There are few dashboard warnings as unsettling as the illumination of your car’s check engine light, especially when it unexpectedly flashes to life late at night. That ominous yellow or orange engine icon can instantly transform a peaceful drive into a moment of anxiety, leaving you wondering if it’s a minor glitch or a harbinger of major trouble. Whether you’re miles from home or just around the corner, this indicator demands attention, signaling a potential issue with your vehicle’s engine or emission system that needs prompt investigation.
This in-depth guide is designed to empower you with the knowledge and practical steps needed to confidently address a check engine light, regardless of the hour. We understand the immediate concern it can trigger, and our aim is to demystify this critical warning. By providing clear, actionable insights, we’ll help you understand what this light means, identify the most common underlying causes, and outline your immediate course of action to ensure your safety and your vehicle’s longevity.
Navigating this unexpected challenge effectively can save you significant time, money, and stress. While some issues are remarkably simple to resolve, others necessitate professional expertise. Learning to distinguish between these scenarios is paramount. By the end of this comprehensive article, you will be equipped with the necessary understanding to react judiciously when that check engine light makes its appearance, ensuring you can get back on the road safely and efficiently.

1. Understanding the Check Engine Light: Solid vs. Flashing
When that yellow or orange engine icon lights up on your dashboard, it’s not merely a suggestion; it’s a direct alert from your vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system, commonly known as OBD-II. This warning indicator specifically points to a potential problem within the engine or the emission system. Unlike a routine maintenance reminder, a check engine light signifies that a sensor has detected an anomaly outside of normal operating parameters, prompting the vehicle’s computer to store a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminate the lamp.
The initial assessment of a check engine light begins with observing its behavior: is it solid or flashing? A steady, solid check engine light is what most drivers encounter, and it typically signals an issue that requires attention soon but doesn’t pose an immediate, critical threat to your vehicle. While it would be prudent to schedule an appointment with a mechanic in the near future, you can usually continue driving short distances without immediate concern, provided no other noticeable problems arise.
A flashing check engine light, however, signals a significantly more serious and urgent problem. This type of illumination almost invariably indicates an ignition malfunction, with an engine misfire being the most likely culprit. An engine misfire means that one or more cylinders are not firing correctly, which can quickly lead to severe and potentially catastrophic damage to vital components, particularly the catalytic converter, if left unaddressed.
If you are driving and the check engine light begins to flash, it is imperative to act with extreme caution. Pay close attention to your vehicle’s performance: observe if it is losing power, shaking noticeably, emitting any strange odors, or exhibiting any other abnormal behavior. Should these critical symptoms manifest, you must pull over as soon as it is safe to do so. Inspect the problem yourself if you feel capable, or, more typically, contact roadside assistance without delay to prevent further, more extensive damage to your engine and associated systems.

2. Common Cause 1: Loose or Faulty Gas Cap
Remarkably, one of the most frequent and easily remedied reasons for a check engine light to illuminate is a loose, damaged, or even missing fuel cap. While seemingly insignificant, the fuel cap plays a crucial role in your vehicle’s emission control system. Along with a series of lines inside the gas tank, it forms a sealed system designed to recirculate gasoline vapors, preventing them from escaping into the atmosphere and contributing to air pollution.
When a gas cap is not screwed on tightly, or if its seal is compromised due to damage or wear, the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system detects a leak within the evaporative emissions (EVAP) system. This perceived leak directly triggers an emissions system alert, causing the check engine light to turn on. The system is designed to maintain a specific pressure and prevent vapor escape, and any breach in this seal will register as a fault.
Beyond just triggering a warning light, a loose fuel cap can have practical consequences for your wallet. It can allow gasoline vapors to evaporate from your tank before the fuel can be effectively used by the engine. This means you could be losing valuable fuel to the atmosphere, effectively reducing your fuel efficiency and costing you money at the pump. Addressing this issue is therefore not only about clearing the dashboard light but also about optimizing your fuel consumption.
