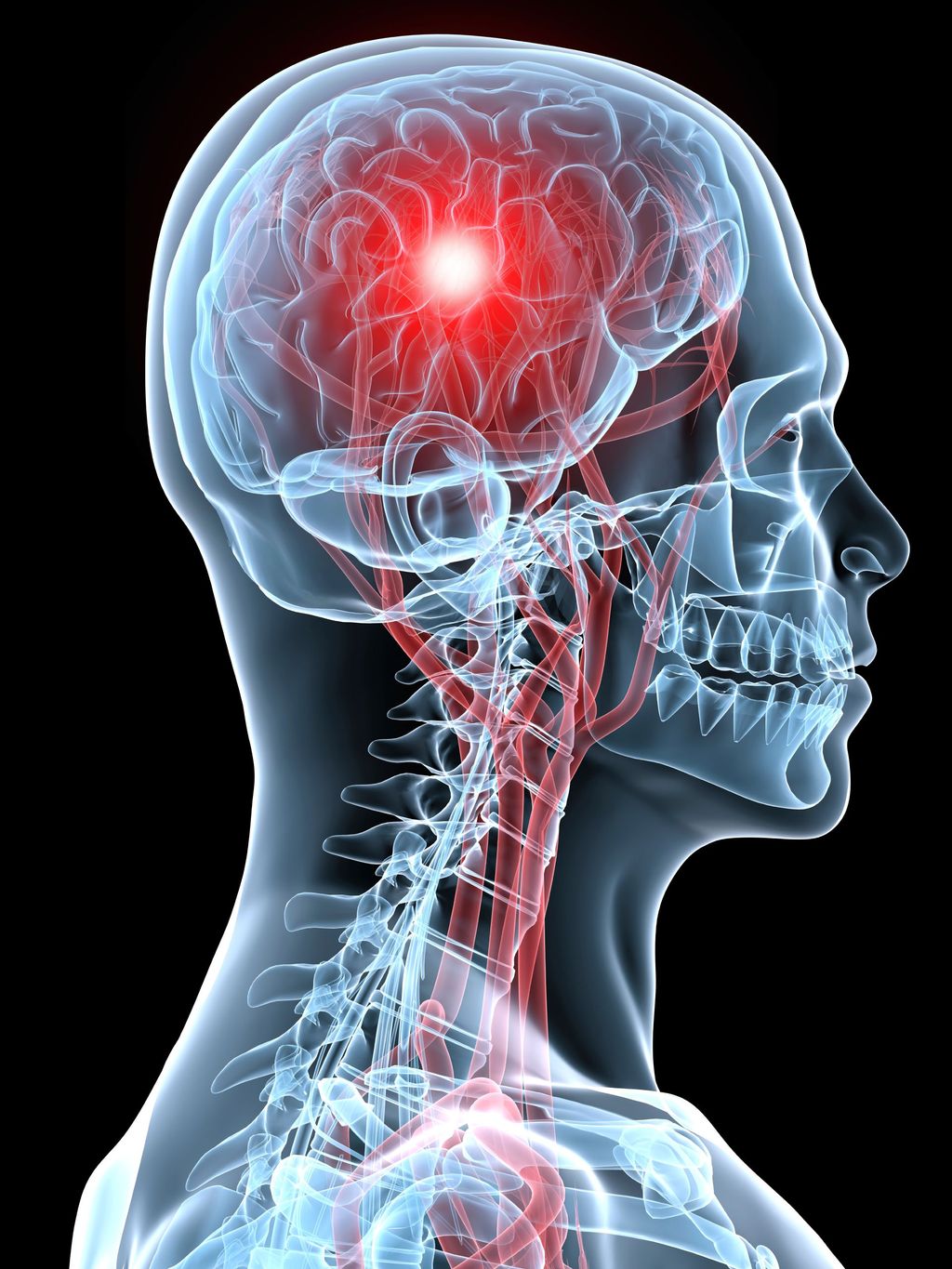
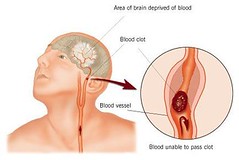
A stroke is a profound medical emergency, a sudden and devastating event where the brain is deprived of the vital blood and oxygen it needs to function. This deprivation, most commonly caused by a blocked artery or less frequently, by bleeding within the brain, can lead to rapid damage to brain cells, potentially resulting in severe disability or even, tragically, death. The effects can vary widely, from a subtle weakness on one side of the body to sudden, dramatic difficulties with speech, movement, or vision.
In the face of such a critical event, every single minute becomes precious. The speed with which someone recognizes the signs of a stroke and acts upon them can profoundly influence the outcome and the extent of recovery. This is not merely about understanding a medical condition; it’s about equipping yourself with the knowledge to potentially save a life—whether it’s your own, a loved one’s, or even a stranger’s. Early recognition is not just beneficial; it is absolutely imperative.
