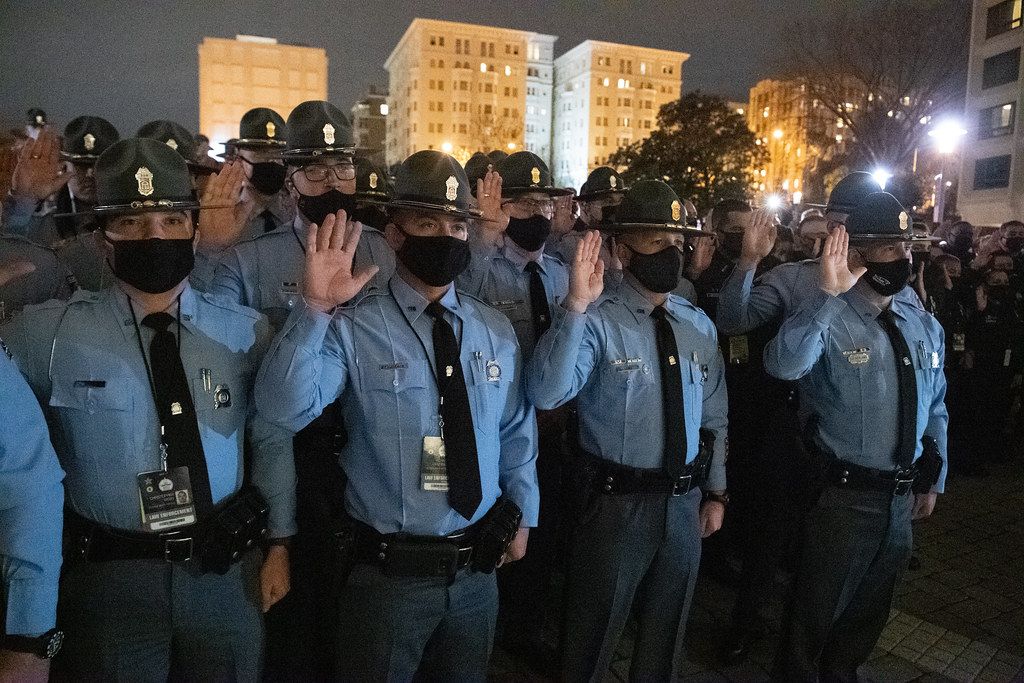
The nation’s capital, Washington D.C., recently found itself under an unprecedented level of federal law enforcement presence, igniting widespread public outcry and a heated debate over governmental authority. On a bustling Wednesday night, the U Street corridor in Northwest Washington became an unexpected flashpoint, as federal agents and local police established a vehicle checkpoint on 14th Street. This highly visible surge in federal personnel, enacted as part of President Trump’s recently announced crackdown on crime in the capital, drew immediate and vocal protests from residents who perceived it as a significant overreach and an unwelcome intrusion on their city’s autonomy.
This deployment, encompassing scores of National Guard troops and hundreds of federal law enforcement agents, marked a substantial escalation in the administration’s declared efforts to address what it termed a “crime emergency.” The move swiftly propelled the District into a critical national spotlight, raising profound questions about jurisdictional boundaries, the veracity of D.C.’s crime statistics, and the delicate balance of power between federal and municipal authorities. The events unfolded with rapid intensity, transforming ordinary urban thoroughfares into direct scenes of confrontation between citizens and a visibly increased federal presence.

1. **The 14th Street Police Checkpoint: A Catalyst for Protest.**
The evening of Wednesday, August 13, 2025, became a pivotal moment on 14th Street in Northwest Washington, as police and federal agents established a significant vehicle checkpoint. Located within the vibrant U Street corridor, this deployment quickly transformed into a flashpoint for public protest. The checkpoint served as a tangible manifestation of the federalization of D.C. law enforcement, bringing abstract concepts of federal oversight directly to neighborhood streets.
Protesters swiftly gathered around the array of law enforcement officers, including homeland security agents, immediately directing drivers away from the block. Chants of “Go home fascists,” “Turn left,” and “ICE is right here” reflected intense community disapproval. Warnings were shouted to drivers, advising them of potential stops for minor infractions like not wearing seatbelts or having busted taillights, underscoring the perceived arbitrary nature of the stops. The collective jeers and triumphant cheers as the checkpoint was finally closed just before 11 p.m. highlighted the public’s direct engagement and a fleeting sense of victory.
An MPD spokesperson provided specific operational figures: “344 vehicles passed through, 28 were stopped, 38 NOI’s were issued, and MPD made one arrest for No Permit and Counterfeit Tags.” The MPD defended these actions by stating they have conducted “weekly traffic safety compliance checkpoints” since 2023, calling them an “education and enforcement tool.” However, the overt involvement of federal agents in this instance fundamentally altered public perception, intensifying local opposition and making this specific checkpoint a symbol of federal overreach.

