The human body is an absolute marvel, a complex symphony of cells, tissues, and organs working in perfect, often surprising, harmony. Even though we inhabit our bodies every single day, there’s an astonishing world of hidden processes and incredible facts that often escape our notice. From the microscopic wonders happening within our bones to the subtle shifts in our height, our physical being is a continuous source of fascination and discovery. This deep dive into some of the most extraordinary aspects of human physiology, as highlighted by health scientists, promises to leave you in awe of your own incredible biological machine.
Prepare to be amazed as we explore phenomena that challenge common perceptions and reveal the intricate engineering behind our very existence. These aren’t just dry scientific tidbits; they are windows into the astonishing capabilities and hidden quirks that make each of us unique and incredibly robust. We’ve compiled a list designed to spark curiosity and provide fascinating insights, perfect for impressing friends or simply deepening your appreciation for the fantastic body you call home.
Let’s embark on this journey of discovery, unveiling the first half of our carefully selected facts, each one a testament to the wonder of the human form. Brace yourself for some truly mind-blowing revelations about your skeletal structure, the strength of your bones, the mechanics of your hands, and even how you literally change shape throughout the day.
1. **You’ll have a brand-new skeleton in 10 years.**Imagine this: the very bones that support you today, the ones you rely on for every movement and posture, won’t be the exact same bones a decade from now. It sounds like something out of science fiction, but it’s a profound reality of human biology. Your skeletal system is in a constant state of flux, diligently regenerating its cells without you even having to think about it. This continuous renewal process ensures that your bones remain robust and adaptable, constantly repairing microscopic damages and responding to the demands placed upon them.
On average, the bones you possess today will have completely regenerated in about a decade’s time. This incredible cellular turnover means that you are, in a very real sense, living with a perpetually updating framework. However, this remarkable regeneration does undergo changes as we age. The pace of regeneration naturally slows down, leading to bones becoming thinner over extended periods. This is a key reason why bone health becomes an increasingly important focus as individuals mature, emphasizing the incredible, lifelong dynamism of our skeletal system.
This ongoing internal renovation is a testament to the body’s sophisticated maintenance systems, showcasing its ability to rebuild and fortify itself from the inside out. It’s a silent, persistent miracle happening within us, a continuous cycle of breaking down old bone tissue and forming new, stronger replacements. So, next time you look at your hand, remember that its structure is a living, breathing testament to continuous renewal, a biological masterpiece in progress.
2. **Your bones are stronger than steel.**When we think of strength and durability, materials like steel often come to mind. Yet, nestled within our bodies is a material far more impressive: our own bones. While we might experience a broken bone at some point in our lives, leading us to perceive them as fragile, the truth is that bone is an incredibly tough substance. Its composition and structure allow it to withstand immense pressure and bearing strength, making it a true marvel of natural engineering.
Indeed, ounce for ounce, our bones are scientifically proven to be stronger than steel. This incredible fact highlights the dense and intricate matrix that makes up bone tissue, capable of enduring forces that would deform many industrial metals. This isn’t just an abstract comparison; it speaks to the remarkable evolutionary design that allows our skeletons to support our weight, facilitate movement, and protect vital organs under diverse conditions, far exceeding the capabilities of a simple steel rod of equivalent width.
Consider the femur, often referred to as the thigh bone, which is the strongest bone in the human body. This single bone can support an astonishing 30 times the body weight of an average person. This incredible load-bearing capacity is a prime example of the exceptional strength embedded within our skeletal system. It’s a powerful reminder that beneath our skin lies a framework built for resilience, durability, and astonishing feats of physical endurance, constantly adapting and maintaining its formidable strength.

3. **You’re taller in the morning than you are at night.**It might sound like an urban myth or a whimsical notion, but the subtle truth is that you genuinely are a tiny bit taller when you first wake up in the morning compared to your height just before you go to bed. This fascinating daily fluctuation in stature is a direct consequence of the continuous pressures and activities our bodies endure throughout the day, and the remarkable way our spine responds to them. It’s a subtle but measurable phenomenon that speaks to the dynamic nature of our physical structure.
