alike. Beyond simply recording moments, these capabilities offer tools for nuanced storytelling, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with a smartphone. The ability to record 4K Dolby Vision video at an impressive 120 frames per second on the main camera provides incredible detail and fluidity, making slow-motion captures truly cinematic.
For professionals, the addition of ProRes RAW recording marks a significant leap, especially when paired with an external storage device. This tried-and-true RAW video format grants considerable flexibility during post-production, offering a much broader canvas for color grading and adjustments than the existing ProRes 422 HQ. Furthermore, the surprising, unmentioned Open Gate feature in ProRes RAW allows videographers to utilize the entire 4:3 image sensor, enabling reframing of videos after the fact, providing unparalleled creative control.
Beyond raw capture, the iPhone 17 Pro integrates sophisticated features like Genlock video synchronization, aimed directly at professional production workflows. It also boasts macro video recording, including slo-mo and time-lapse options, alongside 1080p Slo-mo support at up to 240 fps, or even 4K Dolby Vision at 120 fps for dramatic effects. Continuous autofocus video, cinematic video stabilization, and QuickTake further enhance the video experience, ensuring that every shot is as polished as possible.
The Dual Capture feature, which records simultaneously from the front and rear cameras at up to 4K Dolby Vision at 30 frames per second, opens up novel avenues for creative content, such as dynamic reaction videos or capturing both sides of a conversation with ease. Enhanced audio features like Audio Mix and wind noise reduction underscore Apple’s commitment to providing a comprehensive video production tool, ensuring that sound quality matches the visual fidelity.
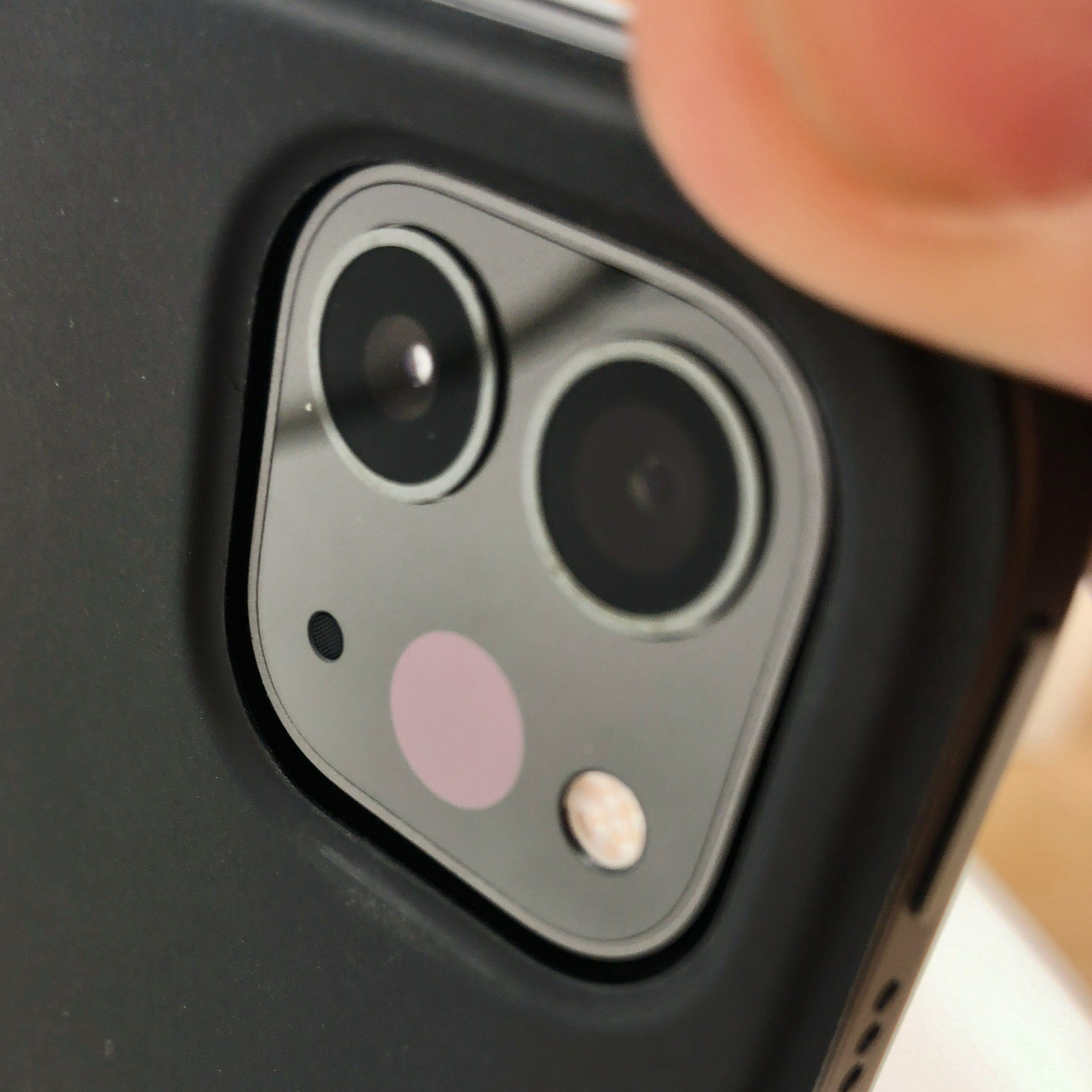