2. **The Scale of Federal Deployment: Army, National Guard, and Agents.**
The federal presence rapidly deployed in Washington D.C. was characterized by a substantial and multifaceted array of personnel from various branches. The U.S. Army anticipated “up to 200 soldiers out on the capital’s streets within the next few days at any given time,” designated to support federal law enforcement. This military-backed presence began arriving on the streets Tuesday evening, signaling the commencement of a prolonged federal operation within the city.
The D.C. National Guard also played a crucial role in this expanded federal footprint. Col. Dave Butler, an Army spokesman, stated the D.C. National Guard would build up to deploying “about 100 to 200 soldiers at any given time.” City officials clarified that these National Guard troops would not possess the power to make arrests. This distinction aimed to define their operational scope as support rather than direct law enforcement, though their visible presence undeniably contributed to an atmosphere of increased federal control.
Beyond these military components, the overall federal footprint was extensive. President Trump’s command included approximately 800 National Guard members and 500 federal law enforcement agents, operating alongside Washington’s municipal police department. The logistical scale was evident at the U.S. Park Police facility in Anacostia, where “hundreds of official vehicles filled the parking lot and grass,” serving as a central staging area. This massing of resources before agents fanned out into the district underscored the profound commitment of federal assets to assert control.

3. **Voices of Dissent: Protesters Confront Federal Presence.**
The sudden influx of federal law enforcement was met with immediate and fervent opposition from a significant segment of Washington D.C. residents. As the 14th Street checkpoint was established, protesters swiftly converged, transforming their outrage into organized and direct action. Their vocal expressions, including “Go home fascists,” “Turn left,” and “ICE is right here,” directly targeted the visible agents, articulating a clear and unequivocal rejection of their presence.
The palpable sentiment on the ground was personified by individuals like Kenneth, a 28-year-old resident of the U Street Corridor, who took swift and decisive action. Upon witnessing officers stopping drivers near his home, Kenneth proactively sought materials to craft a homemade sign. He then used this sign to actively direct traffic away from the checkpoint, demonstrating a profound personal commitment to alleviating what he viewed as an oppressive situation. His immediate response underscored a widespread feeling that the federal presence was unwelcome and unnecessary.
Kenneth passionately articulated his perspective, describing the situation as “a dark period for our city,” and expressing strong opposition to “federal control over our police department.” His actions were driven by a profound conviction to “do your part” in trying to redirect traffic, aiming to protect fellow residents from arbitrary stops. He conveyed a profound sense of unfamiliarity with such an extensive federal operation, stating, “I’ve never seen this in my five-plus years of living in D.C.” This pervasive shock at the scale and nature of the federal intervention solidified residents’ resolve to resist.