The solution to this particular issue is often remarkably straightforward. Begin by pulling over safely and ensuring your gas cap is screwed on tightly until you hear it click several times, confirming a secure seal. Visually inspect the cap’s rubber seal for any cracks, damage, or signs of wear; if compromised, the cap will need to be replaced. After securing or replacing the cap, drive for a day or two, and the check engine light may reset itself, confirming this simple fix as the culprit.

3. Common Cause 2: Faulty Oxygen Sensor
Oxygen sensors, often referred to as O2 sensors, are critical components within your vehicle’s exhaust system, playing a pivotal role in maintaining optimal engine performance and controlling emissions. These sensors measure the amount of unburned oxygen present in the exhaust gases after combustion. This data is then sent to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to precisely adjust the fuel-air mixture entering the engine, ensuring it operates as efficiently as possible.
A faulty oxygen sensor can significantly disrupt this delicate balance. If an O2 sensor fails or provides inaccurate readings, the ECU may receive incorrect information about the oxygen levels in the exhaust. This can lead to the engine running either too rich (too much fuel) or too lean (too little fuel), both of which can trigger the check engine light. Such failures are quite common as these sensors tend to wear out over time, typically after 60,000 to 100,000 miles of operation.
The implications of a bad oxygen sensor extend beyond just an illuminated dashboard light. Incorrect fuel-air mixtures can manifest as noticeably reduced vehicle performance, including sluggish acceleration or rough engine idling. More significantly, it often leads to a considerable decrease in fuel efficiency, as the engine struggles to optimize combustion. Drivers might find themselves making more frequent stops at the gas station than usual, directly impacting their operational costs.
Perhaps one of the most critical consequences of ignoring a faulty O2 sensor is its potential to damage other expensive components. An engine running too rich, due to an inaccurate O2 sensor reading, can send excessive unburned fuel into the catalytic converter. Over time, this can lead to the catalytic converter overheating and failing prematurely, resulting in a repair that can cost hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars. Therefore, addressing a problematic oxygen sensor promptly is essential for both performance and preventing further costly repairs.
Read more about: Tech Geek’s ‘Unknown’ Code: Unlock Your Car’s Hidden Menu Instantly Without Ever Visiting the Dealership

4. Common Cause 3: Failing Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an indispensable component of your vehicle’s exhaust system, serving a vital environmental function. Its primary role is to convert harmful pollutants produced during engine combustion, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and unburned hydrocarbons, into less toxic substances like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and water vapor. Without a functioning catalytic converter, a vehicle would emit significantly more hazardous gases, failing modern emissions standards and harming air quality.
A problem with the catalytic converter is a significant cause for the check engine light to illuminate. Issues can arise if the converter becomes clogged, contaminated, or simply fails due to old age. When the diagnostic system detects that the catalytic converter’s efficiency in converting pollutants has fallen below a set threshold, it triggers the warning light. This usually implies a substantial malfunction within this critical emissions control device.
Symptoms of a failing catalytic converter often include a noticeable reduction in vehicle performance, such as sluggish acceleration or a general lack of power. Drivers might also detect a distinct sulfur-like or rotten egg smell emanating from the exhaust, which is a tell-tale sign of sulfur byproducts not being properly converted. Additionally, a failing converter can lead to a considerable decrease in fuel efficiency, as the engine struggles to process exhaust gases effectively.
It is crucial to understand that while a failing catalytic converter is a serious issue, it is often a symptom of another underlying problem rather than the sole cause. For instance, a persistent engine misfire (which a flashing check engine light would indicate) or a continuously rich fuel mixture from a faulty oxygen sensor can lead to catalytic converter damage. Therefore, simply replacing the converter without diagnosing and resolving the original fault would likely not solve the issue and could lead to repeated failures, making the repair even more costly in the long run.
