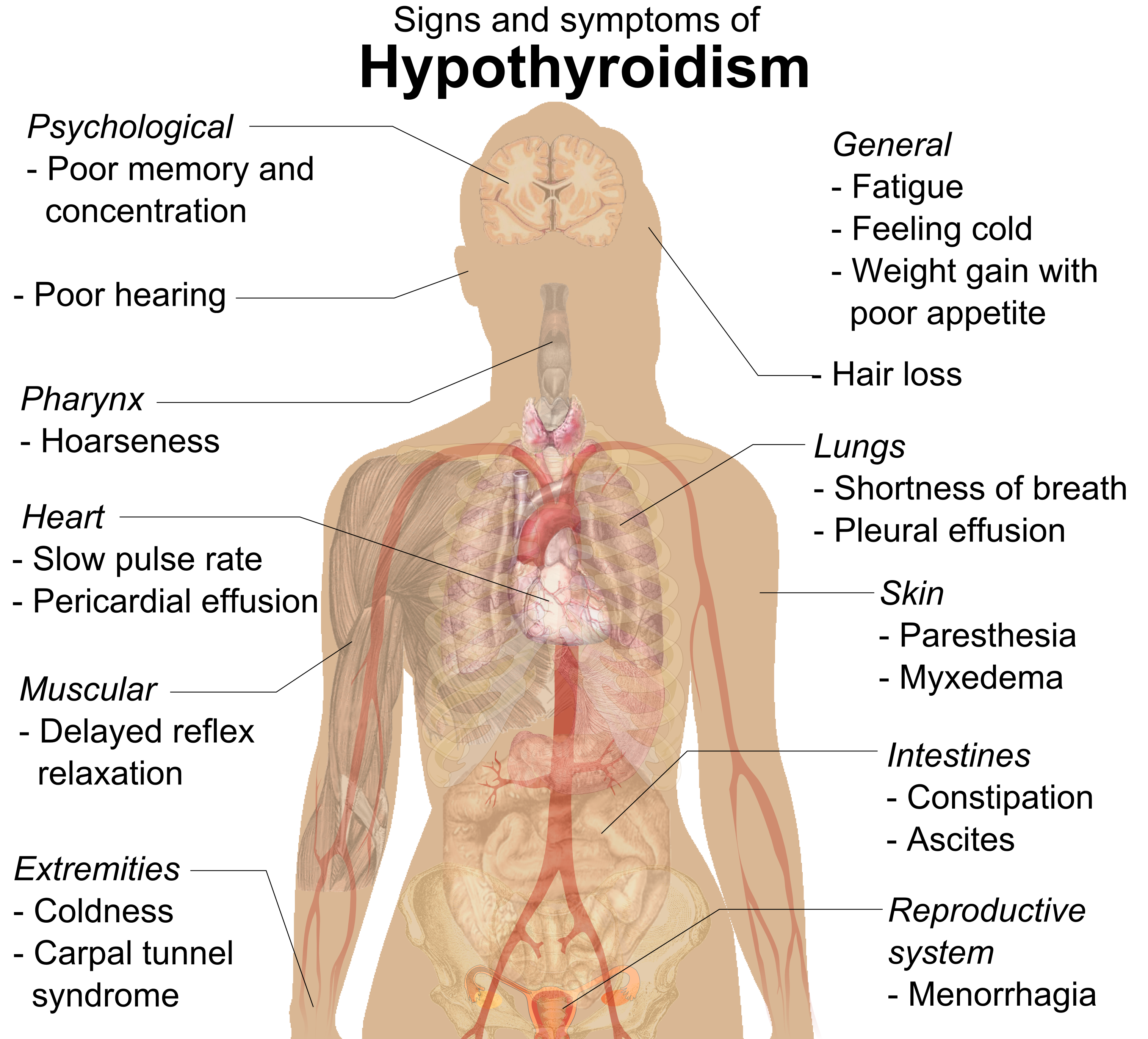
Thyroid issues are incredibly common, representing some of the most frequently encountered hormonal challenges in clinical practice. The American Thyroid Association estimates that a staggering 20 million people in the United States alone grapple with some form of thyroid disorder. Despite this prevalence, many individuals face significant delays, often months or even years, in receiving a diagnosis because they unknowingly overlook the subtle yet crucial early warning signs of their thyroid problems.