4. **President Trump’s Justification: “Crime Emergency” Amid Falling Rates.**
President Donald Trump laid the groundwork for the significant federalization of the Metropolitan Police Department and mobilization of the D.C. National Guard by declaring a “crime emergency” in Washington on Monday. Through this executive action, he vowed the city would become “essentially crime-free” under his watch, announcing a sweeping federal crackdown to restore order. This declaration served as the primary justification for the unprecedented increase in federal law enforcement presence.
However, this bold claim regarding a crime emergency stood in stark contrast to recent, readily available crime statistics for Washington D.C. The context explicitly stated that “violent crime in Washington fell to a 30-year low last year and has continued to fall sharply this year.” Official MPD statistics revealed “violent crime down 26% from last year.” This pronounced discrepancy between the president’s urgent narrative of a city in crisis and verifiable data raised critical questions about the true necessity and proportionality of the intervention.
Further adding to concerns, President Trump, speaking at the Kennedy Center, appeared to suggest an intent to “maintain oversight of crime-fighting in Washington beyond the 30 days that the law allows his administration to be in control of the D.C. police.” This hinted at a potential, more enduring federal entanglement in local policing, intensifying fears among local officials and residents about an “authoritarian push” and an “intrusion on our autonomy.” The president’s characterization of D.C. as an “apocalyptic,” “crime-infested wasteland” was not supported by available statistical evidence.
5. **Mayor Bowser’s Shifting Stance: Navigating Federal Intervention.**
Washington’s Democratic mayor, Muriel Bowser, found herself navigating an exceptionally complex and rapidly evolving political landscape following the president’s takeover of D.C. law enforcement. Her initial public reaction was overtly critical, reflecting deep concerns regarding municipal autonomy. However, her stance underwent several notable shifts, illustrating the intense pressures faced by local leadership.
At one point, Mayor Bowser indicated a willingness to “try to make good use of the federal law enforcement help,” perhaps seeking a pragmatic pathway. Yet, her position hardened significantly by Tuesday night, when she publicly condemned the federal presence as an “authoritarian push” and an “intrusion on our autonomy.” This forceful denouncement underscored a robust reassertion of local control and a clear objection to the manner and scale of the federal deployment.
By Wednesday morning, the mayor’s tone softened once more. In an interview on Fox 5 Washington, she suggested that “additional federal resources could help drive down crime.” When questioned if the crackdown was good for the city, Ms. Bowser deflected, redirecting the conversation to the critical need for more funding to “recruit and retain municipal police officers.” She asserted that “To the extent that you see the federal surge creating more arrests, taking more guns, M.P.D. officers would do the same thing,” framing federal actions as replicable by local police with adequate resources, underscores the intricate political dynamic.

6. **Arrests and Enforcement: The Numbers Behind the Federal Crackdown.**
The extensive federal law enforcement surge across the District of Columbia swiftly translated into a measurable increase in arrests, signaling the immediate operational impact on city streets. Federal officials stated that a minimum of “66 people had been arrested in Washington since Monday,” providing an early indication of the aggressive enforcement posture adopted by the federalized command.
Detailed breakdowns offered a clearer picture of these efforts. Karoline Leavitt, White House press secretary, reported a federal task force, including local officers, made “23 arrests on Monday evening.” The next day, Tuesday, saw a substantial escalation with “43 more people arrested,” confirmed by F.B.I. director Kash Patel. He added the F.B.I. “had assisted in 18 arrests so far this week,” with charges including “unlawful gun possession, assault with a dangerous weapon and theft.”
For context, D.C.’s Metropolitan Police Department made “635 arrests, or about 63 per day,” in the first 10 days of August 2024, with about “10 percent of those arrested were juveniles.” Critically, the number of crimes recorded during the first 10 days of August this year remained “virtually the same this year as last year.” Nonetheless, the combined federal and local officers under the new directive had arrested “over 100 people” by Wednesday evening, demonstrating a rapid and pronounced uptick in arrests attributable to the new federalized command.
The federalization of Washington D.C.’s law enforcement apparatus extended far beyond visible checkpoints, encompassing a complex operational framework that leveraged multiple federal agencies and specific staging areas. This multifaceted approach, driven by a broad mandate, aimed to assert comprehensive federal control over the capital’s security landscape. The deployment unveiled a deeper layer of strategic coordination, which, while intended to project strength and order, simultaneously intensified public scrutiny and a nuanced range of community responses. This section delves into these intricate operational details and the profound societal impacts, including the controversial federal crackdown on the city’s vulnerable homeless population, illuminated by firsthand accounts.

7. **The Inter-Agency Collaboration: A Multi-faceted Federal Force.**
Moving beyond the general presence of federal agents and National Guard troops, the D.C. operation was distinguished by the strategic activation of a diverse array of federal law enforcement partners. This comprehensive inter-agency collaboration indicated a deliberate and broad-reaching federal approach to address what the administration termed a crime emergency. The involvement of multiple specialized units was designed to leverage varied expertise across different facets of law enforcement.
The Trump administration specifically confirmed the activation of several federal partners in the region. These included the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), Homeland Security Investigations (HSI), the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), and Customs and Border Protection (CBP). The U.S. Park Police also played a significant operational role, serving as a key facilitator in the logistical aspects of the deployment.
This extensive list of participating agencies underscores the depth of federal resources committed to the D.C. intervention. It reflected an intent to apply a wide spectrum of federal capabilities, from investigating serious crimes to border-related enforcement, within a municipal jurisdiction. Such widespread agency involvement in local policing efforts raised profound questions about jurisdictional boundaries and the appropriate scope of federal authority.