The primary reason for this temporary change in height lies in the cartilage discs located in your spine. As you move, stand, and carry out your daily activities, gravity and the pressure of your body weight exert a constant compressive force on these spinal discs. This pressure causes the cartilage to slowly compress over the course of the day, reducing your overall height by mere fractions of an inch. While individually small, these compressions accumulate to a noticeable, albeit temporary, difference by evening.
However, the body has a built-in recovery mechanism. As you lie down to sleep and relax, the pressure on your spinal disks is eased. With the forces of gravity no longer bearing down, these resilient cartilage discs are able to rehydrate and decompress, essentially “springing back” to their original height. This restorative process allows you to return to your full, refreshed height by the time you awaken. So, if you feel taller after a good night’s rest, you’re not imagining things – you actually are.
Read more about: The Gear Reviewer’s Definitive Guide: 11 Most Rugged Camping Tents of 2025 Tested for Ultimate Durability and Value

4. **Your feet contain a quarter of your bones.**When you consider the vastness and complexity of the human skeleton, it’s truly astounding to learn that a disproportionately high number of your bones are concentrated in one relatively small area: your feet. Each human foot is an intricate masterpiece of biomechanical engineering, designed for both stability and flexibility, capable of bearing your entire body weight and propelling you forward. This architectural wonder relies on a remarkable assembly of skeletal components.
Specifically, your feet collectively contain 52 bones – 26 in each foot. This number is incredibly significant, representing nearly a quarter of all the bones in your entire body, given that an adult human typically has 206 bones. This concentration of bones is far from random; it speaks to the extraordinary complexity and functional demands placed upon these crucial appendages. Each foot isn’t just a collection of bones, but also contains 33 joints and more than 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working in concert to achieve balance, movement, and shock absorption.
This dense arrangement of bones, joints, and soft tissues allows for the intricate movements and adaptive capabilities that make walking, running, and jumping possible. It’s a testament to the body’s efficient design, where specialization is key to performance. The next time your “dogs are barking” after a long day, consider the immense structural work these relatively small, yet incredibly complex, parts of your body have been undertaking. They truly are foundational to your mobility and an unsung hero of your skeletal system.
5. **There are no muscles in your fingers.**It’s a common misconception that the strong, precise movements of our fingers are directly powered by muscles within the digits themselves. However, the truth is far more intriguing and showcases an elegant design that prioritizes both strength and dexterity. Your fingers perform countless important tasks throughout the day, from the delicate act of typing to the firm grip required for opening jars. Yet, these impressive feats of strength and agility are achieved through an indirect, yet highly efficient, mechanical system.
The reality is that there are no muscles located within your fingers. All the movement and force generated in your fingers come from a sophisticated network of tendons and bones, receiving considerable assistance from muscles situated higher up in your arm. These muscles are primarily located in the palms of your hands and extending into your forearms. Long, slender tendons act like puppet strings, running from these forearm muscles through your wrist and into your fingers, attaching to the various bones of each digit.
When you decide to curl your fingers or straighten them, it’s these forearm muscles that contract, pulling on the tendons. The tendons, in turn, transmit this force to the finger bones, causing them to move. This arrangement allows for incredible power and fine motor control without adding bulk to the fingers themselves, ensuring maximum dexterity. It’s a clever biological pulley system that highlights the body’s engineering brilliance, keeping our hands nimble and powerful without sacrificing flexibility.
Read more about: Exclusive: Behind the Velvet Rope – Paris Hilton’s Harrowing Journey Through a Secret Trauma

6. **Half your hand strength is in your pinkie.**Among the many surprising revelations about the human body, the unassuming pinkie finger holds a truly remarkable secret: its outsized contribution to overall hand strength. Despite its small size, this digit is far from a minor player in the intricate mechanics of your hand. In fact, it’s crucial for the hand’s complete functionality, playing a vital role that most people underestimate, demonstrating the power of interconnected biological systems.