Understanding these early indicators is not just beneficial; it is absolutely critical. Early detection paves the way for prompt treatment, which can swiftly alleviate symptoms and substantially reduce the risk of developing severe complications and long-term health issues. Recognizing these initial signals is your first line of defense in managing your health effectively and preventing the progression of a thyroid imbalance into a more complex, clinically diagnosed disorder.
Your thyroid, that small, butterfly-shaped gland nestled at the front of your neck, is a powerhouse of the endocrine system. It acts as the master regulator of your metabolic rate and the intricate process of converting food into energy. Its hormones exert a profound influence across your entire body, touching everything from your overall hormonal health and digestive system to your nervous, cardiovascular, and reproductive systems. Given its central role, any disruption in thyroid function can precipitate a cascade of significant health challenges.

1. **Unexplained Weight Changes**One of the most widely recognized, yet often misunderstood, indicators of a potential thyroid disorder is unexplained weight change. This isn’t just about a few extra pounds or an unintentional drop; we’re talking about rapid and significant fluctuations in weight that occur without any corresponding alterations in your diet or exercise regimen. Such shifts can be a clear signal that your body’s metabolic engine, controlled by your thyroid, isn’t running as it should.
When your thyroid is underactive, a condition known as hypothyroidism, it leads to insufficient hormone production. This slows down your metabolism considerably, making your body less efficient at burning calories. As a result, you might find yourself gaining weight, even if you haven’t changed your eating habits or activity levels. Conversely, an overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, causes an excessive production of thyroid hormones, accelerating your metabolism to an unusual degree. This can lead to unintended and significant weight loss, despite a normal or even increased appetite, as your body burns through energy at an accelerated pace.
The thyroid’s profound influence on metabolism and energy production is well-documented. A 2020 article published in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism” highlighted how thyroid issues can directly impact metabolism and contribute to metabolic syndrome. These metabolic shifts, whether a slowdown from hypothyroidism or an acceleration from hyperthyroidism, are direct consequences of the hormonal imbalance, making unexplained weight changes a key symptom to monitor closely.
Read more about: The Service Bay Staple: 14 Models That Demand Constant Attention Before 60,000 Miles Are Up

2. **Fatigue and Low Energy Levels**Beyond mere tiredness, experiencing persistent fatigue and profoundly low energy levels, even after adequate rest and a seemingly good night’s sleep, is another critical factor demanding attention when considering thyroid symptoms. This isn’t the fleeting weariness that comes from a busy day; it’s a deep-seated exhaustion that pervades your daily life, hinting at a more systemic issue.
The thyroid gland is central to regulating the body’s energy production and overall metabolism. When there’s an imbalance in thyroid hormones, particularly in cases of hypothyroidism, your metabolism slows down. This deceleration directly impacts your cells’ ability to efficiently produce energy, leading to that pervasive feeling of sluggishness and fatigue. It’s a fundamental disruption in how your body powers itself.
Indeed, a 2023 study published in “Biomedicines” specifically noted that fatigue is a common and often debilitating issue among women with hypothyroidism, emphasizing that addressing the underlying thyroid condition can significantly improve energy levels. If you consistently find yourself feeling tired, heavy, or lacking vitality despite adequate rest, it’s a strong signal that your thyroid function warrants investigation.
Furthermore, difficulty concentrating and experiencing mental fog are often intertwined with thyroid disease, especially with hypothyroidism. This cognitive impairment can manifest as problems remembering things, struggling to follow conversations, difficulty paying attention, or even challenges in completing routine tasks and making decisions. The connection is so significant that a 2023 study in “Endocrine Practice” linked hypothyroidism to both fatigue and cognitive symptoms. The good news is that optimizing your thyroid hormone levels often leads to improved cognitive function and a return of mental clarity.