Read more about: 14 Critical Dashboard Warnings You Should Never Ignore: A Popular Mechanics Guide

5. Common Cause 4: Problematic Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF)
Nestled between the air filter and the throttle body, the Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor is a sophisticated component that plays a critical role in your engine’s combustion process. Its primary function is to measure the precise amount of air flowing into the engine. This vital piece of information is then relayed to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to calculate and inject the correct quantity of fuel required for optimal combustion. This careful balance ensures both efficient performance and effective emission control.
When a MAF sensor becomes problematic, either due to dirt and debris accumulation or an outright electrical failure, it can send inaccurate air intake readings to the ECU. This misinformation leads to an incorrect fuel-air mixture, which the diagnostic system quickly identifies as a fault, thereby illuminating the check engine light. Such an issue can severely disrupt the engine’s ability to run smoothly and efficiently, impacting various aspects of vehicle operation.
The consequences of a faulty MAF sensor are quite noticeable and can significantly impair your driving experience. Drivers often report symptoms such as reduced engine performance, including poor acceleration and a general lack of power. Fuel efficiency also takes a hit, as the engine struggles to maintain optimal combustion. Furthermore, a problematic MAF sensor can cause a rough vehicle idle, leading to noticeable vibrations, or even cause the engine to stall unexpectedly, particularly when starting or at low speeds.
Addressing a MAF sensor issue typically involves one of two approaches. In some cases, if the sensor is merely dirty from accumulated dust and oil, a thorough cleaning with a specialized MAF sensor cleaner can restore its functionality and resolve the problem. However, if the sensor is electrically damaged or has failed completely, cleaning will not suffice, and it will need to be replaced. Prompt attention to a faulty MAF sensor is crucial not only to clear the check engine light but also to restore your vehicle’s performance, safety, and fuel economy.
Navigating the complexities of your vehicle’s health, particularly when an unexpected warning like the check engine light appears, requires both understanding and a clear plan of action. Having covered the fundamental meaning of this crucial indicator and some of its most frequent culprits, we now shift our focus to the proactive steps and lasting solutions you can employ. This includes identifying remaining common causes, empowering yourself with initial diagnostic techniques, knowing when professional help is essential, and implementing preventative measures to safeguard your vehicle’s future.
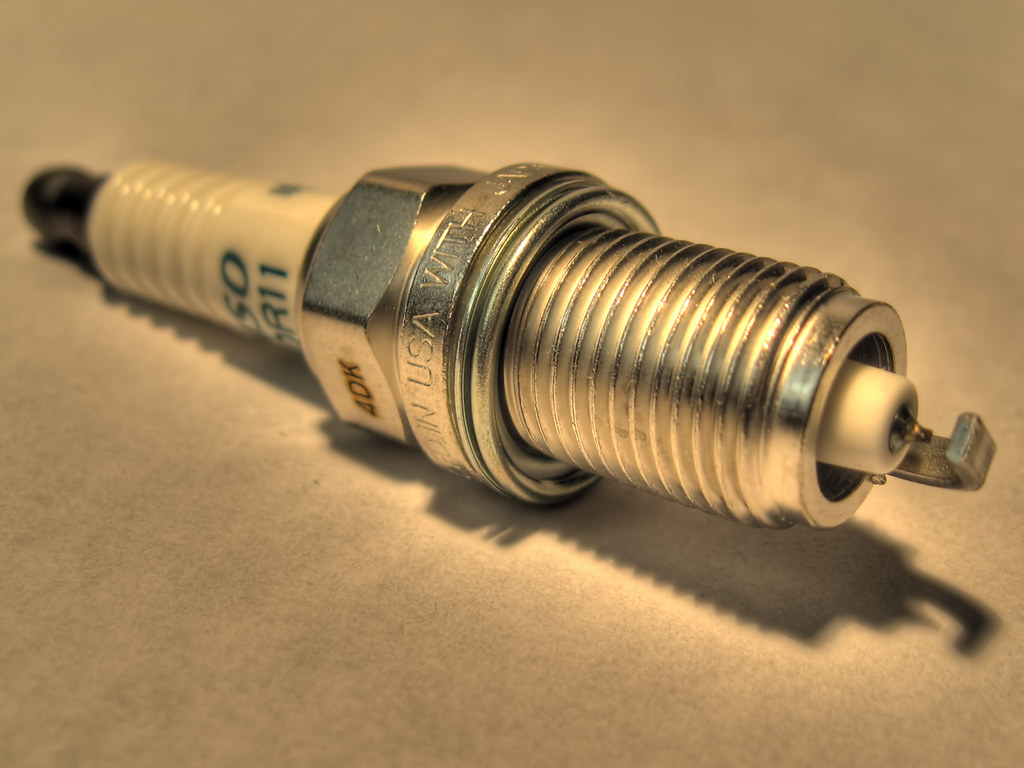
6. Common Cause 5: Spark Plug or Ignition Coil Problems
Beyond sensors and emission components, the very core of your engine’s operation—ignition—can also trigger the check engine light. Spark plugs are vital for igniting the air-fuel mixture in each cylinder, creating the combustion needed for your engine to run. Ignition coils, in turn, are responsible for generating the high voltage necessary for the spark plugs to fire effectively. Over time, these components can wear out, leading to diminished performance or outright failure.
