There are few dashboard warnings as universally unsettling as the dreaded yellow check engine light. It glows with an ominous presence, hinting at a potential problem beneath the hood but leaving most drivers wondering, “What now?” Unlike a simple maintenance reminder, this indicator signals a deeper issue within your vehicle’s engine or emission system, and understanding its message is the first step toward reclaiming control of your car’s health.
This crucial warning, also known as the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), is a vital component of your car’s onboard diagnostics system (OBD-II). When any of the dozens of sensors feeding data to your engine control unit (ECU) detect something outside normal operating ranges—be it too much fuel, low oxygen, or excessive emissions—the light springs to life. A solid light suggests a problem that needs attention soon, but a flashing light is a far more serious signal, often pointing to ignition malfunctions like an engine misfire, which demands immediate action to prevent catastrophic damage.
While the sight of this light can trigger panic, it doesn’t always spell disaster or a hefty repair bill. Sometimes, the fix is surprisingly simple. Our goal here at Popular Mechanics is to demystify this critical dashboard alert, equipping you with the knowledge to understand what might be going wrong, what steps you can take yourself, and when it’s truly time to enlist the help of a professional. Let’s pull back the curtain on the most common reasons your check engine light illuminates, starting with the usual suspects.

1. **Loose or Faulty Gas Cap**Believe it or not, one of the most frequent and easily remedied causes of a glowing check engine light is something as unassuming as your fuel cap. This little cap is a powerhouse of prevention, crucial for maintaining the precise pressure within your car’s fuel delivery system and preventing gasoline vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. When it’s not sealed correctly, either due to being loose, damaged, or simply missing, your car’s sophisticated system detects an evaporative emissions leak, and boom – the check engine light comes on.
The importance of a properly functioning gas cap extends beyond just silencing that warning light. A loose cap isn’t just a minor annoyance; it can lead to tangible financial losses. When fuel vapors can escape, you’re essentially losing gas before your engine even gets a chance to use it, translating directly into reduced fuel efficiency and wasted money at the pump. This seemingly small component plays a significant role in both your vehicle’s performance and its environmental footprint.
If your check engine light makes an appearance shortly after a fill-up, this is absolutely the first place you should investigate. Pull over when it’s safe to do so and simply ensure the cap is tightened securely, listening for those satisfying clicks that confirm it’s seated properly. If the cap itself looks worn, cracked, or simply isn’t sealing well, a replacement is inexpensive and widely available at any auto parts store. This DIY fix can often clear the light after a drive cycle or two, saving you a trip to the mechanic and proving that not all check engine light issues are complex.
Read more about: Beyond 85,000 Miles: A Consumer’s Guide to 10 Minivans – Uncovering Those That Need $2000+ Repairs and Those That Endure