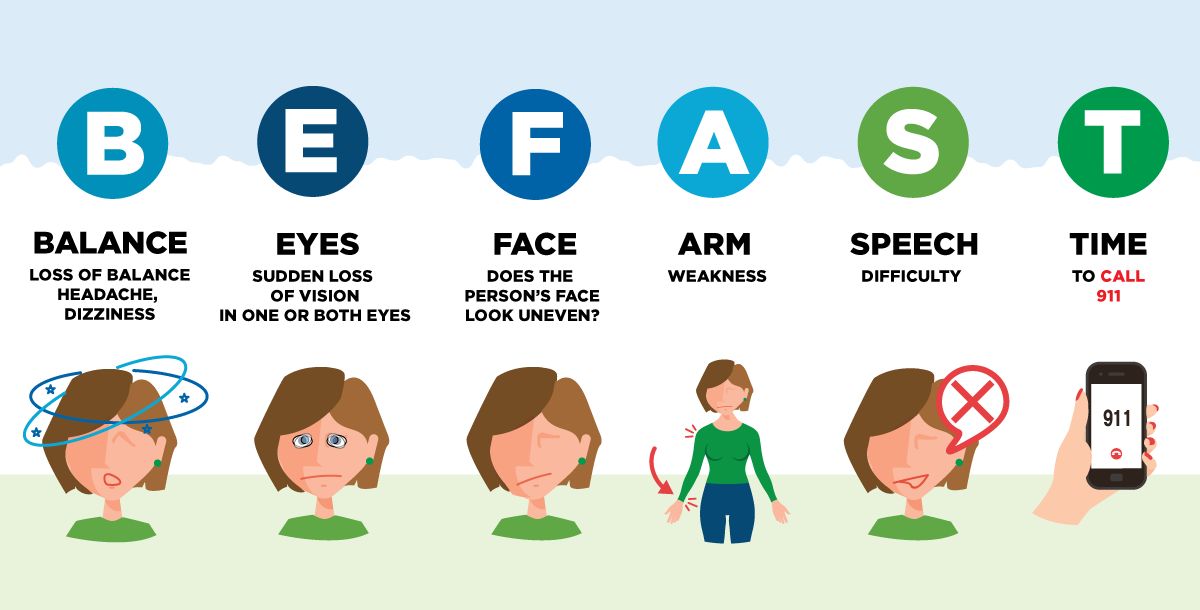
This in-depth guide is designed to empower you with the essential information needed to identify the warning signs of a stroke, focusing on the immediate and crucial indicators. We will explore the widely recognized and easy-to-remember FAST and BE FAST tests, which serve as rapid checklists for assessing stroke symptoms. Understanding these signs and knowing precisely what action to take without delay can make an invaluable difference in securing the best possible treatment and improving the chances of a positive recovery.

1. **Face Drooping: The ‘F’ in FAST**: One of the most identifiable and frequently observed warning signs of a stroke falls under the ‘F’ in the critical FAST acronym: Face drooping. This particular symptom typically manifests as a noticeable weakness or paralysis affecting one side of the face. It’s an immediate visual cue that can alert you to a potential stroke, and it’s something you can quickly check for in yourself or someone else, even without medical training.
To perform this check, simply ask the person to smile. If one side of their face appears to droop or seems uneven when they try to smile, this is a significant red flag. This asymmetry points to a possible issue with muscle control, which is a common consequence when a stroke affects the parts of the brain responsible for facial movement. Recognizing this sign promptly can trigger the necessary immediate action.
Such a sudden change in facial symmetry should never be dismissed. It is a clear indication that a medical emergency might be unfolding. If you observe this symptom, even if it seems minor or inconsistent, it is crucial to move on to the next steps of the FAST test and prepare for immediate medical intervention, as time is of the essence in stroke treatment and recovery.

2. **Arm Weakness: The ‘A’ in FAST**: The ‘A’ in the FAST test stands for Arm weakness, another common and critical indicator of a stroke. Just like facial drooping, this symptom often presents as a one-sided weakness, impacting either the left or right arm. This weakness isn’t necessarily a complete paralysis; it could be a subtle loss of strength or control that becomes apparent when simple movements are attempted.
To check for arm weakness, ask the individual to raise both of their arms simultaneously. Observe carefully to see if one arm drifts downward or is unable to be raised as high as the other. This inability to maintain both arms at the same level against gravity is a strong sign of muscle weakness consistent with a stroke. The brain’s control over motor functions is highly localized, and damage from a stroke can disrupt the signals to specific limbs.