When spark plugs become worn or fouled, or if an ignition coil malfunctions, the result is often an engine misfire. This means one or more cylinders are not combusting fuel correctly, leading to incomplete power strokes. The vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system will detect this irregularity in the engine’s rotation and performance, subsequently storing a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminating the check engine light as a warning.
The symptoms of faulty spark plugs or ignition coils are quite noticeable and can significantly impact drivability. Drivers may experience a rough or shaky engine idle, a noticeable reduction in acceleration, and an overall drop in engine performance. In more severe cases, persistent misfires can even lead to a flashing check engine light, which, as previously discussed, indicates a critical issue that requires immediate attention to prevent catalytic converter damage.
Addressing spark plug or ignition coil issues is crucial not only for restoring smooth engine operation but also for preventing further, more costly repairs. While replacing spark plugs is often a straightforward and relatively affordable maintenance item, identifying and replacing a faulty ignition coil may require more diagnostic precision. Resolving these problems promptly ensures your engine operates efficiently, maintains proper fuel economy, and avoids stress on other vital systems.
Read more about: Buyer’s Remorse on Full Display: 15 Vehicles Motorists Swear They’d ‘Unchoose’ if They Could, According to Driver Confessions

7. Initial Self-Diagnosis: Easy Fixes and Observations
When the check engine light first illuminates, it’s natural to feel a pang of concern, but not all triggers necessitate an immediate trip to the mechanic. Many issues can be resolved with simple, at-home checks, saving you time and money. The key is to start with the most straightforward possibilities and methodically observe your vehicle for any additional clues that might point to the underlying problem.
The simplest and most common culprit is often a loose or faulty gas cap. After refueling, ensure your gas cap is screwed on tightly until you hear it click several times, indicating a secure seal. A compromised seal allows fuel vapors to escape, triggering an emissions system alert. If the cap is old or damaged, its rubber gasket may be cracked, requiring a replacement. After securing or replacing the cap, drive for a day or two, and the light may extinguish itself.
Beyond the gas cap, a critical step involves observing your car’s behavior for any abnormal symptoms. Pay close attention to how the vehicle is running: Is it idling roughly, losing power during acceleration, or making any strange noises? Are you noticing a distinct sulfur-like odor from the exhaust, or perhaps a burning smell? Any changes in fuel efficiency, unusual vibrations, or difficulty starting the engine can provide valuable insights into the severity and nature of the issue.