Read more about: Beyond the Cough: 14 Critical Lung Infection Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore, Including Unexpected Clues on Your Fingernails

3. **Mood Changes**Emotional fluctuations and shifts in your psychological state can also be among the early warning signs of thyroid issues, often manifesting as anxiety, irritability, mood swings, or a persistent feeling of depression. Your thyroid plays a crucial, yet often overlooked, role in influencing brain neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are vital for emotional regulation and overall mental well-being.
In conditions of hyperthyroidism, where there’s an excess of thyroid hormones, individuals commonly report increased nervousness, heightened anxiety, and an elevated sense of irritability. These physical and emotional sensations can mimic the symptoms of anxiety disorders, creating a constant state of unease. The body’s accelerated state often translates into an agitated mind, making it difficult to find calm.
Conversely, hypothyroidism, characterized by insufficient thyroid hormone production, often ushers in feelings of sadness, a tendency toward depression, and profound emotional fatigue. This imbalance can dampen one’s spirits, making even minor stressors feel overwhelming and leading to a persistent low mood. Recognizing these emotional shifts as potential physical symptoms, rather than solely psychological ones, is an important step. Balancing your thyroid hormone levels can often lead to a significant improvement in mood and emotional stability.
Beyond specific mood states, your thyroid gland is instrumental in regulating your body’s overall hormonal balance, including those hormones involved in stress response. When thyroid hormone levels are imbalanced, this intricate system can be disrupted, impairing your ability to effectively manage stress and maintain emotional resilience. Such an imbalance can amplify your stress response, making it harder to cope with daily challenges and potentially leading to heightened emotional vulnerability. Addressing the root cause through improved thyroid health and restoring hormonal balance can significantly enhance your emotional well-being and strengthen your capacity to handle stress.
Read more about: Revitalize Your Ride: 12 Game-Changing Interior Mods to Make Your Car Look Years Newer for Less
4. **Temperature Sensitivity**An unusual and persistent sensitivity to temperature, whether it’s an intolerance to cold or an excessive reaction to heat, often serves as another telling indicator of thyroid disease. This isn’t just feeling a bit chilly or warm; it’s a profound discomfort in environments that others find perfectly amenable, signaling a deeper disruption in your body’s internal thermostat.
Hypothyroidism, with its characteristic slowdown of metabolic processes, is a frequent culprit behind increased sensitivity to cold. Your body’s ability to generate sufficient heat is compromised, leading you to feel cold even in settings that appear warm to those around you. You might find yourself reaching for extra layers, even indoors, feeling a persistent chill that others don’t share. This reduced thermogenesis is a direct consequence of your thyroid’s underactivity.
On the other side of the spectrum, hyperthyroidism accelerates your metabolism, causing your body to produce excess heat. This can result in an increased sensitivity to warmth and a propensity for more sweating than usual. You might feel uncomfortably hot in mild temperatures, experience frequent hot flashes, or find yourself perspiring even at rest, as your body struggles to dissipate the internal heat generated by its overactive state.
Beyond constant cold or heat, thyroid imbalance can also manifest as fluctuating body temperature regulation, leading to unpredictable episodes of sudden chills or hot flashes. This happens because your body’s internal mechanisms, usually adept at maintaining a steady core temperature, are struggling due to the hormonal disruption. Hypothyroidism is more commonly associated with abrupt temperature drops and chills, while hyperthyroidism tends to cause an overproduction of heat and related hot flashes. Correcting the underlying thyroid condition is often key to restoring stable body temperature regulation and alleviating these disruptive symptoms.
Read more about: Winter’s Chill: Unmasking the Infotainment Freezes and Tech Glitches Plaguing Your Car
5. **Hair and Skin Changes**Changes in the texture, volume, or health of your hair and skin can be remarkably insightful early signs of thyroid dysfunction, often serving as visible indicators of underlying hormonal imbalance. These aren’t just cosmetic issues; they reflect systemic disruptions that warrant attention.
One of the most concerning signs for many is thinning hair or significant hair loss. This is a common consequence of prolonged thyroid hormone imbalance, as both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the delicate hair growth cycle. This disruption can lead to increased shedding, a noticeable reduction in hair density, and a generally lackluster appearance. A 2023 review published in “Cureus” highlighted the widespread nature of this symptom, noting that approximately 50% of individuals with hyperthyroidism and 33% with hypothyroidism experience some form of hair loss. While hair loss can occur on the scalp and other body areas, thinning eyebrows, particularly the outer third, are a particularly distinctive and common sign of thyroid issues. Addressing and restoring thyroid health is often crucial for slowing or even improving hair thinning.