This symptom, like face drooping, highlights the impact of a stroke on one side of the body. If you notice any discrepancy in arm strength or coordination when performing this simple test, it’s imperative not to delay. This sign, particularly when combined with others, underscores the urgent need to seek professional medical help without hesitation.

3. **Speech Difficulty: The ‘S’ in FAST**: Speech difficulty, represented by the ‘S’ in the FAST acronym, is a pivotal warning sign of a stroke that affects the brain’s language centers. A stroke can impair a person’s ability to speak clearly, articulate thoughts, or even comprehend spoken language. This can be one of the most distressing symptoms, as it directly impacts communication and can be quite frightening for both the person experiencing it and those around them.
To assess speech, ask the individual to repeat a simple phrase. Listen closely for any signs of slurred speech, words that sound strange or garbled, or difficulty forming coherent sentences. They might struggle to find the right words, or their speech may become entirely unintelligible. The inability to articulate or repeat a simple phrase clearly is a significant indicator that a stroke could be occurring.
This impairment stems from the disruption of blood flow to specific areas of the brain that manage speech and language. Recognizing these changes in communication is vital, as it points to damage in critical brain regions. If speech is affected in any of these ways, it adds to the urgency of calling for emergency medical services immediately, reinforcing the critical nature of the situation.

4. **Time to Call 911: The ‘T’ in FAST**: The ‘T’ in FAST stands for Time to Call 911, and it is arguably the most crucial step in the entire assessment process. If you observe any of the warning signs—face drooping, arm weakness, or speech difficulty—in yourself or someone else, the immediate and decisive action required is to call 911 right away. This is not a moment for hesitation, self-doubt, or attempting to transport the person to the hospital yourself.
Minutes truly matter when it comes to stroke treatment. Effective, life-saving therapies, such as clot-busting drugs, are most beneficial and often only available if administered within a narrow window, typically 3 to 4.5 hours from the onset of symptoms. Every moment wasted can diminish the chances of a good recovery. Furthermore, ambulance workers are equipped to begin life-saving treatment en route to the emergency room, ensuring that critical care starts as soon as possible.
It is also essential to note the exact time when you first observed any of these stroke warning signs. This information is invaluable to healthcare providers, as it helps them determine the most appropriate and effective treatment plan. Do not be tempted to drive to the hospital or let someone else drive you; calling 911 ensures the fastest, most effective, and safest pathway to emergency medical intervention.

5. **Balance Loss: The ‘B’ in BE FAST**: While FAST provides a crucial initial checklist, medical experts have expanded this acronym to BE FAST, incorporating two additional critical warning signs. The ‘B’ in BE FAST stands for Balance, and a sudden loss of balance or coordination is another significant indicator that a stroke might be occurring. This can manifest in various ways, often impacting a person’s ability to move steadily or maintain their posture.
Individuals experiencing a stroke may suddenly feel dizzy, have trouble walking in a straight line, or find themselves losing their balance unexpectedly. They might stumble, struggle with simple movements that were previously effortless, or exhibit general clumsiness or poor coordination. These symptoms arise from disruption to parts of the brain, such as the cerebellum, which are vital for motor control and spatial awareness.
If you observe someone suddenly struggling with their balance, experiencing unexplained dizziness, or demonstrating a distinct lack of coordination, it should immediately raise concerns. This sudden onset of balance issues, especially when combined with any other stroke warning signs, necessitates immediate medical attention. It’s a clear signal that something is critically wrong within the brain’s delicate systems.
6. **Eye and Vision Changes: The ‘E’ in BE FAST**: The ‘E’ in the expanded BE FAST acronym points to sudden changes in a person’s Eyes or vision. Visual disturbances are another significant warning sign of a stroke, and they can range from subtle alterations to complete loss of sight in one or both eyes. These changes are often sudden and can be quite disorienting, highlighting the impact of a stroke on the brain’s visual processing centers.
Someone experiencing a stroke might suddenly lose vision in one or both eyes, experience blurry vision, or even begin seeing double. They may describe a dimming or obscuring of their sight, as if a curtain is falling over their eyes. This visual impairment occurs because the areas of the brain responsible for processing visual information or the blood vessels supplying them are affected by the stroke.
Any sudden, unexplained alteration in vision should be treated with extreme seriousness. It’s not uncommon for these changes to be overlooked or attributed to less severe causes, but in the context of a potential stroke, they are critical indicators. If you notice a person’s vision is suddenly impaired in any of these ways, it reinforces the urgency of the situation and the immediate need to activate emergency medical services by calling 911.
While the FAST and BE FAST tests are indispensable for rapidly identifying the most common and immediate signs of a stroke, they do not encompass the full spectrum of ways this medical emergency can manifest. Understanding other less common, but equally critical, warning signs is vital for a comprehensive awareness of stroke. Some symptoms might appear gradually, or differ depending on the individual, making broad knowledge even more important for early detection and intervention. Knowing these additional indicators can significantly enhance your ability to recognize a potential stroke, reinforcing the crucial need for swift medical attention.