2. **Oxygen Sensor Failure**Next on our list of common culprits is the oxygen sensor, often referred to as the O2 sensor. This vital component is essentially the environmental monitor of your exhaust system, measuring the amount of unburnt oxygen in the exhaust gases. It then relays this critical data to your vehicle’s computer, which uses the information to precisely regulate the air-fuel mixture entering your engine’s cylinders, optimizing combustion for both power and efficiency.
A faulty or failing oxygen sensor can throw your entire engine management system out of whack. When the sensor isn’t providing accurate readings, the ECU struggles to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio. This imbalance can lead to a host of problems you’ll notice in your daily driving, such as a noticeable drop in gas mileage because the engine might be running too rich (using too much fuel) or too lean (not enough fuel). You might also experience a rough engine performance or even a lack of power, indicating that your engine isn’t operating at its peak efficiency.
The consequences of ignoring a bad O2 sensor extend far beyond diminished fuel economy. This issue can have a detrimental ripple effect throughout your vehicle’s emission control system. Prolonged operation with an inaccurate oxygen sensor can lead to damage in other crucial and far more expensive components, most notably the catalytic converter. This interconnectedness means that addressing an O2 sensor problem early on is a smart move that can save you hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars in future repairs and help your car pass those increasingly strict emissions tests.
Most modern vehicles are equipped with more than one O2 sensor, often one before and one after the catalytic converter, each serving a slightly different diagnostic purpose. While a quality replacement O2 sensor itself might cost around $175, the labor involved can vary significantly depending on your car’s make and model. However, knowing that a faulty oxygen sensor is a common cause empowers you to understand the diagnosis and make informed decisions about its repair, preserving both your vehicle’s health and your budget.
Read more about: Mechanics’ Top Frustrations: 14 Bad Car Habits You Need to Stop Now to Save Money and Your Vehicle’s Life
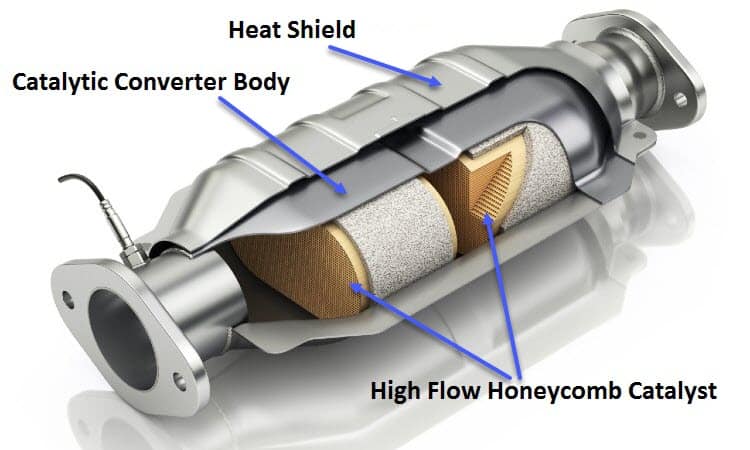
3. **Catalytic Converter Issues**The catalytic converter is a true unsung hero of modern automotive technology, a marvel of engineering integrated into your vehicle’s exhaust system. Its primary mission is to dramatically reduce harmful pollutants by transforming toxic exhaust gases—like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and unburnt hydrocarbons—into far less noxious substances such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and water vapor. Without it, our air quality would be significantly worse, and your car would never pass an emissions inspection.
When a catalytic converter starts to fail, your check engine light will almost certainly come on, signaling a major problem. You might also notice a distinct sulfur-like odor, often described as rotten eggs, emanating from your exhaust. Beyond the smell, a failing converter can severely restrict exhaust flow, leading to noticeable performance issues. This could manifest as sluggish acceleration, a significant reduction in engine power, or even your vehicle struggling to maintain speed on inclines, as the engine essentially chokes itself on its own emissions.
It’s crucial to understand that a problem with the catalytic converter often indicates an issue elsewhere in the vehicle, rather than the converter failing spontaneously. For instance, a long-term unaddressed oxygen sensor fault or persistent engine misfires can send unburnt fuel into the converter, causing it to overheat and melt its internal structure, leading to failure. Replacing only the catalytic converter without fixing the underlying problem is a temporary solution at best, as the new converter will likely fail again. Regular maintenance, including timely oil changes, is key to preventing catalytic converter issues, as is occasionally taking your city-driven car on the highway to help clean it out.
Catalytic converters are among the most expensive components to replace, with new units typically costing between $200 and $600, not including labor. This hefty price tag underscores the importance of preventative care and prompt attention to other check engine light triggers. Addressing issues like faulty O2 sensors or misfires early can prevent the need for this major repair. Keeping an eye and ear out for unusual sounds or discolored smoke from the exhaust can also be early indicators that this critical emissions component needs attention.
Read more about: Mechanics’ Top Frustrations: 14 Bad Car Habits You Need to Stop Now to Save Money and Your Vehicle’s Life