Beyond hair, your skin can also tell a story of thyroid imbalance. Hormonal health, including the precise balance of thyroid hormones, profoundly impacts skin health in numerous ways. Thyroid hormones are pivotal in regulating skin cell turnover, maintaining moisture retention, and ensuring adequate natural oil production. When these hormones are out of balance, the skin suffers.
Hypothyroidism, or low thyroid hormone levels, frequently leads to noticeably dry, flaking, and scaling skin. This occurs because the reduced hormone levels slow down the renewal of skin cells and diminish natural oil production, leaving the skin parched and rough. This dryness often persists stubbornly, resistant to even diligent use of moisturizers and other appropriate skincare products, because the root cause — the thyroid dysfunction — remains unaddressed. Until the underlying thyroid issues are properly managed, your skin may continue to exhibit these persistent symptoms.
Read more about: Where Did the Open Road Go? Revisiting 8 Beloved American Road Trips Families No Longer Explore

6. **Irregular Menstrual Cycles**For women, alterations in the regularity and characteristics of their menstrual cycles can serve as significant, yet frequently overlooked, indicators of a thyroid disorder. These changes are not merely inconveniences; they signal a deeper hormonal imbalance that can have broader implications for reproductive health.
Irregular menstrual cycles, encompassing both periods that are unusually heavy or notably lighter than normal, are among the potential warning signs of thyroid dysfunction. The delicate interplay of hormones governing the menstrual cycle is highly sensitive to thyroid hormone levels. A 2019 article published in “Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology” underscored this connection, highlighting how thyroid issues can impact the menstrual cycle, potentially increasing the risk of fertility challenges and chronic disease.
Specifically, in cases of hypothyroidism, women often experience heavier and longer menstruation. This is attributed to a slower metabolic rate and a disruption in the balance of reproductive hormones, which collectively can lead to more pronounced uterine bleeding. Conversely, hyperthyroidism, with its elevated thyroid hormone levels, can cause an imbalance in estrogen and progesterone, frequently resulting in lighter, shorter, or even entirely missed periods. Addressing and improving your thyroid health is often a crucial step in normalizing your menstrual cycle.
Furthermore, thyroid issues can significantly impact fertility in women, making difficulty conceiving a notable concern. Thyroid dysfunction and the resultant hormonal imbalance can interfere with normal ovulation, a process critical for successful conception, and affect other vital aspects of reproductive health. Both low (hypothyroidism) and high (hyperthyroidism) thyroid hormone levels can impede your body’s ability to release eggs effectively. Moreover, these imbalances can negatively influence the levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), both of which are indispensable for a healthy reproductive cycle. A 2022 research publication in the “Journal of Endocrinological Investigation” even revealed that thyroid issues may impact fertility in men, not just women. Therefore, addressing underlying thyroid problems is absolutely critical for improving fertility outcomes.
Read more about: Your Health Matters: 13 Hidden Cancer Symptoms Women Must Know for Early Detection and Life-Saving Action
7. **Changes in Heart Rate**Your thyroid hormones play a pivotal and critical role in maintaining your heart health, making any unusual changes in your heart rate a significant early warning sign of thyroid problems. It’s essential to recognize and address these alterations promptly to mitigate the risk of developing serious hyperthyroid- or hypothyroid-associated heart conditions.
When the thyroid gland becomes overactive, a condition known as hyperthyroidism, it produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. These elevated hormone levels can accelerate your metabolic rate and directly stimulate the heart, frequently resulting in tachycardia, which is an unusually fast heartbeat. Individuals with hyperthyroidism might notice their heart beating rapidly even when they are at rest, a clear indication that their cardiovascular system is working overtime.
Conversely, an underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism, leads to an insufficient production of thyroid hormones and a generalized slowdown of metabolic processes throughout the body. This deceleration can extend to the heart, often resulting in bradycardia, which is an unusually slow heart rate. Both unusually fast and slow heart rates warrant immediate medical attention to assess underlying thyroid function.