7. **Other General Warning Signs**: Beyond the well-known FAST and BE FAST indicators, strokes can present with a variety of other symptoms that warrant immediate attention. Although these may be less frequently highlighted in initial public awareness campaigns, their sudden onset should always trigger a call to emergency services. These signs reflect the diverse ways a stroke can impact brain function, as different areas of the brain control different bodily processes.
For instance, sudden numbness, particularly affecting one side of the body, can be a critical signal. This sensory loss might occur in the face, arm, or leg, and while it might not be accompanied by visible drooping or weakness, it is a significant warning. Other concerning symptoms include sudden confusion or difficulty understanding what others are saying, unexplained dizziness that goes beyond a momentary lightheadedness, and marked clumsiness or poor coordination that was not present before. Trouble walking, a sudden and severe headache without any apparent cause, or the unexpected loss or dimming of any of your senses—including smell and taste—are also serious indicators. Rarer, but equally serious, signs can include neck stiffness, unexplained personality changes, or the onset of seizures and memory loss, or even passing out. If any of these symptoms appear suddenly, regardless of whether you are certain it is a stroke, calling 911 without delay is the safest course of action.
8. **Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs) – The ‘Mini-Stroke’ Warning**: A transient ischemic attack, commonly known as a TIA or ‘mini-stroke,’ is a crucial warning sign that should never be ignored. Unlike a full stroke, TIA symptoms are temporary, typically lasting only a few minutes to a couple of hours, though they can persist for up to 24 hours. These ‘mini-strokes’ occur due to a brief interruption of blood flow to the brain, which, while clearing up without causing lasting damage on its own, serves as a powerful signal that a more severe stroke may be imminent.
The symptoms of a TIA are identical to those of a full-blown stroke, including one-sided weakness, slurred speech, or sudden vision changes, and can be detected using the FAST or BE FAST tests. The critical distinction is that the symptoms resolve quickly. However, this transient nature often leads people to dismiss them, mistakenly believing that since the symptoms passed, no harm was done. This is a dangerous misconception, as a TIA is a serious health event, indicating that you are at a significantly higher risk of experiencing a full stroke soon, potentially within days or weeks.
Even if the symptoms subside, treating a TIA as a medical emergency by calling 911 immediately is paramount. Emergency medical personnel can assess the situation promptly and initiate vital interventions. Medical evaluation following a TIA is crucial for confirming the event and implementing preventive measures, which might include blood-thinning medications to prevent clotting, procedures to clear blocked arteries, or lifestyle adjustments and medication management to control underlying risk factors like high blood pressure or diabetes. Research indicates that up to 80% of strokes following a TIA are preventable with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, highlighting why every TIA demands immediate medical attention.
9. **Recognizing Warning Signs of Recurrent Strokes**: For individuals who have experienced a stroke, the risk of having another one is significantly elevated, particularly in the days and months following the initial event. The warning signs for a recurrent stroke are fundamentally the same as those for a first stroke. However, recognizing them can be more challenging due to potential lingering effects from the previous stroke, which might mask or alter the presentation of new symptoms.
It is imperative for both stroke survivors and their caregivers to be acutely observant of any changes or shifts in symptoms. For instance, if someone who previously had slurred speech suddenly develops difficulty finding words, or if a pre-existing weakness on one side of the body intensifies or appears on the other side, these are significant red flags. Another critical indicator is a sudden inability to perform tasks that were previously easy, signaling a new neurological impairment.
Crucially, never assume that you cannot be experiencing another stroke simply because you recently had one; in fact, the immediate period after a stroke carries the highest risk for a repeat event, with elevated risks persisting for several months. Timely treatment for a second, third, or even fourth stroke is just as critical as for the first. If any new or changing symptoms arise, immediate action by calling 911 is essential to ensure the quickest possible medical intervention, which can dramatically influence recovery and prevent further brain damage.
Given that approximately 795,000 people in the U.S. experience a stroke each year, and it can affect anyone at any time, preparedness is a powerful tool. Learning the warning signs and educating family and friends on how to respond—specifically, knowing to call 911—is crucial. For households with children, teaching them the FAST test and how to call emergency services, provide an address, and describe the situation empowers them to act in an emergency. Furthermore, wearing medical identification like a bracelet listing conditions, allergies, and medications, and storing this information in smartphone medical ID features, can provide invaluable data to first responders. Remember, being FAST and acting quickly, even for fleeting symptoms, truly makes a life-saving difference in the face of a stroke, bolstering the chances of a positive outcome.