The pinkie finger is absolutely critical for grip strength. It works in conjunction with the ring finger to provide a stable base for the hand, allowing the thumb, index, and middle fingers to exert maximum force. This means that when you’re gripping an object, whether it’s a tool, a handle, or even just making a fist, the stability and leverage provided by your pinkie are indispensable. Its position and the way its tendons and ligaments interact with the rest of the hand create a powerful fulcrum, enhancing the efficiency of the entire hand’s musculature.
Laurie Rogers, a hand therapist at National Rehabilitation Hospital in Washington, emphasized the pinkie’s importance, stating that losing this small finger would result in a significant decrease in hand strength, “You’d lose 50 percent of your hand strength, easily.” This astonishing statistic underscores just how vital the pinkie is. It helps the thumb to pinch effectively and adds substantial power to the ring, middle, and index fingers, proving that even the smallest parts of our anatomy can hold immense functional significance and are integral to our overall physical capabilities.
7. **The smallest bone in your body is in your ear.**Within the intricate and delicate machinery of the human ear lies a bone so remarkably tiny and light that it stands as a testament to the microscopic precision of our anatomy. This minute structure is essential for one of our most vital senses: hearing. It reminds us that grandeur in biology isn’t always about size, but often about the elegance and efficiency of design, even at the smallest scale. It is a true marvel of biomechanical engineering.
No named bone in your body is smaller or lighter than the stapes, which resides in the middle ear. Appropriately named for its shape, the stapes is actually configured like a stirrup. Its unique form, complete with a base and an oval window, is perfectly adapted to its critical function within the auditory system. This structure is covered with a membrane that is exquisitely sensitive to sound vibrations, allowing it to capture and transmit these minute movements with astounding fidelity. It plays an indispensable role in translating the sound waves we perceive into electrical signals that our brain can interpret.
Along with two other tiny bones, the malleus (hammer) and incus (anvil), the stapes forms a chain that amplifies sound vibrations from the eardrum and transmits them to the inner ear. This intricate process allows us to hear everything from a whisper to a symphony. The stapes, in particular, is the final link in this chain, funneling these amplified vibrations into the fluid-filled cochlea. Its minuscule size and precise placement are critical to the accuracy and sensitivity of our hearing, truly making it a small wonder with an enormous impact on our perception of the world.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the astonishing capabilities and hidden quirks that continue to make the human body a perpetual source of fascination. We’ve journeyed through the marvels of our skeletal and muscular frameworks, and it’s time to uncover even more hidden truths about our bodily functions. From the surprising nature of sweat to the vastness of our internal networks, and the unique emotional capacities, regenerative powers, and the multitude of senses that define the human experience, prepare for more revelations that will deepen your appreciation for your own incredible biological machine.
Read more about: Unlocking Peak Performance: A Deep Dive into Mark Wahlberg’s Ultimate Home Gym & How You Can Build Your Own Fitness Sanctuary

8. **Your sweat is actually odorless.**It’s a common and widely accepted belief that sweat itself is the source of body odor. Many of us have experienced the distinct smell after a rigorous workout or on a hot day, and instinctively attribute it directly to the moisture our skin produces. This perception is so ingrained that we often associate the act of sweating with the immediate consequence of an unpleasant scent, leading to a host of antiperspirant and deodorant solutions aimed at managing this perceived issue.
However, health scientists reveal a fascinating truth that challenges this everyday understanding: sweat itself is inherently odorless. The fluid produced by our sweat glands, primarily composed of water, salt, and trace amounts of other substances, doesn’t carry a distinctive smell on its own. It’s a clean, almost neutral secretion designed primarily for thermoregulation, helping our bodies cool down efficiently when internal temperatures rise, a vital physiological function.