Beyond just a fast or slow beat, thyroid problems can also manifest as palpitations or an irregular heartbeat. Hyperthyroidism, in particular, is known to cause arrhythmias, which are irregular heart rhythms. You might experience unsettling sensations such as skipping beats, a fluttering feeling in your chest, or a pounding sensation. Over an extended period, these irregularities can place considerable strain on the heart muscle, potentially leading to more severe cardiac issues.
While hypothyroidism is less commonly associated with pronounced heart palpitations, it can still impose stress on your heart and contribute to irregularities in its rhythm. The connection between thyroid and heart function is so profound that maintaining optimal thyroid hormone levels is absolutely critical for safeguarding your overall cardiovascular health, regardless of whether you have an overactive or underactive thyroid.
Read more about: Echoes of Industry: Unearthing 12 American Factories That Shaped Blue-Collar Towns, Now Rarely Hiring

8. **Swelling or Lump in the Neck**Discovering any swelling or a noticeable lump in your neck is a symptom that should never be ignored and warrants immediate medical evaluation. This visible or palpable change can be a clear indicator of thyroid disease, often signifying an underlying dysfunction of the thyroid gland itself.
A common manifestation of thyroid dysfunction is the development of a goiter, which is a visible or palpable enlargement of the thyroid gland in the neck. This enlargement often occurs because your thyroid is working harder to compensate for hormonal imbalances, attempting to produce enough hormones to meet your body’s demands. In some cases, a goiter may also develop due to an iodine deficiency, particularly in individuals with autoimmune thyroid conditions.
While some goiters are quite pronounced and easily noticeable, others can be more subtle and may only be detected during a thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional. It is important not to dismiss any perceived changes in your neck area, regardless of how minor they may seem, as they could be early signals of a thyroid problem. Addressing the underlying thyroid dysfunction is often key to reducing the size of the goiter and alleviating associated symptoms.
Moreover, an enlarged thyroid gland can exert pressure on surrounding structures in the neck, leading to additional discomforting symptoms. You might experience discomfort when swallowing or a sensation of tightness or fullness in your throat. This occurs because the enlarged gland can compress the trachea (windpipe) or the esophagus (food pipe), making the act of swallowing more challenging.
In some instances, the pressure exerted by an enlarged thyroid can also affect your vocal cords, potentially leading to hoarseness or changes in your voice. If you notice any of these symptoms—difficulty swallowing, a persistent sensation of tightness, or a sudden change in your voice—in conjunction with a visible or palpable lump in your neck, it is imperative to seek prompt medical attention for a comprehensive thyroid evaluation.
Read more about: Unraveling Canine Skin Conditions: An In-Depth Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments for Dog Owners

9. **Acid Reflux**While many people typically attribute acid reflux to an excess of stomach acid, it is a surprising, yet common, and often overlooked symptom in individuals with thyroid issues, particularly those with Hashimoto’s and hypothyroidism. Intriguingly, it is frequently caused by the opposite problem: insufficient stomach acid, a condition known as hypochlorhydria, or even a complete lack of stomach acid, referred to as achlorhydria.
Studies have consistently shown that a significant number of people diagnosed with Hashimoto’s disease and hypothyroidism often experience low stomach acid levels. This deficiency can arise from various factors, including the presence of an H. pylori infection, specific food sensitivities (with dairy being a common culprit), or an underlying digestive enzyme deficiency that impacts the digestive process.
When stomach acid levels are too low, food is not properly digested, and the lower esophageal sphincter—the valve that separates the stomach from the esophagus—may not close completely. This allows undigested food and even small amounts of stomach acid to reflux back into the esophagus, causing the burning sensation and discomfort characteristic of acid reflux. It’s a prime example of how systemic issues, like thyroid dysfunction, can ripple through various bodily systems.
Addressing acid reflux in the context of thyroid issues often requires a multi-faceted approach. A starting point could involve an elimination diet to identify and remove offending foods, with dairy being a particularly common trigger for many. In addition to dietary adjustments, incorporating digestive tract-soothing herbs, such as mastic gum and DGL (deglycyrrhizinated licorice), can be beneficial. These gentle herbs also possess activity against H. pylori, further aiding digestive health.