8. **Central Staging and Deployment Logistics.**
The sheer scale of the federal deployment necessitated a significant logistical footprint, centralizing operations at a key facility in the capital. The U.S. Park Police facility in Anacostia, located in Southeast Washington, emerged as the primary staging area for this large-scale law enforcement and military presence. This facility served as the hub from which federal agents and local police officers coordinated and dispersed across the district.
Visual evidence at the facility clearly depicted the magnitude of the operation. Hundreds of official vehicles filled both the parking lot and the surrounding grass, indicating the vast amount of equipment and personnel mobilized. Scores of National Guard troops were also observed gathering on the lawn of the facility, positioned near a U.S. Marshals tent, further emphasizing the multi-agency coordination inherent in the federalization effort.
From this central point, teams of federal agents and local police officers were observed rolling out, fanning into other areas of the district during the early hours of Wednesday evening. This organized dispersal highlighted the strategic intent to establish a pervasive federal presence throughout the city. The Anacostia staging area, therefore, became a symbol of the operational efficiency and comprehensive reach of the federal intervention.

9. **Broader Community Reactions Beyond the Checkpoint.**
While the 14th Street checkpoint quickly became a flashpoint for immediate, vocal protest, the federal presence elicited a range of more nuanced reactions from the broader Washington D.C. community. Residents expressed concerns that extended beyond mere opposition to federal authority, delving into critiques of resource allocation and the fundamental appropriateness of the intervention.
Kenneth, a 28-year-old resident of the U Street Corridor, articulated a prevailing sentiment regarding the deployment’s impact on local resources. He described the 14th Street checkpoint as “a huge drain on local resources when there are actually areas of our city that might need assistance.” He further questioned the efficacy of the chosen location, noting, “Between V and W on 14th street, you’re not going to find anything,” implying a misdirection of efforts from actual high-crime areas.
Meera, another protester in her mid-20s, conveyed a complex emotional response to the federal presence in her neighborhood. While feeling “empowered by the neighborhood’s resistance,” she also expressed sadness, stating, “it’s just really hard to see them pulling people away in our area.” She highlighted the particular sensitivity of the situation in an area that had been “so rapidly gentrified within the past 10 years,” suggesting that the federal officers’ presence exacerbated existing community tensions and vulnerabilities.

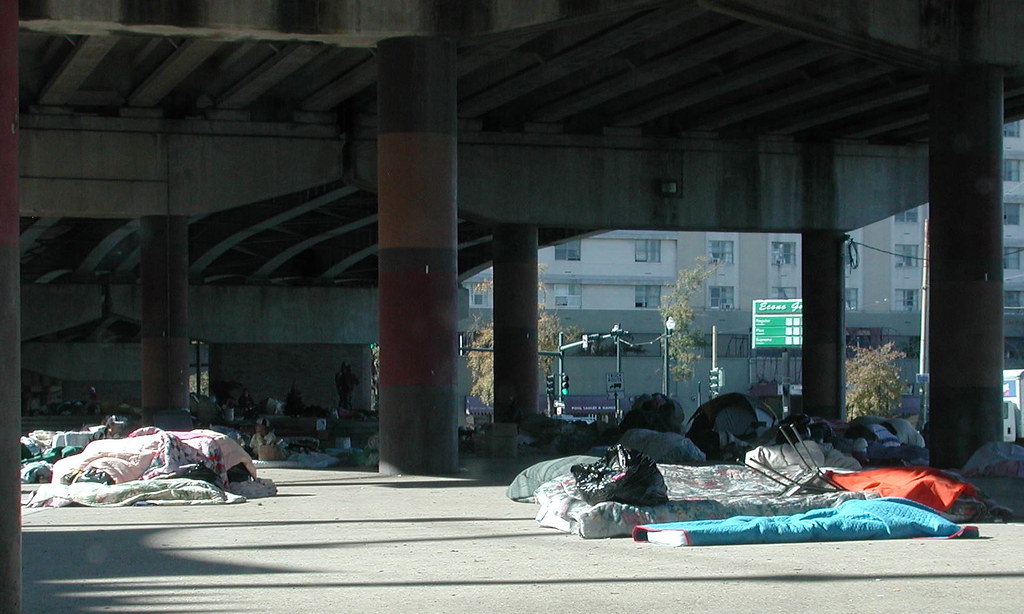
10. **The Federal Crackdown on the Homeless: A New Front.**
Adding another controversial dimension to the federal surge was the Trump administration’s explicit focus on the District’s homeless population. This aspect of the intervention, framed within the broader “crime emergency,” sought to address homelessness through a highly coercive law enforcement lens. It represented a significant shift in how the issue was approached at the federal level.
President Trump publicly articulated this stance by posting images of homeless encampments on Truth Social, accompanied by a direct ultimatum: “The Homeless have to move out, IMMEDIATELY. We will give you places to stay, but FAR from the Capital.” This rhetoric positioned homeless encampments as an immediate problem requiring forceful removal, rather than a social challenge demanding supportive services.
Further detailing the administration’s policy, White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt stated in a press conference that “Homeless individuals will be given the option to leave their encampment to be taken to a homeless shelter to be offered addiction or mental health services.” Critically, she added that “And if they refuse, they will be susceptible to fines or to jail time.” This policy effectively criminalized the refusal of designated services or shelter, drawing widespread condemnation from advocacy groups.

