Modern technology completely changed the way we charge our gadgets; for that fact alone, wireless charging has become an indispensable part of our lives. From the jumbled mess of wires to frantically searching for a place to charge our phones, this is a technology using electromagnetic induction that allows the easy flow of energy between a device and a charging pad, thereby making life so simple. In this article, we enter into the rather fascinating world of wireless charging-how it works, what technologies lie beneath it, and what is the practical application thereof. How does Wireless Charging Work? How It Works On a rather simple principle: electromagnetic induction allows it to function without physical connectors.
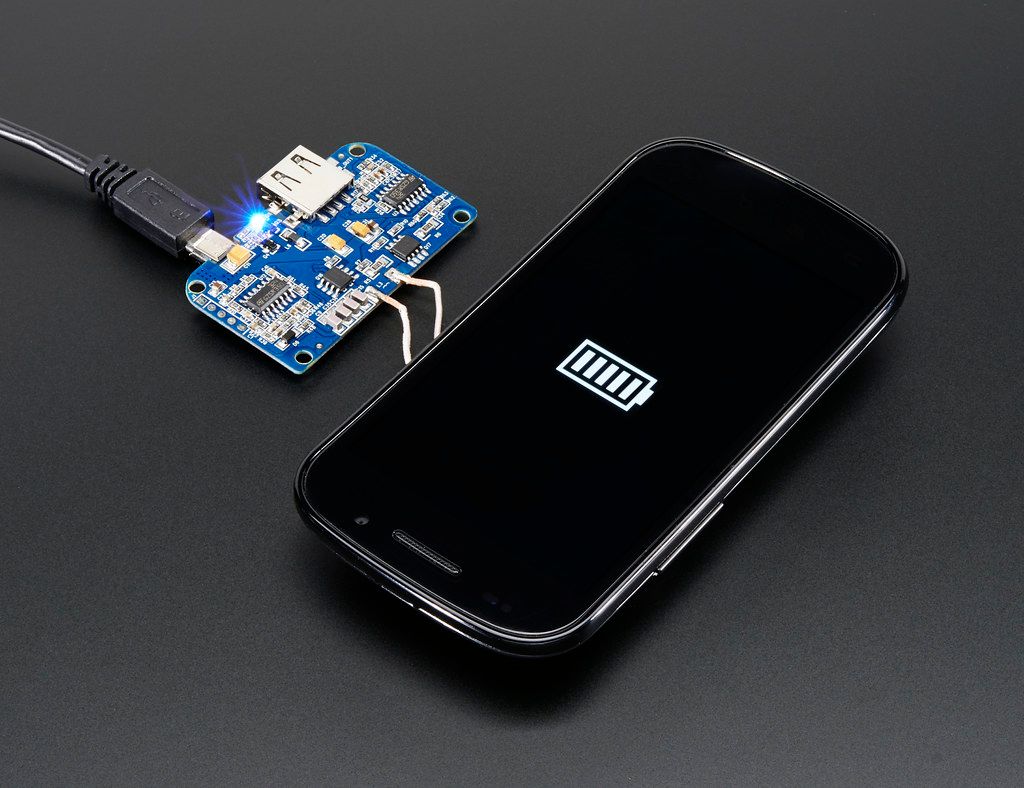

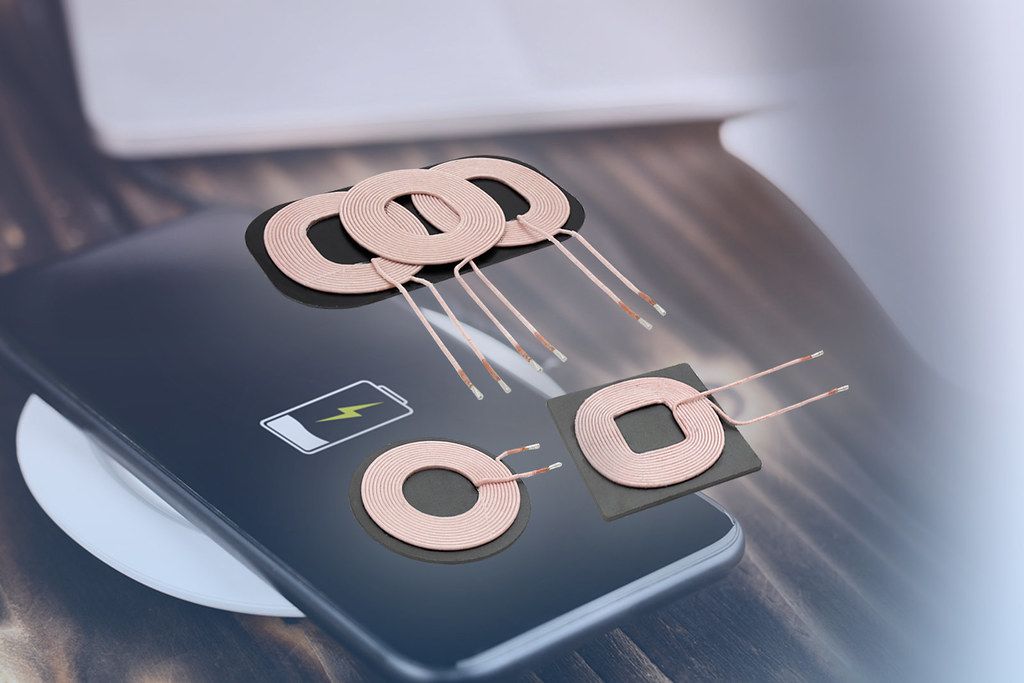
Two important components of this system include two coils: one is the transmitter coil inside the charging pad, while another is the receiver coil inside the device. When the device is put onto the pad, the transmitter coil generates an alternating current; therefore, a changing magnetic field would similarly be created. Due to this changing magnetic field, a flux would induce an alternating current in the receiving coil, hence allowing the device to receive its charge. This induced current at the receiver coil is then converted to direct current, thus powering up the battery of the device. All these interact in an extremely elaborative but interesting manner.