The real culprit behind what we commonly refer to as “body odor” is the interaction between sweat and the bacteria that naturally reside on our skin. These microscopic organisms thrive in warm, moist environments, and when they come into contact with sweat, they break down its components. This metabolic process, rather than the sweat itself, produces the volatile compounds that create the characteristic smells we perceive. It’s a perfectly normal biological interaction, demonstrating the intricate ecosystem of our skin, especially in areas like the armpits and groin where sweat glands are more abundant and conditions are ideal for bacterial activity.
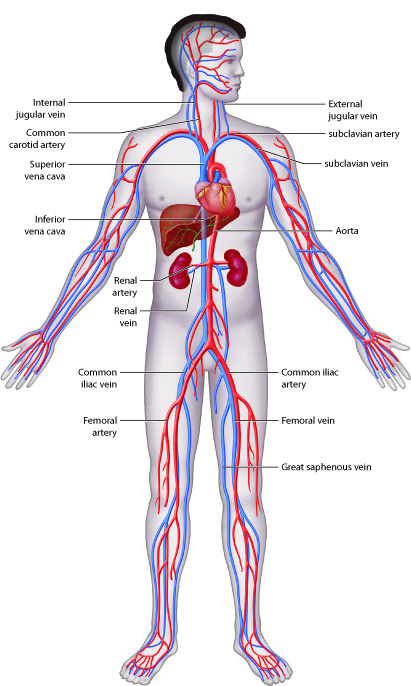
9. **You have over 60,000 miles of blood vessels.**Envisioning the vast internal network that sustains every cell in your body is truly mind-boggling. We often take for granted the silent, ceaseless work performed by our circulatory system, which acts as a superhighway for oxygen, nutrients, and waste. Yet, the sheer scale of this intricate plumbing system is far grander than most can possibly imagine, quietly working every second of every day to keep us alive and functioning at our best.
If you could somehow uncoil and lay out every single blood vessel within an average adult human body in a straight line, the total length would be nothing short of astonishing. This incredible vascular network, comprising arteries, capillaries, and veins, extends well over 60,000 miles from end to end. To put that into perspective, it’s enough to circle the Earth more than twice at the equator, illustrating the immense internal landscape that exists within each of us, a testament to nature’s engineering prowess.
This extensive network ensures that oxygenated blood reaches even the most remote tissues, while deoxygenated blood and metabolic byproducts are efficiently carried away. The capillaries, being the smallest and most numerous, are where the critical exchange of gases and nutrients occurs. The sheer length and intricate branching of these vessels highlight the body’s incredible efficiency in delivering vital resources and removing waste, a constant, silent miracle underpinning all our physical capabilities.
Read more about: Unveiling the Future: Life Aboard the USS Gerald R. Ford, the World’s Largest Aircraft Carrier

10. **Like lizards, we also shed our skin.**When we think of shedding skin, our minds often conjure images of reptiles like lizards or snakes, dramatically peeling away their old outer layers. The idea of humans undergoing a similar, continuous process might seem a bit unsettling, perhaps even a little creepy to some, yet it is a profound and constant reality of our biology. Our skin, the largest organ of our body, is in a perpetual state of renewal, a dynamic protective barrier.
While our shedding isn’t as noticeable or dramatic as a snake slithering out of its old skin, it is just as relentless and effective. According to the American Chemical Society, humans shed their entire outer layer of skin approximately every two to four weeks. This continuous turnover means that you are, in a very real sense, constantly regenerating your outermost shield, ensuring its integrity and functionality against environmental challenges.
The scale of this cellular renewal is truly astounding: we shed roughly 500 million skin cells every single day. These microscopic particles detach from our bodies, often unnoticed, as new cells are pushed up from beneath to replace them. This constant exfoliation is essential for maintaining healthy skin, protecting us from pathogens, regulating temperature, and sensory perception, showcasing the remarkable, self-maintaining nature of our body’s incredible outer layer.