4. **Spark Plug or Ignition Coil Problems**The ignition system is at the very heart of your engine’s operation, responsible for igniting the precise mixture of fuel and air within each cylinder. The stars of this show are the spark plugs and ignition coils. An ignition coil generates the high voltage electricity that the spark plugs need to create a spark. Many modern vehicles use one coil per cylinder, often referred to as a coil pack, while older or simpler systems might use a single coil distributing power through spark plug wires.
When spark plugs become worn, fouled, or if an ignition coil malfunctions, the check engine light is a common consequence. These issues directly impact the combustion process, leading to a variety of noticeable symptoms. You might experience an engine misfire, which feels like a sudden jolt or stumble, particularly under acceleration. Rough idling, where the engine vibrates or runs unevenly at a standstill, is another tell-tale sign. In more severe cases, a faulty coil can even cause the car to shut off unexpectedly, creating a significant safety hazard.
Ignoring spark plug or ignition coil issues can quickly escalate into more serious problems. Consistent misfires can send unburnt fuel into the exhaust system, posing a risk to your catalytic converter, as mentioned earlier. Furthermore, reduced engine performance and lower fuel efficiency are guaranteed outcomes. The good news is that replacing spark plugs is a relatively straightforward and affordable repair, with quality plugs costing between $10 and $20 each. Ignition coils are a bit more, typically around $50 per unit. While swapping out spark plugs is often a DIY-friendly task that requires no special tools, addressing these components promptly will restore smooth performance and prevent further damage to more expensive parts.
Read more about: Mechanics’ Top Frustrations: 14 Bad Car Habits You Need to Stop Now to Save Money and Your Vehicle’s Life

5. **Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF) Failure**The Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor is a crucial component in your vehicle’s engine-management system, acting as the primary meter for the air entering the engine. This tiny but mighty sensor measures the volume and density of incoming air, providing vital data to the ECU. With this information, the ECU can precisely calculate the correct amount of fuel to inject, ensuring optimal combustion, fuel efficiency, and emissions control across various driving conditions, including changes in altitude.
When the MAF sensor becomes dirty, damaged, or fails entirely, the data it sends to the ECU becomes inaccurate. This immediately disrupts the delicate balance of the air-fuel mixture, leading to the illumination of your check engine light. The symptoms of a problematic MAF sensor can be quite diverse and impactful on your driving experience. You might notice your engine struggling with a rough idle, experiencing hesitation under acceleration, or even having difficulty starting the car altogether.
Beyond these immediate driveability issues, a failing MAF sensor can have significant long-term consequences. Since the engine isn’t getting the correct fuel-air mixture, it will often run inefficiently, leading directly to reduced fuel economy—costing you more money at the gas pump. Stalling, poor acceleration, and even a sudden change in throttle pedal response are also common indicators. Cleaning a dirty MAF sensor can sometimes resolve the issue, but if the sensor is truly damaged, replacement is necessary. For a late-model car, a MAF sensor typically costs between $120 and $150, making it a moderately priced repair that pays off in restored performance and efficiency.
Addressing a faulty MAF sensor is important not just for silencing the check engine light, but for the overall health and safety of your vehicle. A car that stalls unexpectedly or accelerates poorly can be a safety hazard, and consistent inefficient operation will take its toll on other engine components over time. Understanding the role of this sensor empowers you to accurately diagnose its issues, ensuring your car breathes correctly and runs as smoothly and efficiently as it was designed to.” , “_words_section1”: “1994

6. **Bad Spark Plug Wires**While spark plugs and ignition coils often steal the spotlight when discussing ignition issues, their humble connectors—the spark plug wires—play an equally critical role in getting your engine to hum. As their name clearly implies, these wires are the electrical conduits, meticulously transferring the high-voltage electricity generated by the ignition coil directly to the spark plug. Without this vital transfer, the carefully calculated fuel and air mixture inside your engine’s cylinders simply wouldn’t ignite, leaving you stranded.
A faulty spark plug wire can easily lead to your check engine light illuminating, signaling a disruption in the combustion process. While most modern vehicles have evolved beyond traditional spark plug wires, many cars still rely on them, typically using one wire per cylinder. However, some models, particularly older Mercedes-Benzes, were designed with two spark plugs per cylinder and, consequently, two wires. This simple component is absolutely essential for consistent, powerful ignition.
When these wires begin to fail or degrade, their ability to conduct electricity efficiently is compromised. This often manifests in several noticeable symptoms that impact your driving experience. You might observe a rough idle, where your engine vibrates unevenly at a standstill, indicating an inconsistent power delivery. Drivers may also experience a noticeable drop in overall engine performance, with reduced power and responsiveness. Furthermore, lower gas mileage is a common outcome, as the engine struggles to burn fuel efficiently without a strong, consistent spark.
The good news is that diagnosing and replacing bad spark plug wires is often a straightforward and budget-friendly fix. A complete set of quality plug wires typically costs around $50, making it an affordable repair. What’s even better is that swapping them out is generally considered an easy DIY task. It usually takes just a few minutes and requires no specialized tools or extensive mechanical knowledge, empowering you to address this issue without a trip to the repair shop.
Read more about: Mechanics’ Top Frustrations: 14 Bad Car Habits You Need to Stop Now to Save Money and Your Vehicle’s Life