The quality and efficiency of the transmitter coil are very important to ensure minimum energy loss during the transfer. However, the quality of the receiver coil lies in its ability to convert a magnetic field into useful energy, which greatly affects the effectiveness and speed with which the charging occurs. Advances continuously in transmitter and receiver technologies now promise greater efficiency and charging capability. Take, for instance, Kew Labs’ UTS-1 Invisible Wireless Charger, ingeniously integrated with furniture, providing a neat appearance without a loss to functionality. In order to further demystify wireless charging, it would be necessary to go a step further into the science behind these mechanisms.
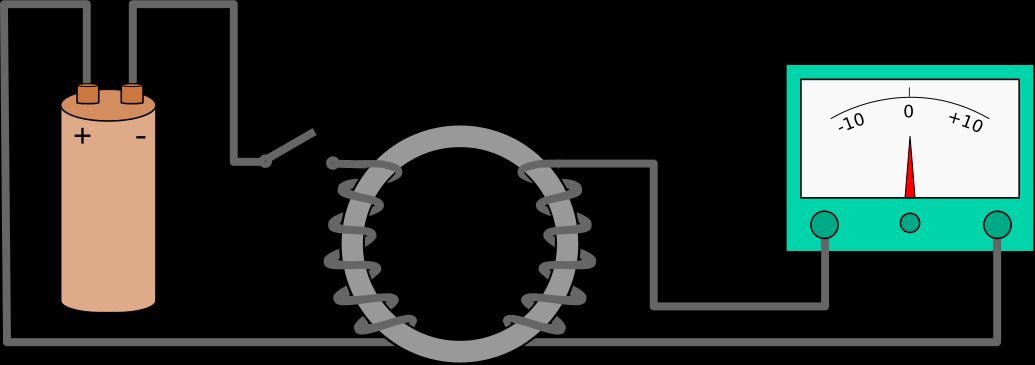
It all depends on the basis of a phenomenon called Faraday’s Law of Induction, which shows how a variable magnetic field may cause electrical current to flow in a conductor. The working concept involves, in practical approaches, the transmitter coil creating a magnetic field whenever the charger is activated that stirs electrons in the receiver coil. That interaction provides the grounds for charging with no apparent direct electrical contact. Of late, the use of wireless technologies is being considered in industries other than personal electronics. Applications in automotive and healthcare, to name a few, are becoming commonplace.