11. **Babies don’t have kneecaps.**It might seem counterintuitive to imagine a human body without kneecaps, considering how integral they are to adult mobility and joint protection. We tend to think of the patella, or kneecap, as a fundamental component of the knee joint from birth. Yet, in a surprising twist of human development, the tiny bundles of joy we welcome into the world arrive without these bony structures fully formed, revealing a fascinating aspect of skeletal maturation.
Instead of fully ossified kneecaps, infants are born with cartilage structures in place of bone. This soft, flexible tissue provides some support, but it’s not the dense, protective bone we associate with adult knees. The process of ossification, where cartilage gradually transforms into bone, is a developmental journey that begins between the ages of two and six years for the kneecaps, a crucial stage in a child’s increasing mobility and ability to bear weight.
This transformation isn’t an overnight event; it’s a gradual process that doesn’t fully conclude until young adulthood. This extended period of development allows the patella to slowly strengthen and harden, adapting to the increasing demands placed upon it as a child learns to crawl, walk, run, and jump. It’s a remarkable example of how the human body adapts and fortifies itself over time, ensuring robust support for a lifetime of movement.

12. **Your stomach growls because it’s full of hot air.**We’ve all experienced that familiar grumbling, rumbling, or growling sound emanating from our stomach, often interpreted as a clear signal of hunger. This audible phenomenon, which can range from a subtle gurgle to a pronounced rumble, is a universal experience, frequently prompting curious glances or a quick check for the nearest snack. While hunger can indeed trigger these sounds, the underlying mechanism is a bit more complex and, frankly, quite surprising.
The truth is, these sounds originate not just from an empty stomach, but from the continuous activity of our digestive system. Specifically, they are a product of the intestines, which undergo a series of coordinated contractions to help move food, liquid, and gas along the digestive tract. Even after all the food has been digested and absorbed, these rhythmic muscle contractions persist, continuing to churn and propel air through the system.
This constant movement of air and fluids through the intestines is what creates those distinctive grumbly, growly noises. Scientifically known as “borborygmus,” this term perfectly captures the sounds produced by gas moving through the gastrointestinal tract. So, next time your stomach decides to make its presence known, remember it’s not just a cry for food, but also a testament to the ceaseless, fascinating mechanics of your digestive system, a symphony of movement and gas.

13. **Your liver can almost completely regrow.**Among the many astounding capabilities of the human body, the liver stands out for its truly remarkable regenerative power. This vital organ, essential for detoxification, metabolism, and numerous other functions, possesses an extraordinary capacity for self-repair and regrowth, a biological marvel that sets it apart from almost any other organ in our system. It’s a testament to the body’s inherent resilience and ability to heal, even from significant damage.
The liver’s regenerative abilities are so profound that even if it is reduced by as much as 75 percent of its original mass, it can still grow back to its normal size and function. This incredible feat is achieved through the rapid replication of its specialized liver cells, known as hepatocytes. When a portion of the liver is damaged or removed, the remaining healthy cells receive signals to proliferate quickly, effectively rebuilding the lost tissue.
This restorative process is surprisingly efficient; the liver can reach its original size, or very close to it, within approximately a month, according to research from institutions like the University of Iowa. This rapid and near-complete regeneration is a cornerstone of modern medicine, making liver transplantation a viable option and highlighting the unique resilience of this powerhouse organ. It underscores the profound and enduring capacity for renewal embedded within our biological makeup.
From the silent, continuous renewal of our cells to the intricate symphony of our internal organs and the surprising breadth of our senses, the human body is a constant source of wonder. Each fact we uncover further illuminates the genius of its design, reminding us that within each of us lies a universe of biological marvels. Your body is truly amazing; it’s the only permanent home you’ll ever know, and every discovery about it only deepens our appreciation for this incredible biological machine. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and continue to be amazed by the fantastic body you call your own.