11. **Firsthand Accounts: Voices from the Encampments.**
The proposed federal policies directly impacted individuals living in Washington D.C.’s homeless encampments, whose firsthand accounts offered crucial insight into the human consequences of the crackdown. Interviews conducted in the Foggy Bottom neighborhood revealed the precariousness of their living situations and their often-complex perspectives on the administration’s directives.
Meghann Abraham, a 34-year-old woman, shared her personal journey, noting she had just completed an associate’s degree in homeland security and planned to pursue a bachelor’s. Despite her educational achievements and active job search, she lived in a tent in Foggy Bottom, unable to afford D.C. rent. She had received two eviction notices from the Metropolitan Police Department within the year, highlighting the constant threat of displacement and the challenges of economic hardship.
Abraham also articulated the profound psychological toll of societal judgment, stating, “When you get treated the same way over and over again, you do start to internalize it.” Her friend, Mr. Spann, 37, echoed this, challenging stereotypes by stating, “I got a job, but I just don’t have enough money to get my own place.” Mr. Spann worked as a custodian in a local hospital through a temporary employment agency, demonstrating that employment does not always guarantee housing stability in an expensive urban environment.

12. **The Debate Over Shelter Alternatives and Personal Autonomy.**
The federal administration’s policy, which conditioned the avoidance of fines or jail time on accepting shelter or services, ignited a critical debate concerning the nature of available alternatives for the homeless population. For many individuals experiencing homelessness, traditional shelters, while intended to offer refuge, present their own set of significant challenges and often perceived limitations on personal freedom.
Mr. Spann succinctly captured the fundamental dilemma posed by the crackdown, asking, “Where are we supposed to go? What are we supposed to do? Are you going to lock them up? What charge do you have?” These questions underscore the perceived lack of viable, humane alternatives for those displaced from encampments. The threat of legal penalties for simply existing in public spaces without alternative housing raised significant concerns about the criminalization of poverty itself.
Meghann Abraham provided a poignant explanation for her aversion to staying in shelters, describing them as able to “feel like prison.” She elaborated on the restrictive environment, stating, “It’s eat when we say you can eat, shower when we say you can shower. From this hour to this hour, just be locked in the room with whatever random person off the street that we decide you get to live with.” For Abraham, the autonomy and personal space afforded by her tent made it “easier” than navigating the stringent rules and lack of privacy often inherent in shelter systems. This perspective highlights the complex, deeply personal reasons behind individuals’ choices regarding their living situations, reasons often overlooked by broad federal mandates and law enforcement approaches.
The events unfolding in Washington D.C., marked by an unprecedented federal presence and the profound reactions it elicited, underscore a multifaceted crisis of governance, community trust, and social welfare. While the stated aim was to address crime, the methods employed ignited vigorous debate over jurisdictional boundaries, the efficacy of aggressive policing, and the humane treatment of vulnerable populations. The narrative of D.C.’s federalization remains a potent case study, revealing the intricate challenges inherent in balancing security imperatives with democratic principles and the fundamental rights of citizens, leaving a lasting imprint on the fabric of the nation’s capital.