For instance, car makers are considering the inclusions of wireless chargers in the design of cars whereby a passenger can have his or her phone charged without having to deal with cords. Similarly, in healthcare facilities, there is assimilation of wireless charging so as to ease operations and give a better user experience. A closer look at several types of wireless charging technologies reveals that it is not one size fits all, but rather a collection of several technologies serving various needs and applications. The three most prevalent forms of such wireless charging are tightly-coupled inductive charging, loosely-coupled resonant charging, and uncoupled radio frequency charging.
- Tightly-Coupled Inductive Charging (Qi Standard): This may be one of the most highly recognized forms of wireless charging; originally, the Qi standard was widely applied to smartphones and other portable devices. Inductive charging is tightly coupled: both the charging pad and the device need to be in close physical alignment for the proper energy transfer. Inside the charging pad, there is a transmitter coil; when powered, this transmitter coil produces an electromagnetic field. A compatible receiver coil on the back of a device would couple with that transmitter field by inducing an electrical current to drive battery charging.
It has been able to gain popularity in the market because it guarantees dependable performance, and it’s pretty easy to use. Most leading smartphone makers around the world have inculcated this technology into their devices. The simplicity of just dropping a device onto a pad has made it a staple among users for those who want an effortless charging experience.
- Loosely-Coupled Resonant Charging: Ground-breaking technology that extends the limit to which energy is being transferred wirelessly over longer distances and more forgiving to the level of alignment. Loosely-coupled resonant charging makes use of resonant coils at particular frequencies, hence delivering effective energy transfer even when devices are not well-aligned. It is that flexibility which opens up some remarkable opportunities, especially within multi-device environments requiring charging from a single location. For example, automotive companies can use this technology by installing it in a manner that allows vehicles to charge while being parked over a larger pad without necessarily being precisely positioned with the device. 3. Uncoupled Radio Frequency RF Charging.
At the leading edge of wireless charging innovation is the leap: uncoupled RF charging. Unlike classic solutions, which require physical contact, RF charging can provide energy from a distance by using radio waves. That is why it’s especially welcome in the name of true wireless freedom: your devices get recharged without being burdened with a particular position. For instance, the Cota Power Transmitter provides such technology through the use of phased array antennas, beaming RF energy toward compatible devices for constant charging, provided it remains within range. Real-life applications could make smart homes and public places a lot ‘smarter’; after all, the availability of power would be easy and smooth, literally with no strings attached.
Understanding the Role of Magnetic Fields
The generation of magnetic fields is essential in wireless charging technologies. The magnetic field produced by the transmitter coil excites electrons in the receiver coil, enabling the conversion of magnetic energy into electrical energy. This process, governed by Faraday’s Law, facilitates the convenient charging of devices without direct electrical contact. As wireless charging technology evolves, the capabilities of both transmitter and receiver coils are being enhanced to increase efficiency and broaden applications, paving the way for a future where charging becomes even more integrated into our environments.
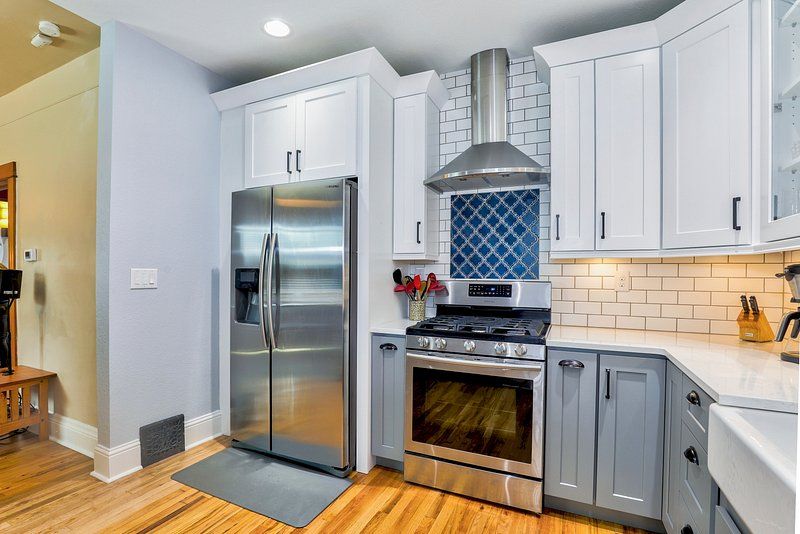

In the future, the possibilities with wireless charging technologies will remain endless, from pending solutions such as integrated wireless charging surfaces in kitchens and workplaces. As a design feature, this has drawn wider acceptance by homeowners in transforming the living area into a seamless, working space that epitomizes the integration of technology into daily existence. In sum, the concept of wireless charging is not about convenience but an evolutionary leap in interaction with technological devices. Knowing the mechanics of wireless charging opens a world of possibility far beyond just making things a bit more convenient. As we go through various technologies and their applications, we come to appreciate how they will shape our future interactions with devices. It is also a glimpse into a cleaner, more efficient world-one that is increasingly connected without cables.