9. **The LiDAR Scanner and Adaptive True Tone Flash: Enhancing Depth and Illumination**
Beyond the primary camera modules, the iPhone 17 Pro’s camera plateau houses essential auxiliary components that play a crucial, albeit often unseen, role in image quality and user experience. Positioned prominently on the right side of the camera plateau are the Adaptive True Tone Flash and the LiDAR Scanner. While not headline-grabbing lenses, their integration is fundamental to the device’s advanced capabilities, particularly in challenging environments.
The LiDAR Scanner, a technology first introduced in previous Pro models, serves as a sophisticated depth-sensing instrument. While the context doesn’t explicitly detail its every function for the 17 Pro, its presence is a strong indicator of its continued role in enhancing autofocus in low-light conditions, which was a point of criticism in our initial review. Furthermore, by collecting precise depth information, LiDAR is instrumental in enabling features like Portrait mode, even allowing depth adjustments post-capture by accurately mapping the scene.
Complementing this is the Adaptive True Tone Flash, designed to deliver more natural and balanced illumination. Unlike traditional smartphone flashes that can produce harsh, artificial-looking light, the Adaptive True Tone Flash intelligently adjusts its intensity and color temperature to match the ambient light. This ensures that subjects are well-lit without appearing washed out or unnaturally colored, an essential detail for indoor photography or any situation where supplemental light is necessary for a quality shot.

10. **Smart HDR 5 and Intelligent Portrait Features: Refining Subject Presentation**
Apple’s commitment to delivering compelling imagery extends beyond basic capture, delving into intelligent processing that enhances the way subjects, particularly people, are rendered. Smart HDR 5 exemplifies this, representing a significant stride in optimizing photographic outcomes. This technology is adept at recognizing individuals within a scene, then meticulously optimizing contrast, lighting, and skin tones, ensuring that every person captured looks their absolute best, an often-overlooked but crucial detail for social photography.
Further refining the art of subject isolation and artistic depth, the iPhone 17 Pro provides sophisticated Portrait features with unparalleled flexibility. Users no longer need to consciously select Portrait mode before snapping a picture. Instead, the camera intelligently collects depth information in real-time if a person or pet is detected in the frame. This allows for Portrait mode to be automatically enabled later, offering the convenience of a blurred background applied retrospectively, even for Night mode captures.
Adding another layer of creative control, Portrait Lighting transforms the ambiance of portrait photos with a range of professional studio effects. Users can choose from options such as Natural, Studio, Contour, Stage, Stage Mono, and High-Key Mono. These effects allow for dramatic alterations to the lighting, enabling photographers to fine-tune the mood and style of their portraits without needing external equipment, thereby elevating the artistic quality of their captures.

11. **Photographic Styles and Panorama: Personalizing and Broadening Perspectives**
While computational photography often works behind the scenes, Apple also provides tools that empower users to actively shape their images with a distinct aesthetic vision. Photographic Styles are a prime example, acting as intelligent, customizable filters that users can apply *before* an image is captured. This allows for real-time previewing as the shot is composed, giving photographers a more immediate and intuitive control over the final look and feel of their pictures, moving beyond simple post-processing.
These styles offer a nuanced approach to image customization, influencing elements like tone, warmth, and vibrancy in a way that respects the subject while introducing a personalized touch. This year, a new ‘Bright’ option expands the palette of available styles, providing even more avenues for users to imbue their photographs with a specific mood or artistic direction. Such features subtly address the critiques of overly aggressive computational processing by giving the user a more active role in the image’s creative destiny.
Shifting from personal aesthetic to expansive storytelling, the Panorama feature remains a staple for capturing breathtaking wide-angle vistas. The iPhone 17 Pro is capable of capturing panoramic shots that are impressively detailed, reaching up to 63 megapixels in size. This allows users to effortlessly stitch together vast landscapes, architectural marvels, or sweeping group photos, creating immersive images that convey a sense of scale and presence. This wide-reaching capability further solidifies the iPhone’s versatility as an all-in-one imaging device.

12. **The Spatial Computing Frontier: Photography for the Vision Pro Era**
In a forward-looking move that transcends traditional photography, the iPhone 17 Pro introduces a groundbreaking capability: the capture of spatial photos and videos. This feature represents Apple’s strategic integration of its mobile camera system into the emerging realm of spatial computing. It’s not merely about capturing a moment; it’s about preserving an experience in a way that allows for immersive re-engagement, bridging the gap between flat images and three-dimensional reality.
The true magic of these spatial captures comes to life when viewed on the Apple Vision Pro. The context explicitly states that “Videos and photos captured in spatial mode can be viewed in 3D on the Vision Pro.” This functionality transforms static memories into dynamic, lifelike experiences, allowing users to step back into their captured moments with unprecedented depth and presence. It’s a testament to Apple’s vision for how we will interact with our digital content in the future.
This development is particularly significant for content creators and everyday users seeking to embrace next-generation immersive media. The ability to create 3D content directly from a smartphone positions the iPhone 17 Pro at the forefront of a new photographic paradigm. It underscores a shift from merely documenting scenes to building immersive digital worlds, hinting at a future where our memories are not just seen, but felt and relived in a truly spatial dimension.