Even if no noticeable symptoms accompany the illuminated light, it’s still prudent to investigate. Sometimes, the issue is minor, a temporary glitch, or a problem that has not yet significantly impacted performance. Reviewing your vehicle’s maintenance records can also be helpful; a light might come on after recent service, possibly indicating a system that needs manual resetting or a sensor that wasn’t properly reconnected. These initial checks empower you to gauge the situation before escalating to professional help.
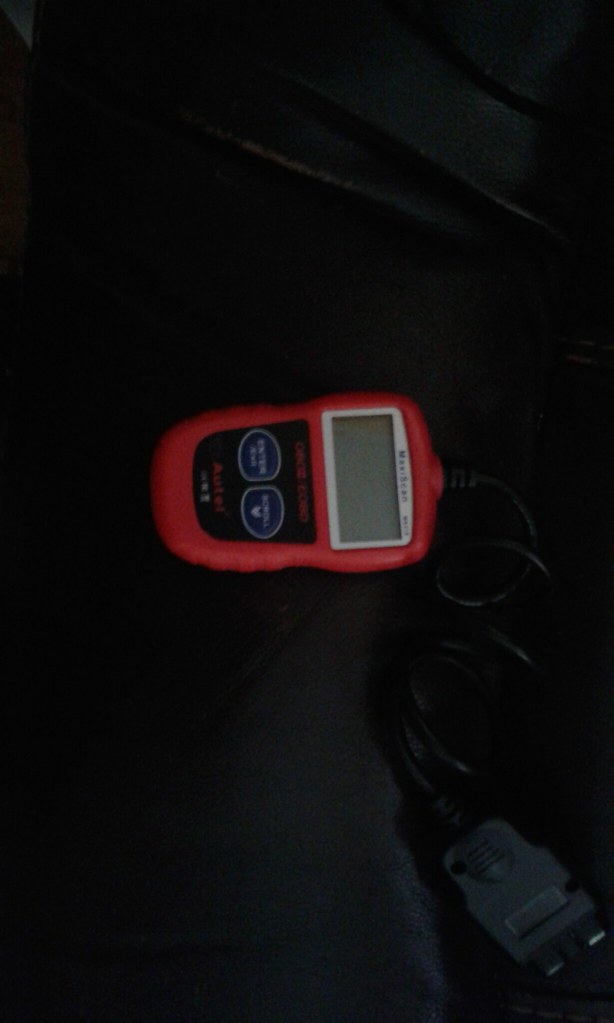

8. Utilizing an OBD-II Scanner for Diagnosis
For those comfortable with a bit of DIY, or simply seeking a clearer understanding before visiting a repair shop, an On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) scanner is an invaluable tool. This device provides a direct line to your car’s computer, allowing you to retrieve specific Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that pinpoint the exact reason for the check engine light’s illumination. It transforms guesswork into a targeted approach to problem-solving.
An OBD-II scanner plugs into a standard electrical port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, and is compatible with most vehicles manufactured after 1996. Once connected, turning the ignition to the ‘ON’ position (without starting the engine) allows the scanner to communicate with the Engine Control Unit (ECU). The scanner will then display any stored trouble codes, such as P0420 for a catalytic converter issue or P0300 for a random misfire.
Having the specific DTC is empowering. With this code, you can research the exact nature of the problem online, gaining a deeper understanding of what components are involved and potential solutions. Many auto parts stores also offer free check engine light scanning services, providing you with the codes without needing to purchase a scanner. This information helps you decide if a repair is within your skillset, or if it requires professional expertise.
Beyond simply reading codes, many OBD-II scanners also offer the functionality to clear the check engine light. However, it is paramount to understand that clearing the light without addressing the underlying issue is only a temporary measure. The light will inevitably return once the vehicle’s system detects the persistent fault again. Therefore, the scanner should primarily be used as a diagnostic tool to inform repairs, not just to suppress the warning indicator. Once the root cause has been fixed, clearing the code allows the system to confirm the repair has been successful.