As we go deeper into the world of wireless charging, it becomes imperative to look at the pros and cons that come with the technology and see how those factors influence the way we apply the technology in our day-to-day life. Wireless charging is more than a modern convenience; it is a shift in paradigm for powering devices, brought forth with considerable complexities yet to be surmised.
Assessing the Advantages of Wireless Charging
Maybe one of the biggest and most intuitive benefits of wireless charging is that it negates clutter: no more tangled cables, fumbling for which charger goes where. For users with several devices, placing their gadgets on a charging pad for convenience is revolutionary in nature. Moreover, aside from simplifying the process of charging itself, this greatly simplifies aesthetics both at home and in the office.
Moreover, much in the trend of modern wireless chargers, they have been designed to inculcate themselves into furniture and daily settings. Can you imagine preparing your meals on a kitchen countertop while it wirelessly charges your smartphone? Such integrations not only expand functionality but even make technology an unsung addition to our lives. Places like cafes, airports, and public transport systems have come to implement this in a way that allows users to charge their devices sans-cord hassle through wireless charging stations.
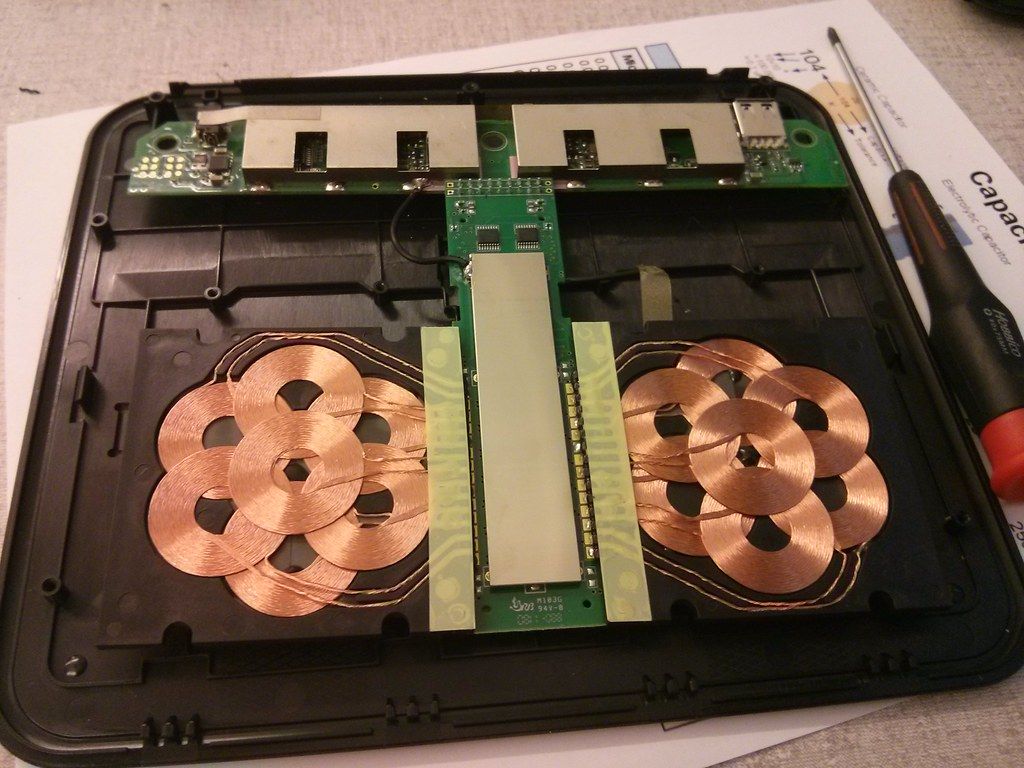
Besides convenience and aesthetics, there are also durability advantages to wireless charging. Cables used in traditional charging usually suffer from wear and tear over time and can result in frayed wires or damaged ports. That is mitigated in wireless charging because there is a minimal connection between the charger and the device. Minimize frequent plug-in and unplug, and this could potentially extend the life span both of the device and its accessories that come with wireless charging.