7. **Issues with an Aftermarket Alarm**It might seem counterintuitive, but an aftermarket alarm system, especially one that hasn’t been installed correctly, can be a surprising culprit behind an illuminated check engine light. These systems, designed to enhance your vehicle’s security, can inadvertently create electrical conflicts or drain your car’s vital power supply if not properly integrated. This disruption in the electrical system sends confusing signals to your car’s engine control unit (ECU), prompting the check engine light to turn on.
Beyond just triggering the warning light, a poorly installed aftermarket alarm can wreak significant havoc on your vehicle’s overall functionality. It can lead to an unexpected battery drain, leaving you with a dead battery when you least expect it. In more severe cases, an improperly wired alarm might even prevent your vehicle from starting altogether, transforming a security feature into a major inconvenience. Imagine stepping out, ready to go, only for your car to refuse to respond, all because of an alarm system gone rogue.
The annoyances don’t stop there. Many drivers who have dealt with poorly installed aftermarket alarms can recount stories of their system going off without any apparent reason. A leaf falling on the hood, a strong gust of wind, or even a passing heavy truck might be enough to trigger a false alarm in the middle of the night, much to your and your neighbors’ chagrin. These frequent false alarms are not only irritating but also indicative of underlying electrical communication issues within the vehicle.
If these frustrating issues sound familiar, the solution lies in addressing the alarm system itself. You’ll need to have the alarm system properly fixed, reinstalled, or in some cases, replaced entirely. It’s crucial to seek out a competent mechanic who specializes in automotive electrical systems and aftermarket installations. While getting it done right initially might involve a slightly higher upfront cost, the peace of mind that comes with a fully functional, properly integrated alarm—one that doesn’t trigger your check engine light or keep you awake at night—is truly invaluable.
Read more about: Beyond the Showroom Shine: 10 SUVs That Either Defy or Succumb to Rust, A Crucial Guide for Drivers

8. **Vacuum Leak**Your car’s engine operates within a delicate balance, and its often-overlooked vacuum system plays a surprisingly wide variety of crucial roles in maintaining that equilibrium. From assisting your brake booster for effective stopping power to meticulously routing gasoline vapors back through the engine to lower harmful emissions, the vacuum system is a silent workhorse. Any disruption to this complex network of hoses and components can upset your vehicle’s operation and, predictably, illuminate your check engine light.
When a vacuum leak develops, it allows unmetered air to enter the engine, disrupting the precise air-fuel mixture that the engine control unit (ECU) strives to maintain. This inconsistency in the air intake can lead to a range of noticeable symptoms that affect your car’s driveability. One of the most common tell-tale signs of a vacuum leak is an engine idle that begins to surge erratically or settles at an unusually high RPM, indicating that the engine is struggling to regulate its speed.
The primary culprits behind vacuum leaks are often the vacuum hoses themselves. Over time, these hoses, typically made of rubber or plastic, can become brittle, dry out, and crack due to constant exposure to the engine’s intense heat and varying temperatures. Extreme cold can also contribute to their degradation. Beyond cracked hoses, other common sources of leaks include damaged or cracked fittings where hoses connect, or simply loose connections that have vibrated free over years of driving.
While individual vacuum lines are remarkably inexpensive, often costing just a few dollars each, tracing the precise source of a leak can be a significantly more challenging and time-consuming endeavor. This diagnostic difficulty often makes a vacuum leak an expensive repair if you’re not performing the work yourself, as mechanics charge for the labor involved in painstaking investigation. However, understanding the symptoms and potential causes arms you with valuable knowledge for discussing potential repairs with your mechanic.
Read more about: Beyond the Disco: Unearthing the Pivotal Events and Enduring Legacies That Shaped the 1970s