13. **Marketing vs. Reality: The Persistent Gap in User Expectations**
The annual fanfare surrounding new iPhone launches, driven by Apple’s masterful marketing, invariably sets sky-high expectations for camera performance. However, as our investigation reveals, a persistent and often frustrating gap exists between the stunning visuals showcased in promotional materials and the actual ‘real-world scenes’ users encounter. This discrepancy stems from what the context describes as “misleading comparisons” and an “overemphasis on features” like higher megapixels or new sensors, without adequately highlighting other vital aspects like dynamic range and color accuracy.
User experience, as illuminated by the ‘Feedback Loop’ and ‘Common Complaints,’ frequently suffers from this misalignment. Reports from customers consistently point to issues such as “overexposed images, poor low-light performance, and subpar autofocus response”—concerns echoed by our analysis. The critical feedback often highlights that despite impressive specifications, the iPhone’s camera might not always capture reality faithfully, leading to disappointment when the final processed image deviates significantly from the user’s initial perception.
Further complicating this dynamic is the “Role Of Software Updates In Perception.” While updates are intended to refine performance, they can also introduce “Inconsistencies in Image Processing” or even “Bugs” that disrupt camera functions and affect image quality. This means that a user’s satisfaction can fluctuate, creating an unpredictable experience even after purchase, undermining the promise of a consistently reliable camera system. The implication is that what Apple promises in its compelling campaigns isn’t always fully delivered in the everyday shooting experience.
Ultimately, this tug-of-war between “Long-term Improvement vs. Immediate Gratification” leaves many users dissatisfied. While Apple may push updates to enhance performance over time, consumers often expect a flawless, high-performing camera from day one, especially from a premium device. This immediate gratification gap is a critical ‘flaw’ that, while not always a hardware defect, significantly impacts overall user satisfaction and challenges the brand loyalty Apple has meticulously built around its perceived technological superiority.

14. **Comparative Analysis: How iPhone 17 Pro Stacks Up Against Rivals**
In the fiercely competitive landscape of smartphone photography, evaluating the iPhone 17 Pro’s camera means contextualizing its performance against its formidable rivals. Brands like Samsung, Google, and OnePlus continually push technological boundaries, each carving out their niche with distinct camera philosophies. This comparative analysis reveals that while the iPhone 17 Pro offers compelling strengths, it also carries weaknesses that, for some users, might make competitors more appealing.
Apple’s camera system is consistently lauded for its “Color accuracy” and “video capabilities,” areas where it often sets the industry benchmark. However, a significant and recurring “Weakness” is its “Poor low-light performance,” an issue that continues to surface in user feedback despite ongoing advancements. This contrasts sharply with competitors who often prioritize and excel in specific imaging aspects, creating a diverse market for discerning consumers.
For instance, Samsung’s cameras are celebrated for their “Vivid colors” and impressive “zoom capabilities,” often surpassing the iPhone’s reach. However, this vibrancy can sometimes lead to “Over-saturation in certain images,” a trade-off some users are willing to make for striking visuals. Google’s Pixel phones, on the other hand, boast “Stunning computational photography,” often delivering remarkable results with minimal user input, though this strength can come with “Less control over manual settings” for advanced users.
Even more affordable alternatives like OnePlus offer “solid performance,” particularly given their price point, though they may encounter “Occasional software issues.” This diverse ecosystem means that “every brand has its strengths and weaknesses,” and the iPhone 17 Pro is no exception. For users whose primary focus is photography and who find the iPhone’s specific shortcomings — like low-light performance — to be deal-breakers, exploring alternatives may indeed lead to a camera experience that better suits their individual needs and photographic style.
The journey through the iPhone 17 Pro’s camera system reveals a fascinating dichotomy: a marvel of engineering brimming with cutting-edge features, yet one still navigating the intricate balance between technological aspiration and real-world execution. While Apple continues to innovate with spatial photography, ProRes RAW, and a robust suite of intelligent enhancements, the lingering concerns regarding low-light performance and the often-aggressive hand of computational photography underscore a persistent tension. It’s a camera that, while undoubtedly powerful and versatile, invites us to look beyond the shimmering veneer of marketing and scrutinize the pixels, the light, and ultimately, the unvarnished truth of the images it produces. For many, it’s a testament to how far mobile photography has come; for others, a reminder that even in the pursuit of perfection, some flaws persist, challenging us to adapt our expectations or seek different horizons. This intricate dance between innovation and imperfection keeps us, the discerning users, forever engaged, forever questioning, and forever eager for the next click.