To directly support stomach acid production, certain nutritional interventions can be considered. Thiamine, herbal bitters, or betaine with pepsin are often recommended as initial steps. Understanding that acid reflux can be a symptom of a deeper thyroid imbalance underscores the importance of a holistic perspective when managing digestive health and overall well-being.
Read more about: Eat Cleaner, Sleep Deeper: The 10 Worst Dinner Choices Disrupting Your Rest, According to Sleep Experts
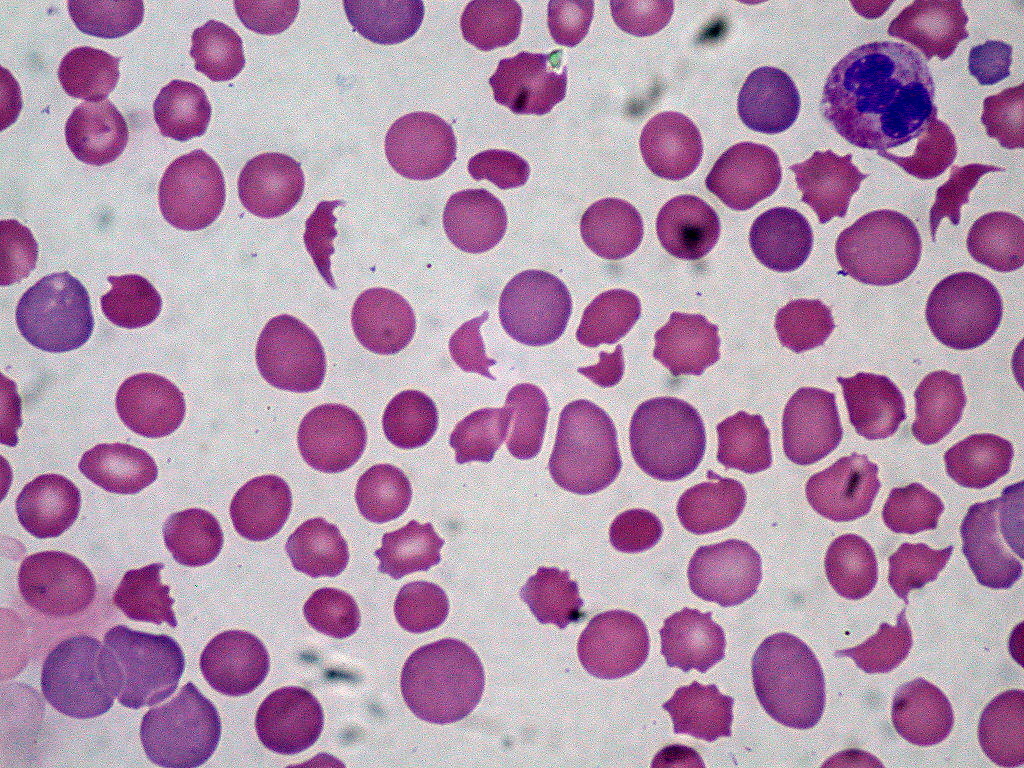
10. **Anemia**Anemia, characterized by low iron levels, is a surprisingly common and often complex issue among individuals with Hashimoto’s disease and other thyroid conditions. What makes it particularly challenging is that it can often be missed during routine blood tests, and its correction may require more than just taking a simple supplement.
Standard medical evaluations for anemia typically include checking red blood cell counts, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and general iron levels. While these tests are important, they may all appear normal even if you are experiencing iron deficiency. This is because these tests primarily reflect iron that is currently circulating, not the iron that is stored within your body, which is crucial for optimal health.
The key to identifying latent iron deficiency lies in testing ferritin levels. Ferritin is the protein responsible for storing iron, and its levels provide a more accurate picture of your body’s iron reserves. Many individuals diagnosed with Hashimoto’s often present with low ferritin levels. Experts suggest that a ferritin level of at least 40 ng/mL is necessary to halt hair loss, while levels of at least 70 ng/mL are often required for hair regrowth. For optimal thyroid function, the ideal ferritin range is considered to be between 90-110 ng/mL.