Challenges and Limitations of Wireless Charging
While highly beneficial, this technology is not without its drawbacks. First, the charging is somewhat slower compared to traditional ways of charging. While advances in technology have given fast wireless charging, a number of people continue to depend on their ordinary cables when they have to get enough juice into their device quickly. And that is quite a troubling fact for many people who always seem to be on the go and want their gadgets charged fast.

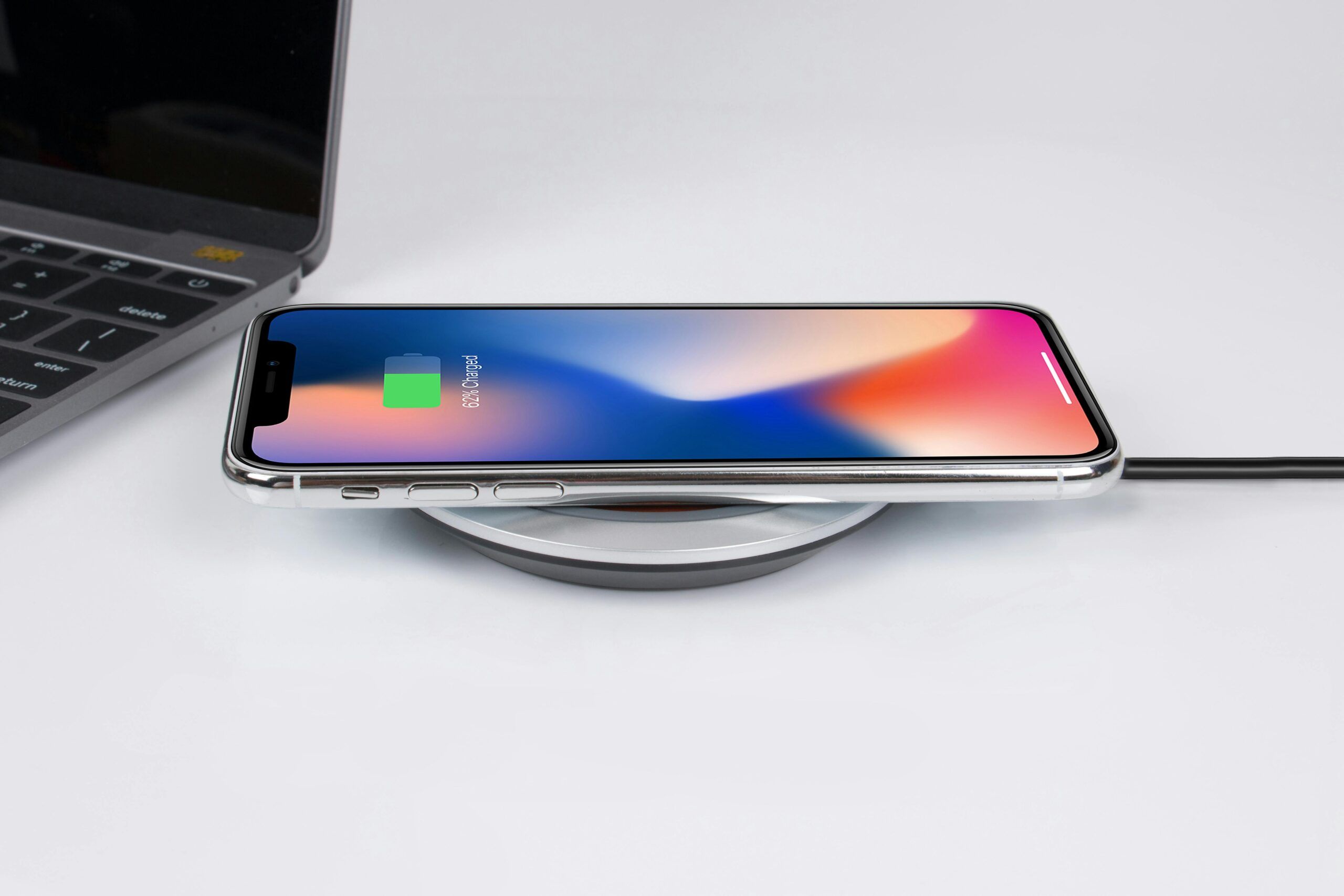
The other problem is one of compatibility and standards. While the Qi standard has begun to prevail and finds widespread usage, the slew of various wireless charging technologies developed naturally raises concerns about compatibility. Not all devices are compatible with all modes of wireless charging, and this might irritate users when they find their device cannot charge on some charging pads. This lack of universal compatibility may slow down the widespread usage of wireless charging solutions, particularly in mixed-device environments.
The Need for Standardization
In light of these issues, there is an increasing desire for standardization in the wireless charging industry. If the latter can succeed in establishing a single, universal standard whereby different devices become compatible with one another, then wireless charging companies will make things a whole lot easier for their customers. This, in turn, will increase adoption rates. In this respect, universal designs could soon mean that charging pads will accommodate a variety of devices, thus eliminating much frustration on the part of consumers.
Environmental Considerations
Equally crucial in gauging the impact of wireless charging within our daily lives is its implication upon the environment. It could lessen electronic waste since the demand for traditional chargers and cables would be reduced with the shift to wireless technology. However, electronic wastes from manufactured wireless charging products contribute to electronic wastes; hence, manufacturers should implement environmentally friendly practices.
There is, of course, energy efficiency to consider. In the process of transferring power, wireless charging can result in energy loss and therefore consumes more energy compared to its wired counterparts. This is one factor that must be considered at both the users’ and the manufacturers’ end so that benefits in terms of convenience will not compromise sustainable means. Once an efficient wireless charging technology is discovered, these issues could be put to rest. Such a move will indeed make the technology very likable to the eco-sensitive consumer.