Read more about: Steering Clear of Costly Car Button Blunders: Essential DIY & Key Fob Mistakes That Could Drain Your Wallet

9. When to Seek Professional Assistance
While preliminary checks and OBD-II scanners can provide significant clarity, there are definitive situations where professional assistance becomes not just advisable, but essential. Recognizing these indicators can prevent minor issues from escalating into major financial burdens or, critically, compromising your safety on the road. A mechanic possesses the specialized tools, extensive knowledge, and diagnostic experience to tackle complex automotive problems effectively.
The most urgent signal for professional intervention is a flashing check engine light. As emphasized earlier, a flashing light almost always indicates a severe issue, most commonly an engine misfire, which can cause rapid and significant damage to the catalytic converter. If your check engine light is flashing, or if your vehicle exhibits severe symptoms like drastic loss of power, violent shaking, or emits thick smoke or strange, strong odors, you must pull over safely and contact roadside assistance or a repair shop immediately. Driving under these conditions can lead to catastrophic engine failure.
Even with a solid check engine light, if your initial self-diagnosis—such as tightening the gas cap—doesn’t resolve the issue, or if the OBD-II scanner reveals complex codes related to the catalytic converter, transmission, or intricate emissions systems, it’s time to consult a professional. These components often require specialized diagnostic equipment and in-depth expertise that goes beyond basic at-home troubleshooting. Attempting complex repairs without the proper knowledge can lead to further damage and increased costs.
Furthermore, if you’ve already attempted a repair or reset the light, and it returns shortly thereafter, it’s a clear indication that the underlying problem has not been resolved, or a new issue has emerged. In such cases, a professional technician can perform advanced diagnostics, interpret deeper system controls, and ensure all components are working correctly. They can also validate emissions readiness for inspection, a critical step that consumer tools may not reliably confirm. Consulting a reputable, AAA-approved facility ensures you receive accurate diagnoses and effective repairs.
Read more about: 14 Unmissable Secrets of TG777 c That’ll Blow Your Mind (and Boost Your Wins!)

10. Proactive Prevention and Maintenance Tips
The most effective strategy against the unwelcome appearance of the check engine light is a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance. By adhering to a few simple habits and regular checks, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering common issues, thereby extending your car’s lifespan, improving its efficiency, and saving you from unexpected repair bills. Prevention truly is the best medicine for your vehicle’s health.
First and foremost, consistently follow your car’s manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedule. This includes timely oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug inspections. Regular servicing ensures that vital fluids are fresh, filters are clean, and ignition components are in good working order, all of which are critical for optimal engine performance and preventing sensor failures that can trigger the check engine light. These routine appointments are an investment in your car’s longevity.
Another crucial preventative measure is the mindful use of fuel. Always ensure your gas cap is tightened securely until it clicks multiple times after refueling. A loose cap is a remarkably common trigger for the check engine light due to evaporative emissions system leaks. Additionally, using quality fuel from reputable stations, and sticking to the octane level recommended by your manufacturer, helps prevent fuel injector clogs and sensor contamination, ensuring cleaner combustion.
Beyond scheduled maintenance, cultivating an awareness of your vehicle’s normal operation can make a significant difference. Pay attention to subtle changes in performance, such as a slight drop in fuel economy, an unusual engine sound, or a minor hesitation during acceleration. Addressing these early warning signs, even before the check engine light illuminates, can prevent minor issues from escalating into more serious problems. Having an OBD-II scanner handy also empowers you to check codes early, offering peace of mind and control over your car’s health.
Read more about: Keep Your Ride Smooth: 9 Essential Ways to Prevent Flat Spotting in High-Performance Tires
Ultimately, dealing with a check engine light isn’t about dreading its appearance, but about empowering yourself with knowledge and action. By understanding its warnings, leveraging diagnostic tools, knowing when to seek professional help, and embracing preventative maintenance, you transform a moment of anxiety into an opportunity for responsible car ownership. This comprehensive approach ensures your vehicle remains safe, reliable, and efficient, keeping you confidently on the road for years to come.