Correcting anemia in the context of thyroid disorders often involves a multi-pronged strategy. Incorporating more iron-rich foods into your diet is a fundamental step, as is supporting healthy stomach acid levels, which are essential for iron absorption. In cases where dietary changes are insufficient, supplementation may be necessary. Lactoferrin is often recommended as a good starting point, though some individuals with severely depleted stores might require iron infusions for faster replenishment.
Furthermore, it’s vital to address any underlying causes of iron loss. For instance, heavy menstrual cycles can contribute significantly to iron depletion. In such cases, managing menstrual flow effectively becomes a crucial part of the strategy to maintain healthy iron levels and support overall thyroid health. A comprehensive approach that considers all these factors is essential for effectively resolving anemia.
Read more about: Chew Wiser, Feel Lighter: The 14 Worst Snacks for Your Liver According to Hepatology Consultants

11. **Brain Fog**Among the most common and often debilitating symptoms reported by individuals with Hashimoto’s or hypothyroidism is brain fog. This isn’t just a fleeting moment of forgetfulness; it’s a profound collection of cognitive conditions that can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. Understanding brain fog is crucial for those navigating thyroid challenges.
Researchers precisely define brain fog as “a constellation of symptoms that include reduced cognition, inability to concentrate and multitask, as well as loss of short- and long-term memory.” While everyone experiences occasional mental confusion, for those with thyroid dysfunction, these moments become more severe, more frequent, and can evolve into a truly debilitating condition, making even routine daily tasks feel incredibly challenging.
This pervasive mental haziness is thought to stem from several common imbalances often observed in individuals with Hashimoto’s and hypothyroidism. Insufficient thyroid hormone levels directly impact brain function, as thyroid hormones are vital for neurological processes. Additionally, systemic inflammation can contribute to cognitive impairment, creating a less than optimal environment for brain cells to function efficiently.
Furthermore, unmanaged blood sugar imbalances, as discussed previously, can lead to fluctuations in energy supply to the brain, manifesting as difficulty focusing and mental sluggishness. Gut permeability, or ‘leaky gut,’ is another factor that can allow inflammatory substances to enter the bloodstream and potentially affect brain health, contributing to the symptoms of brain fog. Addressing these root causes is paramount to regaining mental clarity.
The good news is that by systematically identifying and addressing these underlying factors, such as optimizing thyroid hormone levels, managing inflammation, balancing blood sugar, and improving gut health, individuals can often experience significant improvements in their cognitive function. Reclaiming mental clarity and sharpness is a tangible benefit of comprehensive thyroid care, empowering individuals to live more engaged and fulfilling lives.
**Taking Charge of Your Thyroid Health**
Recognizing the diverse and often subtle early signs of thyroid problems is not merely a matter of awareness; it is a vital step towards reclaiming your health. From unexpected shifts in weight and persistent fatigue to mood swings, temperature sensitivities, changes in hair and skin, and disruptions to menstrual cycles and heart function, the thyroid’s influence is truly pervasive. When you notice symptoms like a lump in your neck, digestive issues like acid reflux, or systemic concerns such as anemia, blood sugar imbalances, or that persistent brain fog, these are your body’s critical signals demanding attention.
Armed with this comprehensive understanding, you are empowered to advocate for your health. Early detection and seeking medical advice without delay are paramount to securing the correct diagnosis, embarking on timely and effective treatment, and ultimately achieving the best possible health outcomes. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of long-term complications and enhances your overall quality of life. Share this invaluable guide with your friends and family, because knowing these signs can make all the difference in preventing a manageable imbalance from progressing into a more complex health challenge.
Read more about: Mastering Emissions: Practical Hacks to Get Your Custom Exhaust System Through Inspection
Remember, your journey to better health begins with understanding your body’s whispers before they become shouts. Partnering with a healthcare professional, especially one focused on functional and integrative medicine, can help you uncover the root causes of your thyroid condition and develop a personalized treatment plan. Take that crucial step today to optimize your hormonal health and alleviate the symptoms of thyroid dysfunction. Your well-being is worth it.