Future of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging’s future will be brilliant yet complicated. It will most definitely hold a place in the automotive, health, and consumer electronics industries. In the future, as different industries begin to look at ways of adding the capability for wireless charging to their products, users will still see innovations that focus on user experience, efficiency, and sustainability.
For instance, in the automotive world, it could mean a certain convenience in charging unparalleled by anything else thus far: wireless charging pads installed in parking spots. One could only imagine driving into one’s garage and having their car charge without having to plug it in. Such a development could change our whole perception of energy use and convenience.

Additionally, medical centers have started using wireless charging to promote efficiency within the operations of said facilities. This could apply to tools like medical devices that need to remain on at all times and would, therefore be able to be used more smoothly if they came fitted with wireless charging technology to better serve the patients.
A Technology on the Rise
This is quite an amazing technology and holds the potential for extending convenience, flexibility, and innovation. Though at the cost of some setbacks, its advantages overshadow the disadvantages. We are still in our experimental phase with this technology and its implementation for different fields, but simultaneously, we have to strive for its standardization, efficiency, and sustainability.

Embracing wireless charging is embracing a future whereby the supply of power will invisibly be integrated into our surroundings, improving human experiences and further reducing clutter. As more and more developments related to wireless charging take place, we’ll reach a point where it isn’t just about convenience; it’s about becoming crucial to how we live. What this means, in essence, is that it ushers us into a wireless charging world: at home, in the office, and even on our way. In fact, the future is brilliant, full of endless possibilities.
Related posts:
1 Invisible Wireless Charger by Kew Labs
Checking Your Phone’s Compatibility with Wireless Charging
How Does Wireless Charging Work: A Comprehensive Guide