9. **Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve Failure**The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is a critical component in your vehicle’s mission to be both environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient. Its primary function is quite ingenious: it takes a controlled portion of your engine’s exhaust gases and directs them back into the combustion chambers. This process serves a dual purpose, effectively lowering the amount of harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) emitted from the engine and simultaneously making the fuel-air mixture easier to burn, thereby enhancing overall engine efficiency.
When the EGR system, particularly the EGR valve, begins to malfunction or becomes clogged, it can significantly impair your engine’s performance and trigger that all-too-familiar check engine light. A clogged EGR valve can prevent the exhaust gases from recirculating properly, leading to an imbalance in the combustion process. This can result in a rough idle, engine hesitation, or even a noticeable reduction in power, as the engine struggles to operate within its optimal parameters.
One of the more appealing aspects of an EGR valve issue is its potential for a DIY solution, especially for those who are even slightly mechanically inclined. In many cases, the valve itself isn’t necessarily broken but rather fouled with carbon deposits from the exhaust gases. Removing the valve, thoroughly cleaning it of these deposits, and then reinstalling it can often resolve the problem and clear the check engine light. This preventative maintenance can save you a trip to the mechanic.
However, if the EGR valve is truly defective or beyond cleaning, replacement becomes necessary. For a brand-new, OEM-quality EGR unit, you can expect to pay at least $125. While this is a more substantial investment than a simple cleaning, addressing a faulty EGR valve is essential. It ensures your car continues to run efficiently, reduces its environmental impact, and prevents potential issues with emissions tests, keeping your vehicle compliant and performing at its best.

10. **Dead Battery**While your car’s battery is often associated with simply getting your vehicle to start, its role extends much further into the complex electrical systems that power your ride. A dead or failing battery can surprisingly trigger not only the dedicated battery warning light on your dashboard but also, in many cases, your check engine light. This occurs because an insufficient power supply can cause a cascade of electrical malfunctions throughout the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD-II) system, registering as an engine fault.
The importance of a robust, fully functional car battery cannot be overstated; it is the silent heart of your vehicle’s electrical support system. Without it, your car quite simply won’t start, leaving you stranded. Modern car batteries are marvels of engineering, designed to last much longer than their predecessors and often requiring minimal to no maintenance. Yet, even with these advancements, problems can still arise from time to time, necessitating attention to prevent broader electrical issues.
When your battery isn’t providing the consistent, adequate energy required by your car’s various electrical components, it can cause erratic behavior and false readings across numerous sensors. This electrical instability is what often confuses the engine control unit (ECU), leading it to believe there’s an engine or emissions problem, hence the check engine light. Beyond the warning light, a failing battery will undeniably make itself known through difficulties starting the vehicle or maintaining consistent electrical performance.
Replacing a dead battery is generally a relatively easy task that many car owners can tackle themselves, though the cost will vary based on your vehicle’s specific needs, typically starting at around $100 for a quality unit. However, it’s worth noting a couple of considerations for late-model cars. Sometimes, the battery might be cleverly tucked away under plastic covers or in less accessible locations, making the process a bit more involved. Furthermore, disconnecting the battery will almost certainly reset your stereo system, potentially requiring a security code to reactivate. Always check with your local dealer for this code before disconnecting the terminals to avoid driving in silence!
Read more about: 12 New Cars Named ‘Best Buys’ for 2025: An Expert Guide for Savvy Shoppers
As we’ve explored, the check engine light, though often a source of dread, is ultimately your car’s way of communicating vital information about its health. Whether it’s a simple fix like tightening a gas cap or a more involved repair concerning a catalytic converter, addressing these warnings promptly is non-negotiable for the longevity, efficiency, and safety of your vehicle. By staying informed, following preventative maintenance schedules, and knowing when to use an OBD-II scanner or seek professional help, you transform this unsettling light into an actionable alert. Armed with this knowledge, you can ensure your ride stays reliable, performs optimally, and keeps you safely on the road, mile after mile.



